Dog laws in Georgia
Navigating the intricate web of dog laws in Georgia is crucial for responsible pet ownership. In the United States, an estimated 800,000 dog bite incidents require medical attention annually, with a significant number of these occurring in Georgia.
As a veterinarian deeply familiar with these laws, I understand that they encompass a variety of regulations designed to protect both the public and the animals themselves. From the “Responsible Dog Ownership Law” to statutes addressing cruelty and authorized killing of dogs, these laws set the framework for ownership responsibilities and public safety.
They are not just legal requirements but a moral compass guiding how we interact with our canine companions. Understanding these laws is not only about compliance; it’s about fostering a community where humans and dogs live in harmony.
Table of Contents
Dog Bite Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian and an expert in dog laws in the USA, I’ve seen firsthand the impact of dog bites and the importance of understanding local laws. In Georgia, dog bite laws are designed to balance the rights of dog owners with the protection of the public. These laws are complex and multifaceted, addressing various scenarios from bites to other injuries caused by dogs.
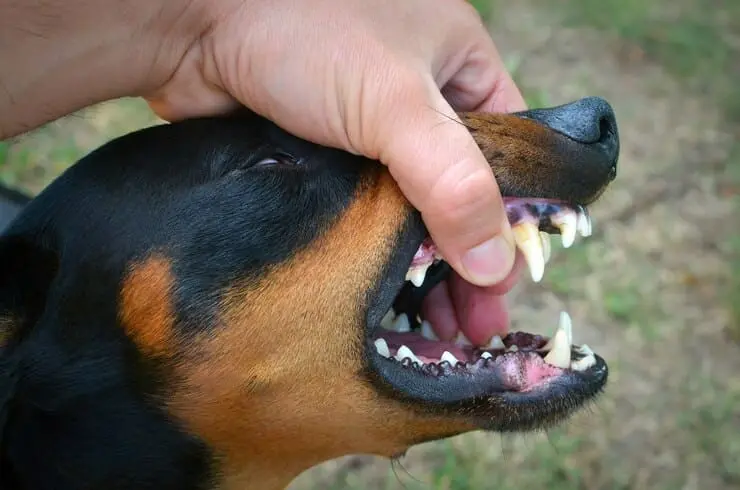
The One-Bite Rule and Beyond
Georgia is known as a ‘one bite rule’ state, which means that a dog’s first bite doesn’t automatically result in liability for the owner. However, once a dog has bitten someone, the owner is expected to be aware of the potential threat their dog presents. This rule is not absolute; owners can still be found liable if negligence can be proven, even without a prior bite incident.
Owner Liability for Dog Bites
Under Georgia law, a dog owner is liable for injuries caused by their pet only when certain conditions are met. The dog must be considered a “vicious or dangerous animal,” the incident must have occurred due to “careless management or by allowing the animal to go at liberty,” and the injured person must not have provoked the injury.
Dangerous Dog Classification
A dog may be classified as “vicious” or “dangerous” in Georgia based on its behavior. If a dog has a history of aggressive behavior or has been involved in an attack, it may be labeled as such. Additionally, if an owner violates local ordinances, such as leash laws, their dog can be deemed “vicious” regardless of past behavior.
Criminal Charges and Penalties
Owners of dogs that are classified as dangerous or vicious may face criminal charges if their dog causes injury. The severity of these charges can range from misdemeanors to felonies, depending on the circumstances of the incident.
Statute of Limitations
In Georgia, there is a statute of limitations for filing a lawsuit related to dog bites. Victims must file their claims within a certain period after the incident to seek compensation for their injuries.
Defenses to Dog Bite Claims
Dog owners in Georgia may raise several defenses in response to a dog bite claim. These can include proving that the victim provoked the dog or that the owner had no knowledge of the dog’s vicious tendencies.
Preventive Measures and Owner Responsibilities
To prevent dog bites, owners are encouraged to take responsible measures such as proper training, socialization, and adherence to local leash laws. Understanding and complying with these laws not only protects the public but also ensures the well-being of the dogs themselves.
Dog Barking and Noise Laws in Georgia
In the tranquil neighborhoods of Georgia, the sound of a dog’s bark is common. However, when this barking becomes excessive, it can disrupt the peace and quiet of the community. As a veterinarian with a keen understanding of dog behavior and local laws, I’m here to guide you through the regulations that govern dog barking and noise in Georgia.
Understanding the Legal Framework
Georgia’s approach to managing dog barking noise is not just about maintaining tranquility; it’s about ensuring that pet ownership is harmonious with community living. The state has specific laws that address the duration and conditions under which a dog can bark legally.
The Ten-Minute Rule
In Georgia, dogs can bark legally for up to 10 minutes before their owners may face consequences for noise disturbance. This rule is designed to provide a balance between a dog’s natural behavior and the rights of residents to enjoy a noise-free environment.
Consequences of Excessive Barking
Should a dog’s barking exceed the legal limit, the owner may incur a fine for their negligence. This fine is a monetary reminder of the owner’s responsibility to control their pet’s noise levels.
The Role of Warnings and Citations
When residents file a complaint about excessive barking, local authorities first issue a written warning to the dog owner. If another complaint is received within 90 days of this warning, a citation is issued. This process ensures that owners are given a fair chance to rectify the situation before facing penalties.
Local Ordinances and Variations
While the state provides a general framework, local municipalities in Georgia may have additional ordinances that further define and regulate dog barking and noise. For instance, some areas may have stricter time limits or higher fines, reflecting the community’s tolerance for noise.
Preventive Measures for Dog Owners
As a responsible dog owner, it’s important to take proactive steps to manage your dog’s barking. This can include training, providing adequate exercise, and ensuring that your dog is not left alone for extended periods, which can often lead to anxiety-induced barking.
Dog Poop Disposal Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian and an expert in dog laws in the USA, I’m here to shed light on a topic that’s crucial for both pet owners and the community at large: dog poop disposal laws in Georgia. With an estimated 78 million dogs in the United States, the proper disposal of pet waste is not only a matter of cleanliness but also public health.
The Importance of Proper Poop Disposal
Proper disposal of dog waste is a legal requirement in Georgia. It’s not just about keeping our sidewalks clean; it’s about preventing the spread of diseases. Dog feces can carry harmful pathogens like E. coli, and salmonella, and parasites such as roundworms and hookworms. These can pose health risks to humans and other animals.
Georgia’s Stance on Dog Waste
In Georgia, it is illegal to leave dog poop on public property, including parks, sidewalks, and trails. The state mandates that all pet owners must pick up after their dogs. Failure to do so can result in fines, which vary depending on the jurisdiction but can range from a nominal fee to several hundred dollars for repeated offenses.
Local Ordinances and Enforcement
While state law provides the overarching legal framework, local municipalities have the authority to enact and enforce their own dog waste disposal regulations. This means that in addition to state laws, dog owners in Georgia must be aware of and comply with local ordinances that may impose stricter rules and higher fines.
The Role of Dog Owners
As a dog owner in Georgia, it’s your responsibility to ensure that you’re always prepared to clean up after your pet. This means carrying bags for waste disposal whenever you’re out with your dog. Many communities provide waste stations with bags and disposal bins, but owners should not rely solely on these provisions.
Environmental Considerations
Beyond the legal implications, there’s an environmental aspect to consider. Dog waste is not a natural fertilizer; it’s a pollutant that can degrade water quality in streams, rivers, and lakes. By properly disposing of pet waste, owners are contributing to the preservation of Georgia’s natural resources.
Dog Licensing Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian with expertise in dog laws across the USA, I’m here to provide a comprehensive guide to dog licensing laws in Georgia. Licensing your dog is not just a legal formality; it’s a critical step in responsible pet ownership and public safety.
The Essence of Dog Licensing
In Georgia, licensing your dog is a mandatory practice that serves multiple purposes. It’s a way to ensure that all dogs are vaccinated against rabies, a dangerous disease that poses a threat to both animals and humans. The license acts as a record, linking pets to their owners and providing a way to reunite lost dogs with their families.
Who Needs a License?
All dog owners in Georgia are required to obtain a license for their pets. This applies to dogs of all breeds and sizes, from the tiniest Chihuahua to the largest Great Dane. The licensing process involves providing proof of rabies vaccination and paying a nominal fee.
The Licensing Process
Obtaining a dog license in Georgia is straightforward. Owners must submit proof of rabies vaccination, which is typically provided by a veterinarian after the vaccine is administered. Once the documentation is verified, a fee is paid, and the license is issued.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to license your dog can result in fines and penalties. These are not just financial inconveniences; they’re legal repercussions that underscore the importance of following the law. By licensing your dog, you’re not only complying with state regulations but also contributing to the health and safety of the community.
Local Variations and Additional Requirements
While the state sets the basic requirements for dog licensing, local municipalities may have additional rules. Some areas might require licenses to be renewed annually, while others may offer multi-year licenses. It’s essential for dog owners to be aware of and comply with both state and local regulations.
The Role of Kennels and Breeders
In Georgia, establishments such as kennels, breeders, and grooming shops are also subject to licensing laws. These businesses must adhere to specific regulations that govern the care and management of animals, ensuring that pets are kept in safe and humane conditions.
Dog Leash Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian with a deep understanding of dog behavior and legal requirements, I’m here to discuss the dog leash laws in Georgia. These laws are essential for ensuring public safety and the well-being of our canine companions.
Georgia’s Approach to Leash Laws
Georgia does not have a statewide leash law. Instead, leash laws are determined by local county or municipal regulations. This means that the requirements can vary significantly depending on where you are in Georgia.
The Importance of Leash Laws
Leash laws are in place to prevent dogs from roaming freely, which can lead to accidents, injuries, or even fatalities. They also help to ensure that dogs do not become a nuisance or a threat to the community.
Common Provisions in Local Leash Laws
While there is no uniform state law, most localities in Georgia have similar provisions in their leash laws. Typically, these laws require that dogs be restrained by a leash, chain, or cord of a specific length when they are off their owner’s property.
Penalties for Violating Leash Laws
Owners who fail to comply with local leash laws may face fines and other penalties. In some cases, repeated violations can lead to more severe consequences, such as the impoundment of the dog.
Exceptions to Leash Requirements
There are often exceptions to leash laws for certain situations. For example, dogs may be allowed off-leash in designated dog parks or while participating in specific activities such as hunting or herding.
The Role of “Dangerous” and “Vicious” Dog Classifications
In Georgia, dogs classified as “dangerous” or “vicious” have stricter leash requirements. These dogs must be restrained by a leash not exceeding six feet in length and under the control of a capable person when off the owner’s property.
Understanding Local Ordinances
It’s crucial for dog owners to understand the specific leash laws in their locality. This may involve checking with local animal control or government offices to get the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Dangerous Dog Laws in Georgia
In Georgia, the laws surrounding dangerous dogs are taken seriously due to the potential risks they pose to the community. As a veterinarian with a comprehensive understanding of these laws, I will provide you with an in-depth exploration of the regulations that govern the ownership and management of dogs deemed dangerous.
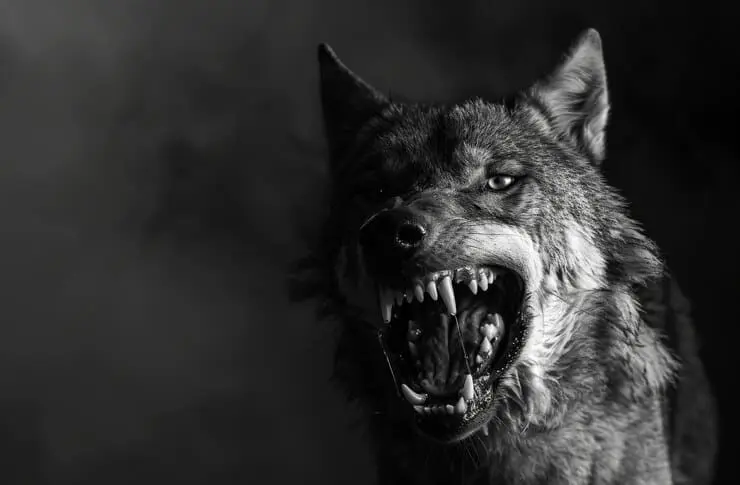

Definition of a Dangerous Dog
Georgia law defines a “dangerous dog” as one that, without provocation, inflicts severe injury on a human being or aggressively bites, attacks, or endangers the safety of humans. This definition is crucial in determining the course of action that authorities take following an incident involving a dog.
Classification and Registration
Dogs that have been classified as dangerous must be registered with the state. This registration serves as a measure of accountability, ensuring that owners are responsible for their pet’s actions and the safety of others.
Containment Requirements
Owners of dangerous dogs are required to keep their pets in a proper enclosure while on their property. This enclosure must be secure enough to prevent the dog from escaping and protect the public from potential harm.
Leash and Muzzle Regulations
When off the owner’s property, dangerous dogs must be fully under the owner’s immediate physical control. They must be on a leash that is less than six feet long and, in some cases, muzzled to prevent bites.
Liability Insurance
Owners of dangerous dogs may be required to carry liability insurance. This financial assurance covers any damages or injuries that the dog might cause, providing protection for victims.
Signage and Notification
Appropriate signage warning of a dangerous dog must be displayed on the owner’s property. Additionally, neighbors and local authorities must be notified about the presence of a dangerous dog.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with dangerous dog laws can result in significant penalties, including fines, criminal charges, and even the removal of the dog from the owner’s custody.
Preventive Measures
To prevent dogs from becoming dangerous, owners should invest in proper training, socialization, and care. These proactive steps can significantly reduce the likelihood of a dog becoming a threat to public safety.
Dog Health and Welfare Laws in Georgia
In the heart of the South, Georgia stands out for its comprehensive approach to canine health and welfare. As a veterinarian, I’m committed to informing pet owners about the legal obligations that ensure the well-being of our beloved dogs. This article will provide a detailed look at the laws in place to protect our four-legged friends.

A Framework for Canine Care
Georgia’s legal framework for dog health and welfare is robust, aiming to safeguard dogs from neglect and abuse. The state’s laws cover a wide range of aspects, from basic care requirements to stringent anti-cruelty measures.
Basic Care Requirements
At the core of Georgia’s dog welfare laws is the expectation of humane care. This includes providing adequate food, water, shelter, and veterinary care. Owners must ensure their dogs have access to clean water and nutritious food, appropriate shelter that shields them from extreme weather, and regular veterinary check-ups.
Anti-Cruelty Provisions
Georgia’s anti-cruelty statutes are clear: any act of neglect or intentional harm towards a dog is punishable by law. This encompasses physical abuse, abandonment, and failure to provide essential care. Violations can lead to fines, criminal charges, and even jail time.
Rabies Vaccination and Control
Rabies control is a critical aspect of dog health laws in Georgia. All dogs must be vaccinated against rabies and owners are required to maintain up-to-date vaccination records. This not only protects the dog but also the community at large.
Licensing and Identification
To further ensure the welfare of dogs, Georgia mandates licensing and identification. This helps in tracking vaccinations, and ownership, and assists in the recovery of lost pets. It’s a simple yet effective way to keep dogs safe and accounted for.
Regulations for Breeders and Kennels
Breeders and kennels in Georgia are subject to specific health and welfare regulations. These establishments must provide a clean, safe environment for dogs and adhere to health standards that promote the well-being of the animals in their care.
Protections for Service and Working Dogs
Service and working dogs have additional protections under Georgia law. These dogs are essential for the tasks they perform, and as such, any interference or harm towards them is met with severe penalties.
Dog Public Access Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian and an expert in dog laws, I understand the importance of public access laws for dogs in Georgia. These laws are essential for maintaining the delicate balance between pet ownership and public rights. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of Georgia’s public access laws for dogs, ensuring pet owners are well-informed and compliant.

Understanding Public Access Laws
Public access laws in Georgia are designed to outline where and how dogs can accompany their owners in public spaces. These laws aim to ensure safety and accessibility for all, including those with service animals.
Service Dogs and Public Access
In Georgia, service dogs are granted extensive access to public areas. Under both state law and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), service dogs can accompany their handlers in most public accommodations, such as restaurants, stores, and parks.
Emotional Support Animals and Access Rights
While service dogs have broad public access rights, emotional support animals (ESAs) are treated differently. In Georgia, ESAs do not have the same level of public access as service dogs. They are, however, protected under the Fair Housing Act, allowing them to live with their owners in housing with a “no pets” policy.
The Responsible Dog Ownership Law
Georgia’s “Responsible Dog Ownership Law” provides a framework for dog owners, emphasizing the need for control and regulation of dogs to protect the public and other pets from injuries and attacks. This law sets the minimum standards for dog control across the state.
Local Ordinances and Variations
While state laws provide a baseline, local municipalities in Georgia may have additional ordinances that govern dog public access. These can include leash laws, restrictions on dog breeds in certain areas, and specific rules for dog parks.
Access Restrictions and Exemptions
Certain areas may be off-limits to dogs, such as food preparation areas, hospitals, or private properties with clear signage. However, exemptions are made for service dogs due to their essential role in assisting individuals with disabilities.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Owners who fail to comply with public access laws may face fines and penalties. It’s crucial for dog owners to understand and adhere to these laws to avoid legal repercussions and ensure the safety of the community.
Dog Travel and Transportation Laws in Georgia
Traveling with dogs in Georgia requires adherence to specific laws and regulations to ensure the safety and well-being of pets during transportation. As a veterinarian, I’m here to provide you with a detailed understanding of these laws, which are designed to protect your furry companions on the go.

State Regulations for Dog Travel
In Georgia, all domestic animals, including dogs, must comply with state requirements and federal regulations when traveling. This includes ensuring that dogs are not infected with or exposed to any infectious or contagious diseases. Vaccinations, particularly against rabies, are mandatory for dogs traveling within or entering the state.
Air Travel with Dogs
When flying, dog owners must follow the airline’s pet policies, which typically include the use of an approved pet carrier and adherence to size and weight restrictions for pets traveling in the cabin. Service dogs are allowed to accompany their handlers in the cabin under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Ground Transportation
For ground travel, dogs must be safely secured in vehicles. This can mean using a crate, harness, or a pet seatbelt. Unrestrained dogs in open vehicles, such as the bed of a pickup truck, are not permitted, as this poses a significant risk to the dog’s safety.
Public Transportation Access
Service dogs have extensive access rights on public transportation in Georgia, including buses and trains. However, emotional support animals do not have the same level of access and may be subject to the transportation provider’s pet policy.
Interstate and International Travel
Dogs traveling interstate must have a Certificate of Veterinary Inspection (CVI) issued by a licensed veterinarian, and owners should be aware of the entry requirements of their destination state. For international travel, owners must comply with the destination country’s pet import regulations.
Local Ordinances
Local jurisdictions in Georgia may have additional ordinances regarding dog travel and transportation. It’s important for dog owners to familiarize themselves with these local laws to avoid penalties and ensure their pets’ safety.
Responsibilities of Dog Owners
Dog owners are responsible for ensuring their pets are comfortable and safe during travel. This includes providing adequate ventilation, regular bathroom breaks, and access to water, especially during long trips.
Dog Housing and Accommodation Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian with expertise in dog laws, I recognize the importance of understanding the housing and accommodation laws that affect dog owners in Georgia. These laws are designed to ensure the welfare of dogs and the rights of their owners when it comes to housing and accommodations.

The Legal Landscape for Dog Housing
In Georgia, the laws governing dog housing are primarily focused on ensuring that dogs have a safe and humane living environment. This includes providing adequate shelter that protects dogs from the elements, sufficient space for exercise, and access to clean water and food.
Service Dogs and Housing Rights
Service dogs in Georgia are afforded special housing rights under both state law and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Individuals with disabilities have the right to be accompanied by their service dogs in all housing accommodations without facing discrimination.
Emotional Support Animals and Accommodation
While emotional support animals (ESAs) do not have the same public access rights as service dogs, they are protected under the Fair Housing Act (FHA). This means that individuals with ESAs cannot be discriminated against in the rental, lease, or purchase of housing.
Pet Deposits and Fees
Landlords in Georgia are allowed to charge pet deposits and pet fees. This is a common practice to cover potential damages caused by pets. However, these fees must be reasonable and not serve as a barrier to housing for pet owners.
Breed Restrictions
Some landlords may impose breed restrictions on their rentals. This means that certain breeds that are perceived as more dangerous may be prohibited. It’s important for dog owners to be aware of these restrictions when seeking housing.
Accommodation for Disabled Persons with Dogs
Georgia law ensures that totally or partially blind persons, physically disabled persons, and deaf persons have the right to be accompanied by their service dogs in all housing accommodations. This is a crucial aspect of the law that supports the independence and quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
Dog Adoption and Sale Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian and an expert in dog laws, I’m here to guide you through the intricate landscape of dog adoption and sale laws in Georgia. These laws are designed to protect the welfare of dogs and ensure ethical practices in their adoption and sale.

Regulatory Framework for Dog Adoption and Sale
Georgia’s regulatory framework for dog adoption and sale is multifaceted, aiming to safeguard the interests of the animals and those of prospective pet owners. The state mandates that all pet dealers, which include breeders and adoption agencies, must be licensed.
Licensing Requirements for Pet Dealers
Pet dealers in Georgia are required to obtain a license from the Department of Agriculture. This ensures that breeders and sellers meet the necessary standards of animal care and ethical business practices.
Protections for Consumers
Georgia’s laws provide protections for consumers purchasing or adopting dogs. This includes the requirement for pet dealers to disclose the health history and vaccination records of the dogs. Consumers have the right to be informed about any known health issues.
The Lemon Law for Pets
While Georgia does not have a specific “puppy lemon law,” consumers can seek remedies under the general lemon law if the dog they purchased is found to have a disease or defect within a certain period after the sale.
Adoption Procedures and Policies
Adoption agencies in Georgia follow strict procedures to ensure that dogs are placed in suitable homes. This includes thorough application processes, home checks, and ensuring that adoptive families are prepared for the responsibilities of pet ownership.
Spay and Neuter Regulations
Many adoption agencies in Georgia require that dogs be spayed or neutered before adoption. This is part of the state’s effort to control the pet population and reduce the number of unwanted animals.
Microchipping and Identification
Microchipping is increasingly becoming a standard practice in the adoption and sale of dogs. This permanent form of identification helps in reuniting lost pets with their owners and is encouraged by Georgia law.
Animal Welfare Act Compliance
Pet dealers in Georgia must comply with the federal Animal Welfare Act, which sets standards for the humane treatment of animals in commerce. This includes proper housing, handling, sanitation, nutrition, and veterinary care.
Dog Park and Recreation Laws in Georgia
In Georgia, dog parks offer a space where dogs can exercise, play, and socialize. As a veterinarian, I understand the importance of these recreational areas for a dog’s physical and mental health. This article will delve into the laws and regulations that govern dog parks and recreational spaces in Georgia, providing pet owners with the knowledge they need to enjoy these facilities responsibly.
The Foundation of Dog Park Laws
Dog park laws in Georgia are established to create a safe and enjoyable environment for all park visitors, both human and canine. These laws cover various aspects, from entry requirements to behavior within the park.
Entry Requirements for Dog Parks
To enter a dog park in Georgia, dogs must be licensed and have a current tag. This ensures that all dogs in the park are registered and vaccinated, promoting a safe environment for everyone.
Control and Supervision
Dogs must be under the control of a responsible adult and obedient to that person’s commands. This rule is crucial to prevent conflicts and ensure that dogs do not become a nuisance or a danger to others.
Children and Dog Parks
Children must be closely supervised in dog parks to ensure their safety. Dog parks can be unpredictable environments, and close supervision helps prevent accidents.
Waste Disposal
Animal waste must be removed immediately by the dog owner and deposited in suitable containers. Proper waste disposal is essential for maintaining the cleanliness and hygiene of the park.
Aggressive Dogs
Aggressive dogs are not allowed in dog parks. If a dog shows signs of aggression, it must be removed from the park to prevent potential harm to other dogs or people.
Leash Laws
While many dog parks have off-leash areas, dogs must be kept on a leash in other public spaces unless designated otherwise. Leash laws help prevent dogs from straying and protect the public.
Enclosures and Fencing
Dog parks in Georgia are typically enclosed with fencing, providing a secure area where dogs can roam freely without the risk of escaping.
Behavioral Rules
Dog owners are expected to monitor their dogs’ behavior and intervene if necessary. This includes preventing excessive barking, digging, or any behavior that could damage the park or disturb other visitors.
Health and Safety
Dogs entering the park should be healthy and free from contagious diseases. Regular vaccinations and health checks are recommended to keep all park visitors safe.
Dog Food and Nutrition Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian, I understand the critical role nutrition plays in the health and well-being of dogs. In Georgia, there are specific laws and regulations that govern dog food and nutrition to ensure that our canine companions receive safe and wholesome meals. This article will provide a detailed exploration of these laws, which are designed to protect dogs and inform pet owners.
Regulatory Oversight of Dog Food
The Georgia Department of Agriculture regulates all aspects of pet food, ensuring that it is safe to eat, produced under sanitary conditions, contains no harmful substances, and is truthfully labeled. This aligns with the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, which sets the standard for animal food safety nationwide.
Labeling Requirements
Dog food labels in Georgia must provide clear information about the contents, including a list of ingredients, guaranteed analysis of nutrient percentages, feeding instructions, and the name and address of the manufacturer or distributor. This transparency allows pet owners to make informed decisions about what they are feeding their dogs.
Nutritional Adequacy
All dog food sold in Georgia must meet nutritional adequacy standards established by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). This ensures that dog food provides the necessary nutrients required for different life stages, from puppies to adult dogs.
Prohibition of Harmful Substances
The inclusion of harmful substances in dog food is strictly prohibited. This includes any chemicals or ingredients that could be detrimental to a dog’s health. The Georgia Department of Agriculture monitors and tests pet foods to ensure compliance with these safety standards.
Safe Handling and Storage
Pet owners in Georgia are advised to handle and store dog food safely to prevent contamination. This includes keeping dry food in a cool, dry place and refrigerating wet food after opening. Proper handling helps maintain the quality and safety of the food.
Specialty Diets and Claims
Any claims made on dog food packaging, such as “organic” or “natural,” must be substantiated according to Georgia law. Specialty diets that cater to specific health needs must also be formulated based on scientific evidence and meet regulatory standards.
Recalls and Consumer Protection
In the event of a dog food recall, the Georgia Department of Agriculture works to protect consumers and their pets by providing timely information and instructions for returning or disposing of affected products.
Dog Health and Veterinary Care Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian, I am deeply committed to the health and well-being of dogs. In Georgia, the laws surrounding dog health and veterinary care are comprehensive, ensuring that dogs receive the highest standard of medical attention. This article will provide an in-depth look at these laws, which are designed to protect our canine companions.
The Role of the Georgia Board of Veterinary Medicine
The Georgia Board of Veterinary Medicine is the primary body responsible for regulating veterinary practices in the state. It sets the standards for veterinary care and oversees the licensure of veterinarians and veterinary technicians.
Licensing Requirements for Veterinarians
To practice veterinary medicine in Georgia, individuals must be licensed by the state board. This ensures that all practicing veterinarians meet the necessary educational and professional standards.
Continuing Education for Veterinary Professionals
Georgia law requires veterinarians and veterinary technicians to complete continuing education. This is to ensure that veterinary professionals stay up-to-date with the latest medical knowledge and techniques.
Standards of Veterinary Practice
Veterinary practices in Georgia are expected to adhere to high standards of care. This includes maintaining a clean and safe environment, providing adequate pain management, and ensuring that all treatments are in the best interest of the animal’s health.
Veterinary Records and Confidentiality
Veterinarians in Georgia are required to keep detailed records of all patient visits, diagnoses, and treatments. These records are confidential and can only be released with the consent of the pet owner or by lawful order.
Rabies Vaccination and Control
One of the key health laws in Georgia is the requirement for all dogs to be vaccinated against rabies. This law is crucial for public health and the prevention of the spread of this deadly virus.
Regulations on Prescription Medications
Veterinarians in Georgia must follow strict guidelines when prescribing medications. This includes keeping detailed records of prescriptions and ensuring that medications are used responsibly.
Emergency Veterinary Services
The state mandates that veterinary facilities provide or arrange for emergency care. This ensures that dogs have access to medical attention during critical situations.
Animal Cruelty and Reporting
Veterinarians in Georgia are obligated to report any suspected cases of animal cruelty. This legal requirement helps protect dogs from abuse and neglect.
Dog Identification and Microchipping Laws in Georgia
In the state of Georgia, responsible dog ownership is not just about providing love and care; it also involves adhering to the laws that govern dog identification and microchipping. As a veterinarian, I am committed to informing pet owners about these regulations, which are crucial for the safety and recovery of lost pets. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the identification and microchipping laws for dogs in Georgia.
Microchipping as a Standard for Identification
Microchipping is widely recognized as the most reliable form of pet identification. In Georgia, while there is no statewide mandate for all dogs to be microchipped, it is highly encouraged and, in some cases, required by local ordinances.
The Role of Shelters and Microchip Scanning
When a lost, stray, or abandoned dog is brought to an animal shelter in Georgia, the facility is required to scan the animal for a microchip within 24 hours or as soon as possible. If a microchip is detected, reasonable efforts must be made to contact the owner. This process is repeated prior to any decision to euthanize the animal, ensuring every opportunity is given to reunite the dog with its owner.
Protection for Dogs and Owners
The laws surrounding microchipping in Georgia provide a layer of protection for dogs and their owners. Microchipping increases the chances of a lost dog being returned home and can also serve as proof of ownership in cases of disputes.
Local Regulations and Compliance
Pet owners should be aware that local municipalities may have their own regulations regarding dog identification and microchipping. Some areas may require microchipping as part of their licensing process, and failure to comply could result in fines or penalties.
Benefits of Microchipping
Microchipping offers a permanent, tamper-proof method of identification that can’t be lost like a collar or tag. It is a simple, relatively painless procedure that can be performed during a routine veterinary visit.
Educating the Public
As a veterinarian, part of my role is to educate pet owners about the benefits of microchipping. This includes discussing how microchipping works, the registration process, and the importance of keeping contact information up to date in the microchip registry.
Dog Breeding and Genetics Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian, I am well-versed in the laws that govern dog breeding and genetics in Georgia. These laws are crucial for ensuring the ethical treatment of dogs and the integrity of breeding practices. This comprehensive article will explore the various regulations that breeders in Georgia must adhere to.
Introduction to Dog Breeding Regulations
In Georgia, dog breeding is regulated to protect the welfare of dogs and to ensure that breeders operate ethically and responsibly. Breeders must comply with the Georgia Animal Protection Act, which sets forth the standards for animal care and business practices related to dog breeding.
Licensing Requirements for Breeders
Breeders in Georgia are required to obtain a license if they sell more than one litter or over 30 adult dogs within a 12-month period. This licensing process involves providing proof of citizenship or legal residency and complying with secure and verifiable document requirements.
Kennel Standards and Inspections
Licensed breeders must maintain kennels that meet specific standards for space, sanitation, and safety. Kennels are subject to regular inspections by the Georgia Department of Agriculture to ensure compliance with the Animal Protection Act.
Health and Genetic Screening
Ethical breeding practices include health and genetic screening to prevent the propagation of hereditary diseases. While Georgia law does not mandate genetic testing, responsible breeders often perform these tests to ensure the health of their breeding stock and puppies.
Record Keeping and Transparency
Breeders must keep detailed records of their breeding activities, including information about the dogs’ health, vaccinations, and sales. This transparency is essential for consumer protection and animal welfare.
Consumer Protections and Disclosures
Breeders are required to disclose the health history and any known genetic issues of the dogs they sell. This protects consumers and helps to ensure that puppies are healthy and free from preventable genetic conditions.
Breeding Limits and Ethical Considerations
While there are no specific state laws limiting the number of breeding females a breeder can have, ethical considerations suggest that breeders should limit their breeding stock to a manageable number that allows for proper care and socialization of the dogs.
Enforcement and Penalties
Failure to comply with breeding and genetics laws can result in penalties, including fines and the revocation of the breeder’s license. The enforcement of these laws is critical to prevent unethical breeding practices and to protect the welfare of dogs in Georgia.
Dog Environmental Impact Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian, I am acutely aware of the environmental impact that dogs can have on our communities. In Georgia, there are specific laws in place to mitigate these impacts and ensure that our furry friends coexist harmoniously with the environment. This article will explore the various environmental impact laws related to dogs in Georgia.
The Significance of Environmental Impact Laws
Environmental impact laws for dogs are designed to address the various ways in which dogs can affect local ecosystems. These laws cover aspects such as waste management, noise control, and habitat protection.
Waste Management and Public Health
One of the primary concerns addressed by Georgia’s environmental laws is the proper disposal of dog waste. Dog owners are required to promptly clean up after their pets in public spaces. This law helps prevent the contamination of water sources and the spread of disease.
Noise Control and Community Well-being
Excessive dog barking can be a source of noise pollution, affecting the quality of life in residential areas. Local ordinances in Georgia often include provisions to control dog barking, ensuring that it does not become a nuisance to the community.
Habitat Protection and Wildlife Conservation
Dogs can have a significant impact on local wildlife and their habitats. Georgia’s laws encourage responsible pet ownership in natural areas, including keeping dogs on leashes where required and respecting wildlife preserves.
The Role of the “Responsible Dog Ownership Law”
Georgia’s “Responsible Dog Ownership Law” provides a framework for minimizing the negative environmental impacts of dogs. This law includes provisions for the control and regulation of dogs to protect public safety and the environment.
Local Ordinances and Enforcement
Local governments in Georgia have the authority to enact ordinances that may be more restrictive than state laws. These local ordinances are crucial for addressing the specific environmental concerns of different communities.
Education and Awareness
Part of my role as a veterinarian is to educate dog owners about the importance of complying with environmental impact laws. This includes discussing the consequences of non-compliance and the benefits of responsible pet ownership.
Dog Behavioural Training Laws in Georgia
As a veterinarian, I am often asked about the legalities surrounding dog behavioral training in Georgia. It’s a topic of great importance to dog owners and trainers alike, as it ensures the welfare of the animals and the safety of the community. This article will provide an in-depth look at the laws governing dog behavioral training in the state of Georgia.
Understanding Dog Behavioral Training Laws
In Georgia, dog behavioral training is subject to state laws and local ordinances that govern how training should be conducted. These laws are designed to protect dogs from inhumane treatment and ensure that training practices are ethical and effective.
Licensing and Certification for Trainers
Professional dog trainers in Georgia may be required to obtain a license or certification to operate legally. This process typically involves demonstrating knowledge of dog behavior, training techniques, and adherence to animal welfare standards.
Humane Training Practices
Georgia law mandates that all training practices be humane. This means that trainers are prohibited from using cruel or harmful methods. Training techniques should focus on positive reinforcement rather than punishment.
Service Dog Training Regulations
Service dogs in Georgia are trained to perform specific tasks for individuals with disabilities. The law provides certain rights and protections for service dogs and their trainers during the training process. Trainers are allowed to bring service dogs in training to public places to acclimate them to different environments.
Public Access for Trainers and Dogs in Training
Trainers are granted the right to be accompanied by dogs in training in public accommodations, provided they are identified as agents or employees of a recognized training school for service dogs.
Consumer Protection Laws
Georgia’s consumer protection laws apply to dog training services. Trainers must provide clear information about their services, fees, and the expected outcomes of the training. Consumers have the right to seek redress if services are not provided as advertised.
Animal Cruelty and Neglect
Any form of animal cruelty or neglect is strictly prohibited in Georgia. This includes during the course of dog training. Trainers who violate these laws face serious legal consequences.
Record-Keeping Requirements
Dog trainers are required to maintain records of their training sessions, including the methods used and the progress of each dog. This ensures transparency and accountability in the training process.
Training Facilities Regulations
Facilities used for dog training must meet certain standards for safety and cleanliness. This includes adequate space for exercise, proper sanitation, and access to veterinary care.
Dog Protection and Rescue Laws in Georgia
In the state of Georgia, the welfare of dogs is a matter of legal importance. As a veterinarian, I am often at the forefront of implementing these laws, which are designed to protect dogs from harm and ensure their humane treatment. This comprehensive article will delve into the dog protection and rescue laws that are in place in Georgia, providing a detailed understanding of the legal landscape.
The Georgia Animal Protection Act
At the heart of dog protection in Georgia is the Georgia Animal Protection Act (O.C.G.A. § 4-11-1). This act serves as the cornerstone of legal protections for dogs, outlining the responsibilities of pet owners and the standards for animal care.
Licensing and Regulation of Pet Dealers and Shelters
The law requires all pet dealers, kennels, and animal shelters to be licensed by the Commissioner of Agriculture. This licensing ensures that these entities meet the standards set forth for the care and sale of animals.
Humane Care and Adequate Facilities
Under the Georgia Animal Protection Act, dogs must be provided with humane care, which includes adequate food, water, shelter, and veterinary attention. Kennels and shelters are required to maintain facilities that provide sanitary shelter and wholesome food and water.
Prohibitions Against Cruelty
Georgia law strictly prohibits cruelty to animals, including dogs. This includes physical abuse, neglect, abandonment, and other forms of mistreatment. Violations can result in misdemeanor or felony charges, depending on the severity of the offense.
Rescue Operations and Transport Regulations
Rescue groups in Georgia are subject to specific regulations, especially those that bring in animals from out-of-state. These regulations ensure that rescued dogs are healthy, vaccinated, and spayed or neutered before adoption.
Mandatory Reporting of Animal Cruelty
Veterinarians and other professionals are mandated to report any suspected cases of animal cruelty. This legal obligation helps to identify and prevent instances of abuse and neglect.
Spay and Neuter Requirements
To combat overpopulation and reduce the number of stray dogs, the Georgia Department of Agriculture requires that all dogs adopted from shelters be spayed or neutered. This policy is crucial for controlling the stray population and promoting responsible pet ownership.
Protection for Service and Working Dogs
Service and working dogs are afforded special protections under Georgia law. Interference with or harm to these dogs carries significant legal penalties, recognizing their vital role in assisting individuals with disabilities.
Emergency Response and Disaster Preparedness
Georgia law includes provisions for the rescue and protection of dogs in the event of natural disasters or emergencies. This ensures that dogs are not forgotten during times of crisis and that there are plans in place for their care and evacuation if necessary.
Dog Entertainment and Work Laws in Georgia
In Georgia, dogs are not only beloved pets but also partners in work and entertainment. As a veterinarian, I’m aware of the specific laws that regulate the roles dogs play in these areas. This article will explore the legalities surrounding dog entertainment and work in Georgia, providing a detailed understanding of dog owners, trainers, and enthusiasts.
Understanding the Legal Framework
Georgia’s legal framework for dog entertainment and work is designed to ensure the welfare of dogs while they perform or provide services. These laws cover a range of activities, from service dog regulations to the use of dogs in entertainment settings.
Service Dog Laws
In Georgia, service dogs are granted extensive rights under both state law and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). These laws allow service dogs to accompany their handlers in public accommodations, including entertainment venues, shopping centers, and grocery stores. The law specifies that an “assistance dog” must be specially trained to perform physical tasks by a licensed or certified trainer.
Emotional Support Animals
While service dogs have broad access rights, emotional support animals (ESAs) do not enjoy the same level of access under Georgia law or the ADA. However, ESAs are protected under the Fair Housing Act, allowing them to live with their owners in housing with a “no pets” policy.
Working Dogs in Law Enforcement and Security
Working dogs in law enforcement and security are protected under Georgia law, which recognizes their role in public safety. These dogs are trained to perform tasks such as search and rescue, detection of substances, and protection of property and personnel.
Animal Performance and Exhibition
Dogs used in performances and exhibitions must be treated humanely, with adequate rest periods, proper nutrition, and veterinary care. Georgia law prohibits any form of cruelty or neglect in the training and exhibition of performing dogs.
Film and Television Work
Dogs working in film and television in Georgia are subject to regulations that ensure their safety and well-being on set. This includes provisions for adequate housing, temperature control, and supervision by a qualified animal handler.
Racing and Sporting Events
While dog racing is not a prominent sport in Georgia, dogs that participate in legal sporting events, such as agility competitions, are protected by laws that require humane treatment and proper care.
Breeding and Training Regulations
Dog breeders and trainers in Georgia must adhere to the Georgia Animal Protection Act, which sets standards for the humane care of animals. This includes providing adequate food, water, shelter, and veterinary attention.
Licensing and Inspection
Facilities that breed or train dogs for entertainment or work must be licensed and are subject to regular inspections to ensure compliance with state laws and animal welfare standards.
Dog Technology and Innovation Laws in Georgia
In the ever-evolving landscape of pet care, Georgia stands at the forefront of embracing technological advancements aimed at enhancing the lives of our canine companions. As a veterinarian, I’ve witnessed the transformative impact of pet tech products and innovations in dog health technology. This article delves into the legal framework that governs these advancements in Georgia, ensuring they serve the best interests of pets and their owners.
The Legal Terrain of Pet Tech in Georgia
Georgia’s approach to regulating pet technology is rooted in the broader “Responsible Dog Ownership Law,” which sets the minimum standards for dog control and regulation. While this law does not explicitly address pet tech products, it provides a foundation for ensuring the safety and welfare of pets in all aspects, including the use of technology.
Innovations in Dog Health Technology
The state has witnessed a surge in innovations designed to monitor and improve canine health. From wearable activity trackers to advanced diagnostic tools, these technologies are revolutionizing veterinary care. However, the deployment of such devices must comply with state laws that prioritize animal welfare and consumer protection.
Regulatory Oversight
While specific laws for pet tech products are not explicitly outlined, general consumer protection laws apply. These regulations ensure that products are safe, reliable, and marketed truthfully. Manufacturers and distributors of pet tech products must navigate these laws to ensure compliance and protect consumers.
Data Privacy and Security
With the rise of smart devices that collect and store data on pets’ health and behavior, data privacy has become a critical concern. Georgia’s laws mandate that companies safeguard this data and uphold privacy standards, preventing unauthorized access or misuse.
Ethical Considerations
The use of technology in dog training and care must align with ethical standards. Georgia law prohibits cruelty and neglect, which extends to the use of technology in training and behavior modification. Training devices must not cause harm or distress to the animals.
Consumer Education and Transparency
Educating consumers about the capabilities and limitations of pet tech products is essential. Georgia’s consumer protection laws require clear labeling and instructions, enabling pet owners to make informed decisions about the technology they use with their dogs.
Veterinary Integration
Technological innovations must integrate seamlessly with veterinary practices. Georgia law requires that any health-related tech product used for diagnostic or treatment purposes must be approved by a licensed veterinarian, ensuring that it meets professional standards of care.
Future Developments
As technology continues to advance, Georgia’s legal system may adapt to address new challenges and opportunities. This could include specific regulations for pet tech products, ensuring they meet rigorous safety and efficacy standards.
Human Coexistence Laws in Georgia
In Georgia, the bond between humans and dogs is not only cherished but also protected by law. As a veterinarian, I’ve seen how these laws promote cohabitation and strengthen the bond between our species. This article will explore the legal measures in place that encourage the harmonious coexistence of dogs and humans in Georgia.
The Essence of Human-Dog Cohabitation Laws
Georgia’s cohabitation laws are designed to create environments where humans and dogs can live together safely and respectfully. These laws address various aspects of daily life, from housing regulations to public access rights.
Housing and Accommodation
In Georgia, fair housing laws ensure that individuals with service dogs have the right to live with their animals without facing discrimination. This extends to emotional support animals under certain conditions, promoting the therapeutic benefits of pet companionship.
Public Access and Service Dogs
Service dogs are granted extensive access to public spaces in Georgia. This includes restaurants, stores, and parks, allowing individuals with disabilities to fully participate in society with their canine helpers by their side.
Responsible Dog Ownership Law
The “Responsible Dog Ownership Law” sets the foundation for coexistence by outlining the responsibilities of dog owners. This includes proper care, control, and consideration for the safety and comfort of others.
Leash and Waste Disposal Regulations
Leash laws and waste disposal regulations are enforced to ensure that dogs do not pose a nuisance or health risk in public areas. These laws are crucial for maintaining cleanliness and order in shared spaces.
Animal Welfare and Anti-Cruelty Statutes
Georgia’s animal welfare and anti-cruelty statutes protect dogs from mistreatment, ensuring they live in safe and humane conditions. These laws also foster compassion and respect for animals among the public.
Education and Awareness Programs
The state supports education and awareness programs that teach the importance of cohabitation and bonding between dogs and humans. These initiatives help to prevent conflicts and promote understanding.
Dispute Resolution and Mediation Services
To address conflicts that may arise between dog owners and others, Georgia provides dispute resolution and mediation services. This approach encourages peaceful solutions and mutual respect.
Community Planning and Pet-Friendly Spaces
Urban planning in Georgia increasingly includes pet-friendly spaces, such as dog parks and trails. This integration reflects the state’s recognition of the importance of dogs in human lives.
Other Relevant Dog Laws in Georgia
Georgia, known for its rich history and diverse landscapes, is also a state that values the bond between humans and their canine companions. This article provides an in-depth look at the various laws that affect dog owners in Georgia, ensuring that their furry friends are well-cared for, protected, and integrated into society.
Canine Good Citizen Programs and Legal Benefits in Georgia
The Canine Good Citizen (CGC) Program, established by the American Kennel Club, is a two-part program that teaches responsible dog ownership and certifies dogs who have good manners at home and in the community. In Georgia, while there is no direct legal benefit to CGC certification, it can serve as a testament to a dog’s training and temperament, which may be favorable in legal situations or when seeking housing accommodations.
Dog Insurance and Coverage Laws in Georgia
In Georgia, the Responsible Dog Ownership Law enforces measures for the registration of dangerous dogs, mandating owners to possess a minimum liability insurance of $50,000. This legislation ensures that victims of dog-related incidents are compensated, and encourages owners to be responsible for their pets’ actions.
Laws Regarding Dogs in Hot Cars and Animal Endangerment in Georgia
Georgia does not have a specific statute against leaving dogs in hot cars; however, general animal cruelty laws apply. It is considered a misdemeanor to intentionally cause pain or suffering to an animal or to fail to provide necessary sustenance or shelter, which can include leaving a dog in a hot car.
Legal Aspects of Dog Parks and Shared Spaces in Georgia
Dog parks in Georgia provide designated off-leash areas where dogs can exercise and socialize. While there are no specific state laws governing dog parks, local ordinances often include rules to ensure safety and proper conduct within these spaces. These may include leash requirements upon entering and exiting the park, vaccination requirements, and the separation of spaces based on dog size.
Dog-Related Property Damage and Homeowner’s Insurance in Georgia
In Georgia, homeowner’s insurance policies typically cover liability for dog bites and other dog-related injuries to third parties. However, damage caused by a dog to the owner’s property is generally not covered, as pets are considered the owner’s responsibility. Homeowner’s insurance may also be affected by the breed of the dog, with some insurers excluding certain breeds from coverage.
Service and Working Dog Laws in Employment and Public Access in Georgia
Georgia law and the ADA protect the rights of individuals with disabilities to be accompanied by their service dogs in public accommodations and employment. Service dogs must be trained to perform specific tasks related to the owner’s disability, and emotional support animals, while not granted the same access rights, are protected under housing laws.
Animal Welfare and Protection Laws Against Neglect and Abandonment in Georgia
The Georgia Animal Protection Act provides comprehensive protection against cruelty, neglect, and abandonment. It requires humane care for animals, including adequate food, water, and shelter. Violations can lead to serious legal consequences, emphasizing the state’s commitment to animal welfare.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the article has provided a comprehensive exploration of the multifaceted dog laws in Georgia, highlighting the state’s dedication to fostering a society where dogs are respected, protected, and well-integrated. From the Canine Good Citizen Programs that recognize well-behaved dogs to stringent regulations against leaving dogs in hot cars, these laws collectively ensure the welfare of dogs and the safety of the community.
The significance of compliance with these laws cannot be overstated; it not only ensures the well-being of our canine friends but also upholds public safety, promotes responsible pet ownership, and maintains harmony within society. Adherence to these laws reflects a collective commitment to ethical treatment and responsible stewardship of dogs, which ultimately enhances the quality of life for all, both humans and animals alike.
FAQs
What are the requirements for registering a service dog in Georgia?
In Georgia, there is no formal state-wide registration process for service dogs. However, service dogs must be trained to perform specific tasks related to their handler’s disability. It’s important for service dog handlers to carry proof of their dog’s training and purpose if required.
Are there breed-specific laws in Georgia that I should be aware of?
While Georgia does not have state-wide breed-specific legislation, certain cities and counties may have their own restrictions or regulations regarding specific dog breeds. It’s essential to check with local ordinances to understand any breed-specific laws that may apply in your area.
Can landlords in Georgia refuse to rent to me if I have a dog?
Landlords in Georgia can set their own pet policies, which may include the refusal to rent to tenants with dogs. However, for individuals with service dogs or emotional support animals, landlords must make reasonable accommodations under the Fair Housing Act.
Is it legal to leave my dog in the car in Georgia?
While Georgia does not have a specific statute against leaving dogs in hot cars, general animal cruelty laws apply. If leaving a dog in the car is deemed to cause suffering or endanger the dog’s life, it could be considered a criminal offense.
What should I do if my dog accidentally causes property damage in Georgia?
If your dog causes property damage in Georgia, you may be held liable for the cost of repairs or replacement. It’s advisable to have homeowner’s insurance or pet liability insurance that covers such incidents. Always report any damage to your insurance provider and the property owner to resolve the situation responsibly.







