Dog Laws in Idaho
Navigating the intricate web of dog laws in Idaho is essential for every pet owner. They impact both humans and their canine companions. In the United States, approximately 66% of households own a pet, with dogs being the most popular choice. This underscores the importance of being well-versed in the laws that govern pet ownership.
In Idaho, these laws encompass a variety of areas, including licensing, leashing, and liability. They are designed to ensure public safety, protect animal welfare, and promote responsible pet ownership. With the ever-evolving landscape of pet laws, staying informed is not just a legal obligation but also a moral one, ensuring that our beloved dogs live harmoniously within our communities. Understanding these laws is the first step towards fostering a safe and nurturing environment for all.
Table of Contents
Dog Bite Laws in Idaho
When it comes to dog bite laws in Idaho, the state takes a strict liability stance, holding dog owners accountable for any injuries their dog’s cause. This is irrespective of the dog’s past behavior or the owner’s knowledge of such tendencies. Here’s an in-depth look at the dog bite laws in Idaho:

Strict Liability for Dog Bites
Idaho Statutes Title 25, Chapter 28, Section 25-2810, establishes that dog owners are liable for any harm their dogs inflict upon a person, even if it’s the first incident of its kind for the dog.
Definitions of Dangerous and At-Risk Dogs
- A dangerous dog is one that has inflicted serious injury on a person without justified provocation or has a known history of such behavior.
- An at-risk dog is one that bites a person without causing serious injury and without justified provocation.
Penalties for Owners of Dangerous or At-Risk Dogs
Owners of dogs classified as dangerous or at-risk may face misdemeanor charges unless they comply with specific court orders regarding the management of their pets.
Defenses for Dog Owners
The law provides defenses for dog owners in cases where the bite was a result of justified provocation or if the victim was trespassing at the time of the incident.
Court Orders for Dog Management
In cases where a dog is deemed dangerous or at-risk, the court may issue orders for the dog’s management, which could include restrictions or requirements for its keeping, or in some cases, its destruction.
Restitution for Victims
The court may order individuals found guilty of violating dog bite laws to pay restitution to the victim, covering medical expenses, property damage, and other related costs.
Time Limitations for Filing a Lawsuit
Victims of dog bites have a statute of limitations within which they must file a lawsuit. In Idaho, this period is generally two years from the date of the incident.
No “One-Bite Rule”
Unlike some states that follow the “one-bite rule,” Idaho does not require a previous history of biting for the owner to be held liable.
Dog Owner Responsibility
Idaho law mandates that dog owners must exercise reasonable care in controlling their pets to prevent harm to others. This includes keeping dogs on leashes in public places and securely confining them within the owner’s property.
Homeowner’s Insurance and Dog Bites
Dog owners should review their homeowner’s insurance policies to understand coverage for dog bites, as this can be crucial in the event of an incident.
Dog Barking and Noise Laws in Idaho
In the serene state of Idaho, the harmony of neighborhood living is sometimes disrupted by the all-too-common issue of dog barking. While there is no specific statewide statute that dictates the exact duration for which a dog can bark, local ordinances are in place to ensure peace and quiet. Here’s an SEO-optimized overview of dog barking and noise laws in Idaho, tailored to provide clarity and guidance for dog owners and their neighbors.

Addressing Barking Issues Neighborly
The Idaho Humane Society recommends a neighborly approach to resolving barking issues. If a dog’s barking becomes a nuisance, a polite conversation with the dog owner is encouraged as the first step. Owners are often unaware of the disturbance caused by their pets, especially if they are away from home during the day.
Filing a Complaint
Should the barking persist, affected individuals have the option to file a complaint with local authorities. In Idaho, excessive barking can be considered a misdemeanor, and the dog owner may face fines up to $300. In severe cases, the court may even order the removal of the animal.
Local Ordinances
Each municipality in Idaho may have its own set of regulations regarding dog barking and noise. For example, some areas may have time limits on how long a dog can bark continuously before it is deemed a nuisance. It’s important for residents to familiarize themselves with the specific laws in their locality.
Preventive Measures
Dog owners are advised to take preventive measures to minimize barking. This can include ensuring that dogs have enough exercise, are not left alone for extended periods, and are trained to respond to commands to stop barking.
Legal Recourse for Continuous Disturbance
If a dog’s barking continues to be a problem and the owner fails to address it, neighbors can seek legal recourse. This may involve presenting evidence of the disturbance, such as video recordings, to the court.
Responsibility of Dog Owners
Under Idaho law, dog owners are responsible for the proper care and control of their pets to prevent them from becoming a public nuisance. This includes managing their barking behavior to avoid disturbing the peace.
Community Mediation
Some communities offer mediation services to help resolve disputes between neighbors over dog barking. This can be a constructive way to reach an agreement without resorting to legal action.
Educational Resources
The Idaho Humane Society and other organizations provide resources and tips for dog owners on how to manage barking and maintain good relations with neighbors.
Dog Poop Disposal Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, responsible dog ownership extends beyond providing food, shelter, and love; it includes adhering to dog poop disposal laws to maintain public health and environmental quality. Here’s an SEO-optimized, comprehensive guide to the dog poop disposal laws in Idaho, designed to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Understanding the Importance of Dog Poop Disposal
Proper disposal of dog waste is not just a matter of cleanliness; it’s a public health concern. Dog feces can contain harmful bacteria and parasites like giardiasis, salmonella, and E. coli, which can contaminate water sources and pose health risks to humans and wildlife.
Local Ordinances and Regulations
While Idaho does not have a statewide law specifically for dog poop disposal, local municipalities have ordinances in place. These regulations typically require pet owners to immediately pick up their dog’s waste from public property and dispose of it properly.
Fines and Penalties
Failure to comply with local dog poop disposal laws can result in fines. The amount can vary depending on the city or county, but it generally ranges from a small fee for first-time offenders to higher amounts for repeated violations.
Proper Disposal Methods
The recommended method for dog waste disposal is using a plastic bag to pick up the waste and then disposing of it in a trash can. Environmentally-conscious pet owners may opt for biodegradable bags, which are designed to break down over time and reduce plastic waste.
Environmental Impact
Improper disposal of dog poop can lead to environmental degradation. It’s illegal to dispose of pet waste in storm drains or waterways in some areas, as it can lead to water pollution.
Dead Animal Disposal
While not directly related to dog poop, it’s worth noting that Idaho has rules governing the disposal of dead animals. These rules are designed to protect natural resources and prevent the spread of disease.
Littering Laws
Dog poop left on public or private property can be considered littering under Idaho law. Littering is punishable by a fine, and this includes not picking up after your pet.
Solid Waste Disposal
Throwing away, dumping, or discarding any type of solid waste, including dog poop, on public lands or private land without permission is a misdemeanor in Idaho.
Best Practices for Dog Owners
To avoid legal issues and contribute to a clean community, dog owners should always carry waste bags when walking their dogs and promptly dispose of waste in designated trash receptacles.
Community Health and Safety
By following these laws, dog owners help protect the health and safety of the community, ensuring that public spaces remain clean and enjoyable for everyone.
Dog Licensing Laws in Idaho
In the picturesque state of Idaho, where the bond between humans and their canine companions runs deep, understanding and adhering to dog licensing laws is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership. Here’s an SEO-optimized, comprehensive guide to the dog licensing laws in Idaho, designed to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Mandatory Licensing and Registration
In Idaho, all dog owners are required to license and register their pets. This process typically involves submitting an application to the local animal control agency or city clerk’s office, providing details such as the dog’s breed, age, gender, and proof of current rabies vaccination.
Benefits of Licensing Your Dog
Licensing your dog serves several important purposes:
- It helps in the identification and return of lost pets.
- It ensures that dogs are vaccinated against rabies.
- It provides funding for local animal control initiatives.
County-Specific Regulations
While the state mandates licensing, specific requirements can vary by county. For instance, some counties may offer a discounted rate for spayed or neutered pets or require licensing for dogs as young as three months old.
Kennel Licensing
For those who keep dogs for breeding or commercial purposes, Idaho offers a kennel license option, covering up to fifteen dogs. This is particularly useful for breeders and those operating dog-related businesses.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to license a dog can result in fines and penalties. In some cases, unlicensed dogs may be impounded until the owner complies with the licensing requirements.
Licensing Exemptions
Certain exemptions to licensing requirements may apply, such as for service dogs or dogs belonging to non-resident visitors staying in Idaho for a short period1.
Renewal and Updates
Dog licenses in Idaho are not lifetime and require renewal. The frequency of renewal varies by county, but it is typically annual. Owners must also update their information if they move or if there are changes in the dog’s status.
The Role of Licensing in Public Safety
Licensing plays a crucial role in public safety by ensuring that dogs are vaccinated against rabies, a disease that poses a significant health risk to both humans and animals.
Online Licensing Options
To simplify the process, many counties in Idaho now offer online licensing services, allowing owners to apply for and renew licenses from the comfort of their homes.
Dog Leash Laws in Idaho
In the beautiful state of Idaho, where the great outdoors is a significant part of life, dog leash laws play a vital role in ensuring the safety and well-being of both pets and the community. Here’s an SEO-optimized, comprehensive guide to the dog leash laws in Idaho, designed to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Statewide Leash Requirements
Idaho does not have a statewide leash law, but it mandates that dogs must be kept on a leash or under proper control when in public areas. This is to prevent dogs from wandering off, approaching strangers or other animals without consent, and potentially causing harm or damage.
Local Ordinances
Each municipality in Idaho may have its own leash laws. For example, some cities require dogs to be on a leash no longer than 6 feet when in public spaces, while others may have specific off-leash areas designated for dogs.
Eagle City’s Leash Law
In Eagle City, dogs must be on a leash no more than 8 feet long unless they are in a car, with their owner at a dog park, or are immediately responsive to verbal or non-verbal direction, like a highly trained hunting dog.
Leash Law Enforcement
Violating leash laws can result in fines and penalties. Enforcement is typically carried out by local animal control officers who respond to complaints and patrol public areas.
Leash Laws and Aggressive Dogs
Special regulations may apply to dogs deemed dangerous or aggressive. These dogs may be required to be muzzled and on a leash at all times in public, regardless of the local leash law specifics.
Public Spaces and Parks
Most public parks in Idaho require dogs to be on a leash. However, there are designated dog parks where dogs can roam freely without a leash, provided they are under the owner’s control.
Responsibilities of Dog Owners
Dog owners in Idaho are responsible for keeping their pets on a leash in public areas and ensuring their dogs do not become a nuisance or a danger to others.
Fenced-In Requirements
Owners are required to keep their fences maintained to prevent dogs from escaping and running at large in the city. If a dog does escape and is found by an animal control officer or bites someone, the owner will be required to fix the fence.
Dangerous Dog Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the safety of the community and the welfare of dogs are of paramount importance. The state has enacted specific laws to address the issue of dangerous dogs, ensuring that both human and canine residents can live together harmoniously. Here’s an SEO-optimized, comprehensive guide to the dangerous dog laws in Idaho, designed to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.
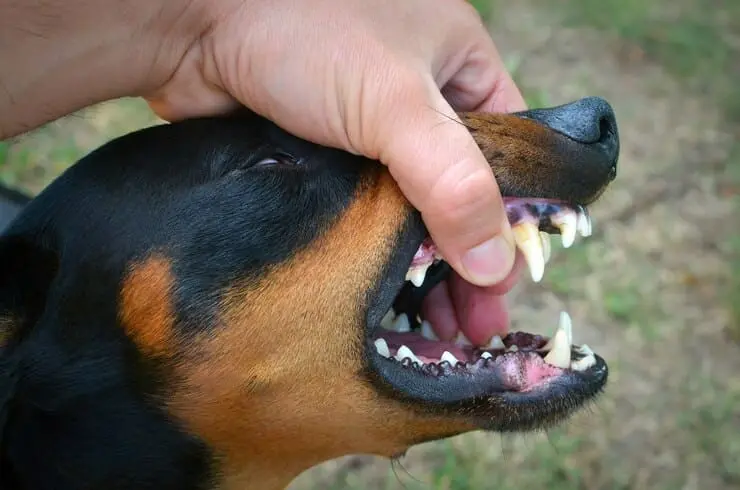
Idaho’s Definition of Dangerous and At-Risk Dogs
Idaho law defines a dangerous dog as one that, without justified provocation, has inflicted serious injury on a person or has a known history of such behavior. An at-risk dog is defined as one that bites a person without causing serious injury and without justified provocation.
Legal Consequences for Owners
Owners of dangerous or at-risk dogs may face misdemeanor charges unless they comply with the provisions of a court order pursuant to subsection (7) of Section 25-28101. This section also allows the court to order the owner to pay restitution related to medical expenses, property damage, and other costs incurred as a result of the dog’s actions.
Court Orders for Dog Management
If a dog is found to be dangerous or at-risk, the court may issue orders for the dog’s management, which could include restrictions or requirements for its keeping, or in some cases, its destruction.
Justified Provocation
No dog may be found to be dangerous or at-risk if, at the time an injury or damage was sustained, the cause constituted justified provocation. This includes scenarios where the dog was protecting a person from an attack or assault, the person was committing a crime on the property of the dog’s owner, or the person had previously tormented, abused, or assaulted the dog.
Running at Large
Idaho law prohibits owners from allowing their dogs to run at large without a competent and responsible attendant. Violation of this law can result in an infraction punishable as provided in section 18-113A, Idaho Code.
Preventive Measures: Dog owners are encouraged to take preventive measures to ensure their dogs do not become a public threat. This includes proper socialization, training, and secure confinement when the dog is not under direct supervision.
Public Awareness and Education
The state promotes public awareness and education regarding responsible dog ownership and the potential risks associated with dangerous dogs.
Dog Health and Welfare Laws in Idaho
Ensuring the health and welfare of dogs is a priority in Idaho, where comprehensive laws are in place to protect our four-legged friends. This SEO-optimized guide will delve into the dog health and welfare laws in Idaho, providing a detailed understanding for pet owners and animal enthusiasts alike.

Comprehensive Animal Welfare Legislation
Idaho’s animal welfare laws cover a broad spectrum of health and safety regulations for dogs. These include provisions for adequate shelter, food, water, and necessary veterinary care to prevent suffering and disease.
Rabies Vaccination Requirements
While Idaho does not mandate rabies vaccinations for resident animals, it is strongly recommended, and imported animals over 12 weeks old must be vaccinated. This law is crucial for preventing the spread of rabies, a fatal disease affecting both animals and humans.
Licensing and Identification
Idaho requires dog owners to license their pets, providing a means of identification and ensuring that dogs are vaccinated against rabies. Licensing helps in the quick return of lost pets and supports animal control efforts.
Cruelty and Neglect Laws
Idaho has strict laws against cruelty and neglect, which include abandoning a dog, failing to provide necessary care, or inflicting pain and suffering. Violations can lead to significant legal consequences.
Dangerous Dog Regulations
Idaho defines dangerous dogs and sets forth specific containment and handling requirements for them. Owners of dangerous dogs must adhere to these laws to prevent harm to the public and other animals.
Leash and Restraint Laws
Local ordinances often dictate leash laws, requiring dogs to be restrained in public spaces to prevent accidents and protect the community. These laws vary by municipality but are essential for public safety.
Humane Euthanasia Standards
The state sets standards for humane euthanasia, ensuring that when necessary, the process is carried out with the least amount of pain and distress to the animal.
Shelter and Rescue Regulations
Idaho regulates animal shelters and rescue organizations, setting standards for the care and housing of dogs to ensure their health and well-being while in the shelter system.
Breeder and Kennel Laws
Breeders and kennels in Idaho must comply with specific health and welfare standards, providing adequate space, nutrition, and care for all dogs in their custody.
Enforcement and Reporting
Animal control officers and law enforcement agencies are responsible for enforcing dog health and welfare laws. The public is encouraged to report suspected cases of abuse or neglect.
Educational Efforts
The state promotes educational programs to inform the public about responsible dog ownership, including proper care, training, and the importance of spaying and neutering to control the pet population.
Dog Public Access Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws surrounding dog public access are designed to balance the rights of pet owners with the safety and comfort of the community. This comprehensive guide will explore the various statutes and regulations that govern where and how dogs can accompany their owners in public spaces.

Statewide Public Access Laws
Idaho’s statewide laws require that dogs be kept on a leash or under proper control when in public areas. This is to prevent dogs from wandering off and to ensure the safety of both the dogs and the public.
Service Dog Access
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), service dogs are allowed to accompany their handlers in all public areas, including businesses and government buildings. Idaho law aligns with the ADA, ensuring that individuals with disabilities have full access to public spaces with their service dogs.
Local Ordinances
Local municipalities in Idaho may have additional regulations regarding dog public access. These can include specific leash length requirements, designated off-leash areas, and restrictions on dogs in certain public spaces like playgrounds or beaches.
Dog-in-Training Access
Idaho permits dogs-in-training to access public spaces as long as they are properly identified with a jacket, collar, scarf, or other article indicating their training status. This allows trainers to socialize and acclimate dogs to various environments as part of their training.
Enforcement of Public Access Laws
Violations of public access laws can result in fines and penalties. Enforcement is typically carried out by local animal control officers who respond to complaints and patrol public areas to ensure compliance.
Public Accommodation Rights
Places of public accommodation in Idaho must allow service dogs and dogs-in-training to enter. This includes restaurants, hotels, stores, and other businesses that serve the public.
Exclusion of Dangerous Dogs
Dogs that are deemed dangerous or have a history of aggressive behavior may be excluded from certain public areas for the safety of the community. Owners of such dogs must adhere to specific containment and handling requirements.
Responsibilities of Dog Owners
Dog owners in Idaho are responsible for ensuring their pets behave appropriately in public spaces. This includes preventing their dogs from jumping on or intimidating others, and promptly cleaning up after their pets.
Public Health Considerations
To protect public health, dogs must be vaccinated against rabies and other communicable diseases as required by local health departments before being allowed in public spaces.
Dog Travel and Transportation Laws in Idaho
Traveling with dogs in Idaho requires adherence to specific laws and regulations to ensure the safety and comfort of both pets and people. This comprehensive guide will explore the dog travel and transportation laws in Idaho, providing a detailed understanding for pet owners planning to move around with their furry companions.

Statewide Travel and Transportation Laws
Idaho’s statewide laws mandate that dogs must be safely restrained during travel. This can include using a crate, harness, or other secure methods to prevent distractions to the driver and to protect the dog in case of sudden stops.
Service Dog Travel Rights
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), service dogs are allowed to accompany their handlers on all forms of public transportation, including buses, taxis, and trains. Idaho law aligns with the ADA, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can travel freely with their service dogs.
Air Travel Regulations
When traveling by air, dog owners must comply with airline-specific policies as well as the Animal Welfare Act, which sets standards for the transportation of animals. Dogs must be housed in appropriate carriers and have access to food and water.
Importation of Dogs
For those bringing dogs into Idaho from other states or countries, a Certificate of Veterinary Inspection (CVI) is required. The CVI must confirm that the dog is free from infectious diseases and has been vaccinated against rabies.
Local Transportation Ordinances
Local municipalities may have additional regulations regarding the transportation of dogs. For example, some cities may require dogs to be leashed or in a carrier when on public transit, while others may have restrictions on dogs in taxis or ride-sharing services.
Restraint in Vehicles
Idaho does not have a specific law requiring dogs to be restrained in moving vehicles, but it is recommended for the safety of the pet and passengers. Unrestrained dogs can be a distraction to the driver and can be injured in an accident.
Traveling with Dogs in Recreational Vehicles (RVs)
For those traveling with dogs in RVs, it is important to ensure that the dog has a safe and comfortable space. Dogs should not be left unattended in parked RVs, especially in extreme temperatures.
Accommodations for Traveling Dogs
Many hotels and motels in Idaho are pet-friendly, but it’s essential to check the establishment’s pet policy beforehand. Some may have restrictions on the size or breed of dogs allowed.
Responsibilities of Dog Owners
Dog owners are responsible for ensuring their pets are well-behaved during travel and do not pose a risk to others. This includes managing barking, cleaning up after the dog, and preventing aggressive behavior.
Dog Housing and Accommodation Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws concerning dog housing and accommodation are designed to ensure the well-being of dogs and the rights of their owners, while also considering the rights of landlords and neighbors. This SEO-optimized guide will provide a detailed look at the dog housing and accommodation laws in Idaho, aiming to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Fair Housing Act and Assistive Animals
The federal Fair Housing Act requires housing providers to make reasonable accommodations for persons with disabilities, which includes allowing assistive animals even in properties that have a “No Pets” policy. This ensures equal opportunity for individuals with disabilities to use and enjoy their living spaces.
Idaho Service Dog Laws
Idaho state law protects the right to bring service dogs to public places, but it is more limited than the ADA because it covers only animals that assist the physically disabled, not those that assist individuals with mental disabilities. However, public accommodations in Idaho must comply with both sets of laws.
Public Accommodation for Service Dogs
Under Idaho law, individuals with disabilities are permitted to be accompanied by their service dogs in all areas of public accommodation, including common carriers, hotels, lodging houses, or places where the public is invited.
Housing Accommodations for Service Dogs
Landlords in Idaho are required to provide reasonable accommodations for service dogs without charging extra fees or deposits. This includes allowing service dogs in units that otherwise have a no-pet policy.
Local Ordinances
Local municipalities may have additional regulations regarding dog housing and accommodation. It’s important for dog owners to check with their city or county to understand any specific laws that may apply to their situation.
Responsibilities of Dog Owners
Dog owners in Idaho are responsible for ensuring their pets do not pose a nuisance or health hazard to others. This includes proper waste disposal, noise control, and ensuring the dog does not damage property.
Animal Welfare Laws
Idaho’s animal welfare laws require that dogs be provided with adequate shelter, food, water, and necessary veterinary care. These laws are in place to prevent suffering and ensure the health and welfare of dogs.
Dog Adoption and Sale Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws governing dog adoption and sale are designed to protect the welfare of dogs and ensure responsible practices by breeders, shelters, and pet stores. This SEO-optimized guide will provide a detailed look at the dog adoption and sale laws in Idaho, aiming to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Idaho’s Pet Dealer Regulations
Idaho requires pet dealers, which may include breeders and pet stores, to comply with certain standards of care. These standards ensure that dogs are housed in safe, clean environments and receive proper nutrition and veterinary care.
Licensing Requirements for Breeders
Breeders in Idaho must obtain a kennel license if they own more than a specified number of intact female dogs for breeding purposes. This license helps regulate breeding practices and promotes the health and welfare of the dogs.
Health Certificates for Sold or Adopted Dogs
When a dog is sold or adopted, Idaho law requires the provision of a health certificate. This certificate, issued by a licensed veterinarian, confirms that the dog is free from visible signs of infectious, contagious, or communicable diseases.
Consumer Protection for Pet Purchases
Idaho has “puppy lemon laws” that provide protections for consumers who purchase dogs from pet dealers. If a dog becomes ill or is found to have a congenital disorder shortly after purchase, the buyer may be entitled to remedies such as reimbursement for veterinary expenses.
Spay and Neuter Requirements
Some Idaho municipalities require that dogs adopted from shelters or rescue organizations be spayed or neutered. This is part of an effort to reduce pet overpopulation and the number of animals in shelters.
Disclosure Requirements
Pet dealers in Idaho must disclose specific information to buyers, including the dog’s medical history, vaccinations, and any known health issues. This transparency helps buyers make informed decisions about pet ownership.
Regulations on Dog Sales
Idaho prohibits the sale of dogs in certain public places, such as streets, parking lots, or flea markets, to prevent impulsive pet purchases and ensure that dogs are obtained from reputable sources.
Shelter and Rescue Adoption Policies
Animal shelters and rescue organizations in Idaho have their own adoption policies, which often include an application process, interviews, and home visits to ensure a good match between the dog and the adoptive family.
Protections for Service Dogs
Idaho law provides protections for service dogs, ensuring that they cannot be denied to individuals with disabilities based on breed or size restrictions that may apply to other dogs.
Dog Park and Recreation Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, dog parks and recreational areas offer a space for dogs to exercise and socialize, which is essential for their physical and mental well-being. The state has specific laws and regulations to ensure these areas are safe and enjoyable for everyone. Here’s an SEO-optimized, comprehensive guide to the dog park and recreation laws in Idaho, designed to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

State Department of Parks and Recreation Regulations
The Idaho Department of Parks and Recreation has established rules to maintain order and safety in parks. Pets, including dogs, are allowed within lands administered by the department only if confined or controlled on a leash not longer than six feet in length. This ensures that dogs do not disturb wildlife or other park users.
Behavior and Noise Control
Dogs must not create a disturbance that might be bothersome to other users. This includes excessive barking or aggressive behavior. Owners are responsible for controlling their pets and ensuring they behave appropriately.
Service Animals
Service animals are exempt from some of the restrictions that apply to pets. They are permitted to accompany their handlers throughout public parks and recreational areas as required by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Off-Leash Areas
Some parks in Idaho have designated off-leash areas where dogs can roam freely. However, even in these areas, owners must demonstrate control over their animals and are responsible for their behavior.
Clean-Up Rules
Owners are required to clean up after their pets. This is crucial for maintaining the cleanliness and hygiene of public spaces. Failure to do so can result in fines and penalties.
Quiet Hours
Within lands administered by the department, quiet hours are typically between 10 p.m. and 7 a.m. During this time, noise that may disturb other users, including that from pets, is restricted.
Alcohol and Littering Regulations
State laws regulating alcoholic beverages and public drunkenness are enforced within parks. Littering, which includes not picking up pet waste, is prohibited.
Trespass and Restricted Areas
It is unlawful to enter, use, or occupy land or facilities administered by the department where such lands or facilities are posted against entry, except as authorized by the department.
Fires and Camping with Dogs
The use of fires is restricted to designated areas, and all fires must be controlled and extinguished before leaving the site. When camping with dogs, owners must ensure their pets do not disturb other campers.
Local City Ordinances
Cities like Boise have their own regulations regarding dogs in parks. Dogs may not harass humans or other animals and must be on a leash unless in an area otherwise indicated. Owners are required to pick up after their pets.
Dog Food and Nutrition Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the regulations surrounding dog food and nutrition are an integral part of ensuring the health and well-being of our canine companions. This SEO-optimized guide will delve into the dog food and nutrition laws in Idaho, providing a detailed understanding for pet owners, breeders, and manufacturers alike.

Idaho Commercial Feed Law
Under the Idaho Commercial Feed Law, pet food is regulated as feed. This law stipulates that any commercial feed prepared and distributed for consumption by dogs and cats must meet certain standards.
Definition and Standards
The term “pet food” in Idaho encompasses all commercial feed intended for dogs and cats. This definition is crucial as it sets the stage for the regulation of dog food products within the state.
Adulteration Prohibition
The law strictly prohibits the distribution of adulterated commercial feed. Adulteration refers to the presence of any harmful or deleterious substances which may render the feed injurious to health when consumed.
Labeling Requirements
Dog food products in Idaho must be accurately labeled. Labels should include the product name, brand, net weight, list of ingredients, guaranteed analysis, feeding directions, and the name and address of the manufacturer.
Nutritional Adequacy
The Idaho State Department of Agriculture requires that all dog food products sold in the state must be nutritionally adequate. This means they must provide the necessary nutrients in appropriate amounts for the animal’s life stage, whether it be for growth, maintenance, or reproduction.
Manufacturing Practices
Manufacturers of dog food in Idaho must adhere to good manufacturing practices. This includes maintaining clean facilities, using quality ingredients, and ensuring that the production process does not compromise the nutritional value of the food.
Inspections and Compliance
The Idaho State Department of Agriculture conducts inspections to ensure compliance with the feed laws. Manufacturers found in violation may face penalties, including fines and product recalls.
Consumer Protection
Idaho’s laws also serve to protect consumers. This includes ensuring that dog food products are free from contaminants and that labels provide clear and accurate information to help consumers make informed choices.
Health Certificates for Imported Pet Food
For pet food imported into Idaho, a health certificate may be required to ensure that the products meet the state’s standards and are safe for animal consumption.
Dog Health and Veterinary Care Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the health and veterinary care of dogs are governed by a series of laws and regulations that ensure the well-being of these beloved animals. This comprehensive guide will delve into the dog health and veterinary care laws in Idaho, providing a detailed understanding for pet owners and veterinary professionals alike.
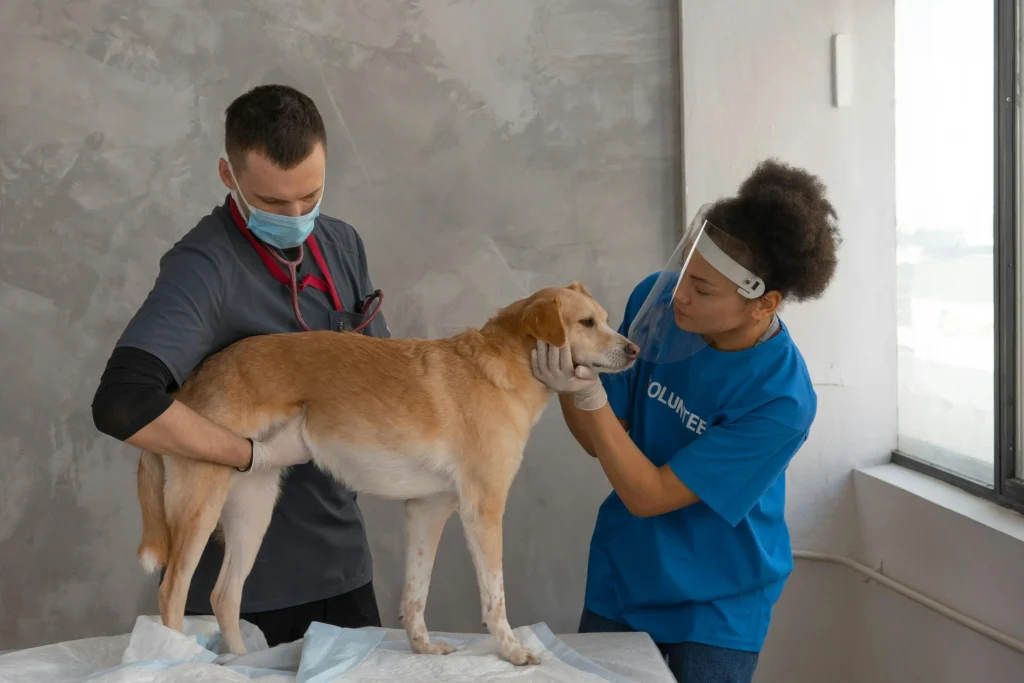

Idaho Veterinary Practice Act
The Idaho Veterinary Practice Act outlines the standards for veterinary medicine in the state. It includes licensing requirements for veterinarians, standards of professional conduct, and the scope of veterinary practice.
Rabies Vaccination Requirements
Idaho law requires that all dogs over the age of three months be vaccinated against rabies. The vaccination must be administered by a licensed veterinarian and kept up to date.
Veterinary Reporting of Zoonotic Diseases
Veterinarians in Idaho are required to report cases of zoonotic diseases—illnesses that can be transmitted from animals to humans—to the appropriate health authorities. This helps in monitoring and controlling potential outbreaks.
Standards for Veterinary Facilities
Veterinary facilities in Idaho must meet specific standards regarding sanitation, equipment, and animal housing to ensure the safety and health of both animals and humans.
Licensing and Inspection of Kennels and Breeders
Kennels and breeders may be subject to licensing and inspection to ensure that dogs are kept in healthy conditions and receive appropriate care.
Control of Dangerous Dogs
Idaho has laws in place to control dangerous dogs, which may include mandatory spaying or neutering, microchipping, and liability insurance for owners of dogs that have been deemed dangerous.
Animal Cruelty and Neglect Laws
Idaho’s animal cruelty laws prohibit neglect and mistreatment of dogs. This includes failing to provide necessary sustenance, adequate shelter, or veterinary care when needed.
Emergency Veterinary Care
In cases of emergency, Idaho law allows for immediate veterinary care to be provided to a dog without the explicit consent of the owner if it is necessary to save the animal’s life or relieve suffering.
Prescription and Use of Veterinary Drugs
Only licensed veterinarians can prescribe and administer veterinary drugs. The use of such drugs is strictly regulated to prevent abuse and ensure the health of the animal.
End-of-Life Care and Euthanasia
Idaho regulates the euthanasia of animals, ensuring that it is performed in a humane manner by qualified individuals. The state also provides guidelines for the disposal of animal remains.
Dog Identification and Microchipping Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws surrounding dog identification and microchipping are integral to ensuring the safety and proper management of pets. This SEO-optimized guide will delve into the dog identification and microchipping laws in Idaho, providing a detailed understanding for pet owners.

Microchipping as a Form of Identification
In Idaho, microchipping is recognized as a reliable form of pet identification. While not mandated statewide for all dogs, microchipping is highly recommended by veterinarians and rescue organizations as a permanent way to link pets to their owners.
Dangerous and At-Risk Dogs
For dogs that have been classified as dangerous or at-risk, Idaho law mandates specific identification requirements. These dogs must be permanently identified by means of a color photograph in a file maintained by the court and local enforcement agency and by a microchip or tattoo used for the identification of companion animals at the expense of the owner.
Microchip Registration
Owners of dangerous or at-risk dogs are required to report microchip registration in a timely manner to the local agency responsible for the control of such dogs. Upon demand, the owner must provide access to the dog to any such agency or local law enforcement entity for the purposes of verifying microchip implantation or tattoo.
Benefits of Microchipping
Microchipping offers numerous benefits, including:
- Facilitating the return of lost or stolen dogs to their rightful owners.
- Providing a form of identification that cannot be lost, altered, or intentionally removed.
- Assisting in the identification of owners in cases of abuse or neglect.
Microchipping Process
The microchipping process involves the insertion of a small chip, about the size of a grain of rice, under the dog’s skin, typically between the shoulder blades. The procedure is quick, relatively painless, and can be performed during a routine veterinary visit.
Updating Microchip Information
It is crucial for dog owners to keep their contact information up to date in the microchip registry. This ensures that they can be promptly contacted if their dog is found.
Local Ordinances
Some localities in Idaho may have their own ordinances regarding dog identification and microchipping. Pet owners should check with their local animal control or city clerk’s office to understand any additional requirements specific to their area.
Encouraging Responsible Ownership
Microchipping is part of responsible pet ownership. It demonstrates a commitment to the dog’s welfare and a proactive approach to pet management.
Dog Breeding and Genetics Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws governing dog breeding and genetics are designed to ensure the ethical treatment of animals and the integrity of breeding practices. This SEO-optimized guide will provide a detailed look at the dog breeding and genetics laws in Idaho, aiming to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Idaho’s Pet Dealer Regulations
Idaho requires pet dealers, which may include breeders, to comply with certain standards of care. These standards ensure that dogs are housed in safe, clean environments and receive proper nutrition and veterinary care.
Licensing Requirements for Breeders
Breeders in Idaho must obtain a kennel license if they own more than a specified number of intact female dogs for breeding purposes. This license helps regulate breeding practices and promotes the health and welfare of the dogs.
Health Certificates for Sold or Adopted Dogs
When a dog is sold or adopted, Idaho law requires the provision of a health certificate. This certificate, issued by a licensed veterinarian, confirms that the dog is free from visible signs of infectious, contagious, or communicable diseases.
Genetic Testing and Disclosure
While Idaho does not have specific laws mandating genetic testing for breeding dogs, ethical breeders often perform genetic testing to identify potential hereditary conditions. If genetic testing is performed, breeders are expected to disclose the results to potential buyers.
Consumer Protection for Pet Purchases
Idaho has “puppy lemon laws” that provide protections for consumers who purchase dogs from pet dealers. If a dog becomes ill or is found to have a congenital disorder shortly after purchase, the buyer may be entitled to remedies such as reimbursement for veterinary expenses.
Breeding Restrictions
Certain municipalities in Idaho may have their own breeding restrictions, including limitations on the number of litters a dog can have per year and the minimum age for breeding.
Spay and Neuter Requirements
Some localities in Idaho require that dogs adopted from shelters or rescue organizations be spayed or neutered. This is part of an effort to reduce pet overpopulation and the number of animals in shelters.
Record Keeping
Breeders are required to keep detailed records of their breeding activities. This includes tracking the lineage of dogs, health screenings, and the outcome of any genetic testing.
Enforcement and Penalties
The Idaho State Department of Agriculture is responsible for enforcing the state’s pet dealer regulations. Violations can result in penalties, including fines and the revocation of a breeder’s license.
Educational Requirements
While not mandated by law, many reputable breeders in Idaho pursue education in animal husbandry and genetics to improve their breeding programs and ensure the health of their dogs.
Dog Environmental Impact Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the environmental impact of dogs is a matter of concern for both pet owners and the community. The state has implemented laws to mitigate the negative effects dogs may have on the environment. This SEO-optimized guide will provide a detailed look at the dog environmental impact laws in Idaho, aiming to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Waste Disposal and Sanitation
One of the primary environmental concerns related to dogs is waste management. Idaho law requires dog owners to promptly clean up after their pets in public spaces. This helps prevent contamination of water sources and maintains public hygiene.
Leash Laws and Wildlife Protection
To protect local wildlife, Idaho has leash laws that require dogs to be restrained in certain areas, especially where there is a presence of sensitive wildlife habitats. These laws help prevent dogs from disturbing or harming native species.
Barking and Noise Control
Excessive barking can be a source of noise pollution. Idaho’s laws mandate that dog owners prevent their pets from creating a public nuisance with persistent barking, which contributes to a more peaceful environment.
Dog Park Regulations
Idaho has specific regulations for dog parks to ensure they do not adversely affect the local environment. This includes maintaining the cleanliness of the parks and preventing the overuse of any single area, which could lead to soil erosion and vegetation damage.
Water Quality Protection
Idaho’s laws also address the protection of water quality from dog waste. Owners are encouraged to dispose of waste properly and avoid allowing their dogs to defecate near water bodies, which can lead to eutrophication and harm aquatic ecosystems.
Air Quality and Odor Control
While not directly related to dogs, Idaho’s air quality laws require the control of odors that may affect the comfort and health of the community. This indirectly impacts how dog waste and kennels must be managed to prevent foul odors.
Responsible Breeding Practices
Responsible breeding practices are encouraged to prevent overpopulation, which can have a significant environmental impact due to the increased number of strays and the pressure they put on local ecosystems.
Public Education and Awareness
The state promotes public education on the environmental impact of dogs. This includes providing information on best practices for dog ownership that aligns with environmental conservation efforts.
Enforcement and Penalties
Violations of environmental impact laws related to dogs can result in fines and penalties. Enforcement is typically carried out by local animal control officers who respond to complaints and ensure compliance.
Collaboration with Environmental Agencies
Idaho encourages collaboration between animal control agencies and environmental protection agencies to address the impact of dogs on the environment comprehensively.
Dog Behavioural Training Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws pertaining to dog behavioral training are designed to ensure the safety and well-being of both the animals and the public. While there are no specific state-wide statutes that dictate the methods or practices of dog behavioral training, there are regulations that indirectly affect how training should be conducted. Here’s an overview of the relevant laws in Idaho:

Service Dog Training Regulations
Idaho recognizes the importance of service dogs and has provisions for their training. Dogs-in-training must wear a jacket, collar, scarf, or other similar article identifying them as such. This helps the public recognize and respect the training process.
Public Accommodation for Trained and In-Training Service Dogs
Both service dogs and dogs-in-training are allowed in places of public accommodation. This ensures that service dogs can be properly socialized and accustomed to various environments as part of their training.
Trainer Identification for Dogs-in-Training
Non-disabled handlers training service dogs must present an ID card from a trainer or training organization when accessing public accommodations with a dog-in-training.
Animal Welfare Act Compliance
Dog trainers in Idaho must comply with the federal Animal Welfare Act, which sets standards for the humane care and treatment of animals. This includes providing adequate housing, nutrition, and veterinary care during the training process.
Cruelty and Neglect Laws
Idaho’s cruelty and neglect laws apply to all animals, including those undergoing training. Trainers must not engage in any form of cruelty, abuse, or neglect, and must provide necessary sustenance, care, and protection from the elements.
Licensing and Zoning Regulations
Professional dog trainers may be subject to local licensing and zoning regulations. These laws can dictate where training facilities can be located and the conditions under which they operate.
Liability for Dog Behavior
Under Idaho law, dog owners and trainers may be held liable for the behavior of the dogs under their care. This includes any damage or injury caused by a dog, emphasizing the importance of effective behavioral training.
Leash Laws
While not specific to training, leash laws in Idaho require dogs to be under control in public spaces. Trainers must adhere to these laws to prevent dogs from becoming a nuisance or a danger to the public.
Noise Ordinances
Excessive barking during training sessions can be a violation of local noise ordinances. Trainers must ensure that their activities do not disturb the peace in residential areas.
Consumer Protection Laws
Dog training services are subject to Idaho’s consumer protection laws. Trainers must represent their services honestly and fulfill any agreements made with clients.
Dog Protection and Rescue Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the protection and rescue of dogs are governed by a series of laws that ensure the humane treatment and welfare of these animals. This SEO-optimized guide will delve into the dog protection and rescue laws in Idaho, providing a detailed understanding for pet owners, rescuers, and the general public.

Animal Welfare Act Compliance
Idaho adheres to the federal Animal Welfare Act, which sets standards for the humane care and treatment of animals, including dogs in shelters and rescue organizations.
Cruelty and Neglect Laws
Idaho’s cruelty and neglect laws prohibit the mistreatment of dogs. This includes abandoning a dog, failing to provide necessary care, or inflicting pain and suffering. Violations can lead to significant legal consequences.
Dangerous Dog Laws
Idaho has specific statutes regarding dangerous dogs. Owners of dogs that have been classified as dangerous must adhere to strict regulations, including proper containment and identification, to protect the public and other animals.
Dog Bite Laws
The state follows a strict liability approach for dog bites, holding owners accountable for any injuries their dogs cause, regardless of the dog’s previous behavior.
Rescue and Shelter Regulations
Rescue organizations and shelters in Idaho must comply with regulations that ensure the health and safety of dogs in their care. This includes providing adequate shelter, food, water, and necessary veterinary care.
Licensing and Zoning Regulations
Rescue organizations may be subject to local licensing and zoning regulations, which dictate where they can operate and the conditions under which they must maintain their facilities.
Spay and Neuter Programs
Idaho encourages spay and neuter programs to reduce pet overpopulation and the number of dogs in shelters. Some municipalities may have ordinances requiring the spaying or neutering of adopted dogs.
Reporting of Animal Cruelty
The law requires individuals to report suspected cases of animal cruelty or neglect. This helps authorities intervene and provide necessary protection for dogs at risk.
Disaster Response and Evacuation
Idaho has provisions for the rescue and protection of dogs during natural disasters. This includes evacuation plans that account for pets and service animals.
Humane Euthanasia
The state sets standards for humane euthanasia, ensuring that when necessary, the process is carried out with the least amount of pain and distress to the animal.
Lost and Found Dogs
Idaho has procedures for reporting and handling lost and found dogs. This helps reunite lost pets with their owners and provides care for unclaimed dogs.
Public Education and Awareness
The state promotes public education on responsible dog ownership and the importance of protecting and rescuing dogs. This includes information on adoption, proper care, and legal obligations.
Collaboration with Law Enforcement
Rescue organizations often collaborate with law enforcement to address issues related to dog protection and rescue. This partnership is crucial for effective animal welfare enforcement.
Volunteer and Foster Program
Idaho supports volunteer and foster programs that provide temporary homes for dogs awaiting adoption. These programs play a vital role in the rescue and rehabilitation of dogs.
Dog Entertainment and Work Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the laws concerning dog entertainment and work are designed to ensure the welfare of dogs engaged in various activities, from service roles to recreational pursuits. This SEO-optimized guide will provide a detailed look at the dog entertainment and work laws in Idaho, aiming to meet the search intent for this topic and optimized for search engines.

Service Dog Laws
Idaho legislation aligns with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in recognizing service dogs’ rights to accompany their handlers in public areas. However, Idaho’s laws are more restrictive, applying only to animals that aid the physically impaired, not those assisting individuals with mental disorders. Public accommodations in Idaho must follow both sets of rules.
Working Dog Regulations
Dogs used for work, such as herding livestock or assisting law enforcement, are subject to regulations that ensure their proper treatment and care. These dogs must be provided with adequate rest, shelter, and veterinary care to maintain their health and well-being.
Entertainment Industry Standards
Dogs involved in the entertainment industry, such as film or live performances, must be treated humanely. Idaho adheres to the guidelines set forth by the Animal Welfare Act, which includes provisions for the animals’ handling, housing, and transportation.
Anti-Cruelty Laws
Idaho’s anti-cruelty statutes protect dogs from abuse and neglect, including those used for work or entertainment. It is illegal to subject any dog to cruel treatment, and violators can face legal penalties.
Dog Racing Prohibition
While Idaho does not have a specific statute banning dog racing, the state does not have any operational dog racing tracks, and the practice is not prevalent.
Performance and Exhibition Licensing
Organizers of dog-related performances or exhibitions may be required to obtain a license. This ensures that events involving dogs are conducted responsibly and with consideration for the animals’ welfare.
Breeding and Sales Regulations
Breeders and sellers of working or entertainment dogs must comply with Idaho’s pet dealer regulations. This includes providing a health certificate for each dog sold and adhering to consumer protection laws.
Training Standards
Trainers of working or entertainment dogs must use humane methods. The use of excessive force or cruel training techniques is prohibited under Idaho law.
Restraint and Confinement Rules
When not performing or working, dogs must be kept in humane conditions. This includes proper tethering practices and ensuring that confinement areas are clean, safe, and allow the dog to move freely.
Reporting Abuse or Neglect
Individuals who witness the abuse or neglect of working or entertainment dogs are encouraged to report these incidents to local authorities or animal welfare organizations.
Dog Technology and Innovation Laws in Idaho
In the state of Idaho, the intersection of technology and pet care is an evolving landscape, with laws and regulations adapting to the advancements in pet tech products and innovations in dog health technology. This comprehensive guide will explore the legal framework that governs these developments, ensuring that pet owners and industry professionals are well-informed and compliant.

Veterinary Practice Act
Idaho’s Veterinary Practice Act sets the standards for veterinary medicine, including the use of technology in veterinary care. It outlines the licensing procedures, supervision requirements, and standards of practice for veterinarians and veterinary technicians.
Rabies Vaccination and Microchipping
Idaho law mandates rabies vaccinations for dogs and recognizes microchipping as a reliable form of pet identification. While not required statewide, microchipping is encouraged as a permanent means of linking pets to their owners.
Animal Welfare Act Compliance
Pet tech products used in Idaho must comply with the federal Animal Welfare Act, ensuring humane treatment of animals during their use. This includes devices used for monitoring, training, or therapeutic purposes.
Consumer Protection Laws
Products designed for pet care, such as health monitors or training devices, fall under Idaho’s consumer protection laws. These laws ensure that products are safe, reliable, and marketed truthfully.
Data Privacy and Security
With the rise of smart pet tech products that collect and store data, Idaho’s laws on data privacy and security become relevant. Manufacturers and service providers must protect the personal information of pet owners and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Telemedicine Regulations
Innovations in dog health technology include telemedicine services. Idaho’s laws permit veterinary telemedicine under certain conditions, allowing remote consultations and diagnoses while ensuring the standard of care is maintained.
Prescription and Use of Veterinary Drugs
The use of technology in dispensing and administering veterinary drugs is regulated in Idaho. Only licensed veterinarians can prescribe medications, and certain tech-based dispensing methods may require additional scrutiny to ensure compliance with state laws.
Standards for Veterinary Facilities
Veterinary facilities employing health technology must adhere to Idaho’s standards regarding sanitation, equipment, and animal housing. This ensures that technological innovations do not compromise the health and safety of pets.
Ethical Considerations
As technology advances, ethical considerations come into play. Idaho’s laws and veterinary ethics guidelines dictate that any use of technology in pet care must prioritize the well-being and humane treatment of animals.
Innovation and Research
Idaho supports innovation and research in animal health technology. However, any new developments must be rigorously tested and approved to ensure they meet the state’s standards for safety and efficacy.
Human Coexistence Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, the coexistence between humans and dogs is fostered through a variety of laws and regulations that promote harmonious living and strong bonds between the two species. This SEO-optimized article will explore the legal framework that supports this relationship, ensuring that pet owners and the general public can live together with dogs in a way that benefits both parties.

Anti-Discrimination Laws
Idaho’s anti-discrimination statutes ensure that individuals cannot be denied access to housing or public accommodations based on their ownership of a dog. This is particularly important for those with service animals, as these laws guarantee their right to live and move freely with their canine companions.
Service Dog Regulations
Service dogs in Idaho are protected under state and federal laws, allowing them to accompany their handlers in all public areas. These laws recognize the vital role that service dogs play in the lives of individuals with disabilities and ensure that they can perform their duties without hindrance.
Leash and Animal Control Laws
Leash laws in Idaho are designed to protect the safety of both dogs and humans. By requiring dogs to be on a leash in public spaces, these laws prevent accidents and encourage responsible pet ownership, which in turn promotes positive interactions between dogs and the community.
Responsible Pet Ownership Education
Idaho encourages educational programs that teach responsible pet ownership. These programs cover topics such as proper dog care, training, and understanding canine behavior, which are essential for fostering a strong and healthy bond between dogs and their human families.
Animal Welfare Legislation
The state’s animal welfare laws mandate that dogs receive proper care, including adequate food, shelter, and veterinary attention. By ensuring the well-being of dogs, these laws indirectly support the bond between dogs and humans, as healthy and happy dogs are more likely to form strong relationships with their owners.
Dog-Friendly Public Spaces
Idaho has made strides in creating dog-friendly public spaces, such as parks and trails, where dogs and their owners can enjoy recreational activities together. These areas not only provide exercise and stimulation for dogs but also opportunities for socialization and community building among dog lovers.
Disaster Preparedness and Response
Laws related to disaster preparedness and response in Idaho include provisions for pets, ensuring that dogs and their owners are not separated during emergencies. This reflects the understanding that the human-canine bond is important to maintain, even in times of crisis.
Adoption and Rescue Support
Idaho supports the adoption and rescue of dogs through legislation that regulates shelters and rescue organizations. By facilitating the adoption process and ensuring the humane treatment of dogs in these settings, the state helps create the foundation for strong bonds to form between rescued dogs and their new families.
Public Health and Safety
Public health and safety laws in Idaho take into account the presence of dogs in the community. Regulations on vaccination, waste disposal, and noise control are all aimed at ensuring that dogs can coexist with humans without posing health or safety risks.
Encouraging Volunteerism and Community Involvement
The state encourages volunteerism and community involvement in dog-related activities and organizations. This not only benefits the dogs but also strengthens the community’s appreciation for the human-canine relationship.
Other Relevant Dog Laws in Idaho
In Idaho, a variety of laws exist to ensure the well-being of dogs and to regulate their interaction with humans and the environment. Here’s an overview of some relevant dog laws in the state:

Canine Good Citizen Programs and Legal Benefits
The Canine Good Citizen (CGC) program is recognized as a standard for dog behavior and provides a foundation for other activities such as therapy dog training. While Idaho does not have specific legal benefits for CGC certification, it can be advantageous in demonstrating responsible pet ownership.
Dog Insurance and Coverage Laws
Idaho does not have specific laws mandating dog insurance, but homeowners’ insurance policies may cover dog-related liabilities. It’s important to check with insurance providers as coverage can vary, especially concerning certain breeds or dogs with a history of aggression.
Laws Regarding Dogs in Hot Cars and Animal Endangerment
Idaho law prohibits leaving a dog in a hot car under its animal cruelty statutes. Law enforcement or animal control officers are authorized to take necessary action to rescue pets from such situations.
Legal Aspects of Dog Parks and Shared Spaces
While specific statewide laws for dog parks are not detailed, local ordinances often govern the use of these shared spaces. These regulations typically include leash requirements, waste disposal, and behavior standards to ensure safety and cleanliness.
Dog-Related Property Damage and Homeowner’s Insurance
Generally, homeowners’ insurance policies do not cover damage caused by the policyholder’s own pets. However, liability coverage may apply if a dog injures a person or damages someone else’s property.
Service and Working Dog Laws in Employment and Public Access
Idaho law and the ADA protect the rights of individuals with disabilities to be accompanied by service dogs in public places and employment. The state’s laws are more limited than the ADA, covering only dogs that assist with physical disabilities.
Animal Welfare and Protection Laws Against Neglect and Abandonment
Idaho has laws against the cruelty, neglect, and abandonment of animals. Owners must provide proper care and attention, and failure to do so can result in misdemeanor charges.
In conclusion, the comprehensive overview of Idaho’s dog laws underscores the state’s commitment to fostering a society where humans and dogs can coexist harmoniously. From ensuring the humane treatment of dogs in various settings to promoting responsible pet ownership, these laws cover a wide spectrum of activities including breeding, adoption, public access, and welfare. The significance of these regulations cannot be overstated; they not only protect the well-being of dogs but also address public health and safety concerns. Compliance with these laws is essential for maintaining a balanced ecosystem where the rights of pet owners, the needs of the dogs, and the interests of the community are all respected. By adhering to these legal standards, dog owners contribute to a culture of care and respect for animal life, and help uphold the social fabric that values the bond between dogs and humans. It’s a shared responsibility that enhances the quality of life for all involved.
FAQs
Are there breed-specific laws in Idaho?
No, Idaho does not have statewide breed-specific legislation. However, individual cities or counties may have ordinances that place restrictions on certain dog breeds. It’s important for dog owners to check the local laws in their area.
What are the requirements for traveling with a dog in Idaho?
When traveling with a dog in Idaho, owners should ensure their pets are safely restrained in vehicles, have up-to-date vaccinations, and are accompanied by any necessary health certificates, especially if crossing state lines.
How does Idaho law address dogs that are service animals in training?
Idaho law allows service animals in training to access public places provided they are properly identified and accompanied by a trainer. This helps ensure that service dogs are well-prepared for their roles.
What should I do if I find a lost dog in Idaho?
If you find a lost dog in Idaho, you should report it to the local animal control or a nearby animal shelter. They can assist in locating the owner and ensure the dog is cared for properly.
Can landlords in Idaho refuse to rent to dog owners?
Landlords in Idaho can set their own pet policies, which may include restrictions or refusal to rent to dog owners. However, they must make reasonable accommodations for service animals as required by the Fair Housing Act.






