Dog Laws in Wisconsin
As a dog owner in the United States, with over 85 million canine companions gracing our homes, understanding dog laws is crucial. Not only does it ensure a happy and safe life for our furry friends, but it also protects the well-being of our communities.
Navigating dog laws in Wisconsin can seem complex, but knowing your rights and responsibilities becomes much easier when you break it down. This guide will explore the different areas of dog law coverage, from licensing and leash regulations to animal cruelty prevention and responsible pet ownership practices.
By understanding these legal frameworks, we can build strong bonds with our dogs and contribute to a dog-loving community that prioritizes the safety and welfare of all.
Table of Contents
Dog Bite Laws in Wisconsin
Dogs are cherished members of countless families in Wisconsin. However, even the most well-behaved dog can inflict a bite. When a dog bite incident occurs, understanding the legal landscape in Wisconsin becomes crucial.

The Importance of Dog Bite Laws
Dog bite laws serve several critical purposes:
- Protecting Public Safety: These laws aim to deter dog owners from neglecting their responsibilities and hold them accountable for their dog’s actions, promoting public safety.
- Ensuring Victim Compensation: Dog bite victims deserve fair compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, and emotional distress caused by the bite.
- Encouraging Responsible Dog Ownership: Dog bite laws act as an incentive for responsible pet ownership practices, such as proper training and secure containment.
Wisconsin’s Strict Liability Dog Bite Laws
Wisconsin has a strict liability dog bite statute, meaning a dog owner is liable for the full amount of damages caused by their dog biting a person, regardless of the owner’s prior knowledge or negligence. This stands in contrast to “one-bite” laws, which only hold owners liable if their dog has a history of aggression. Here’s a breakdown of Wisconsin’s key dog bite laws:
- Wis. Stat. § 174.02(1)(a): This statute outlines the strict liability principle. The owner of a dog is liable for the full amount of damages caused by the dog injuring or causing injury to a person, domestic animal, or property. There’s no requirement to prove the owner knew their dog was likely to bite.
- Wis. Stat. § 174.02(1)(b): This statute addresses subsequent bite incidents. If a dog owner has been previously notified or knew their dog had bitten someone before, and the dog bites again, the owner is liable for twice the full amount of damages caused by the bite.
Exceptions to Strict Liability
While Wisconsin’s dog bite laws hold owners strictly liable, there are some exceptions:
- Trespassing: If the victim was trespassing on private property where the dog is kept, the owner might not be liable. However, this exception doesn’t apply to children trespassing unintentionally.
- Provocation: If the victim provoked the dog, the owner’s liability might be reduced or eliminated.
Determining Liability in Dog Bite Cases
Several factors can influence the determination of liability in a dog bite case:
- Severity of the Bite: The seriousness of the injury will likely impact the amount of compensation awarded to the victim.
- Dog’s History of Aggression: Prior bite incidents or aggressive behavior on the dog’s part can strengthen the case against the owner.
- Leash Laws: If the dog was unleashed in violation of leash laws at the time of the bite, it might strengthen the victim’s case.
- Victim’s Actions: If the victim provoked the dog, it could weaken their claim.
Steps to Take After a Dog Bite
If you’re bitten by a dog in Wisconsin, here are some crucial steps to take:
- Seek Medical Attention: Your primary concern should be your health. Get immediate medical attention to address the bite wound and document your injuries.
- Report the Bite: Report the incident to animal control to ensure the dog’s vaccination status is verified and appropriate action is taken, if necessary.
- Gather Evidence: If possible, take pictures of the bite wound, the scene of the incident, and any witnesses.
- Contact a Lawyer: An experienced personal injury lawyer can advise you on your legal rights and help navigate the process of seeking compensation.
Preventing Dog Bites
Dog bites are preventable. Here’s how both dog owners and the community can contribute:
- Responsible Dog Ownership: Proper training, socialization, and secure containment of dogs are essential to preventing bites.
- Obeying Leash Laws: Always keep your dog leashed in public spaces as required by law.
- Teaching Children How to Interact with Dogs: Educate children on respectful and safe ways to interact with dogs.
- Reporting Aggressive Dogs: If you witness a dog exhibiting aggressive behavior, report it to animal control.
Dog Barking and Noise Laws in Wisconsin
Dogs enrich our lives with companionship and unconditional love. However, their vocal nature can sometimes lead to disturbances, particularly excessive barking. When persistent barking becomes a nuisance, understanding Wisconsin’s noise ordinances and responsible pet ownership practices becomes crucial.

The Impact of Excessive Dog Barking
While some barking is natural canine behavior, excessive barking can create significant problems:
- Disturbance for Neighbors: Constant barking can disrupt sleep, work, and overall peace of mind for those living nearby.
- Stress and Anxiety: Excessive noise can contribute to stress and anxiety in both humans and other animals.
- Strained Relationships: Chronic barking can strain relationships between neighbors and potentially lead to legal disputes.
Noise Ordinances and Dog Barking
Wisconsin doesn’t have a statewide law specifically addressing dog barking. However, most cities and municipalities have their own noise ordinances that might reference animal noise, including dog barking. Here’s what you need to know:
- Local Noise Ordinances: These ordinances typically define acceptable noise levels and timeframes during which noise restrictions apply. Some ordinances might have specific decibel limits, while others might use subjective terms like “unreasonable” or “annoying” noise.
- Focus on Duration and Frequency: Noise ordinances often focus on the duration and frequency of barking rather than just the existence of barking itself. Occasional barking is generally tolerated, but persistent or excessive barking throughout the day or night could be considered a violation.
- Enforcing Noise Ordinances: Noise complaints are typically handled by local law enforcement or animal control officers. If a barking complaint is filed, the officer might issue a warning or citation to the dog owner.
Addressing Dog Barking Responsibly
While legal repercussions exist, prioritizing responsible pet ownership goes beyond simply avoiding fines. Here’s how to address dog barking issues effectively:
- Identify the Cause: First, understand why your dog is barking excessively. It could be boredom, separation anxiety, fear, or a territorial response.
- Provide Training and Enrichment: Proper training and addressing the underlying cause of barking are key to reducing the behavior. Consider positive reinforcement training techniques, providing mental and physical stimulation for your dog, and addressing any anxiety issues.
- Communicate with Neighbors: Talk to your neighbors about the issue and explore solutions together. Maybe they can alert you if your dog barks while you’re away.
- Consider Noise-Buffering Solutions: Providing your dog with a shaded area or visual barriers in the yard can help reduce environmental triggers for barking.
Resources
- Association of Professional Dog Trainers (APDT): The APDT website provides resources on finding qualified dog trainers in your area who can help address barking issues.
- American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA): The ASPCA website offers resources on preventing and addressing dog barking.
- Your Local Animal Shelter or Rescue: Shelters and rescues might offer training classes or behavior consultations to address dog barking.
Preventing Barking Issues
By taking proactive measures, you can minimize the likelihood of excessive barking becoming a problem:
- Proper Training and Socialization: Start training and socialization early on to prevent boredom and behavioral issues that can lead to barking.
- Provide Adequate Exercise and Mental Stimulation: A tired dog is a less vocal dog. Ensure your dog gets enough physical and mental exercise to stay calm and content.
- Address Separation Anxiety: If your dog barks excessively when left alone, work on addressing separation anxiety through training and desensitization techniques.
- Desensitize Triggers: If your dog barks in response to specific triggers like mail delivery or passersby, work on desensitizing them to those stimuli through training.
Dog Poop Disposal Laws in Wisconsin
Dog ownership brings immense joy, but with it comes the responsibility of responsible pet waste management. In Wisconsin, like most states, cleaning up after your dog isn’t just a matter of courtesy; it’s the law.

The Importance of Responsible Dog Poop Disposal
Beyond the unpleasant sight and smell, dog poop poses several significant risks:
- Public Health Hazards: Dog waste carries harmful bacteria and parasites that can spread diseases to humans and other animals.
- Water Pollution: Rainwater runoff can carry dog waste into waterways, contaminating drinking water sources and harming aquatic ecosystems.
- Environmental Issues: Left-behind dog poop attracts flies and other pests, contributing to unpleasant odors and potential infestations.
Wisconsin’s Dog Poop Disposal Laws
While Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, statewide law specifically addressing dog waste disposal, most cities and municipalities have ordinances mandating responsible pet waste management. Here’s what you need to know:
- Local Poop and Scoop Laws: These ordinances typically require dog owners to pick up and properly dispose of their dog’s waste in all public spaces, including parks, sidewalks, trails, and even your neighbor’s yard (unless you have permission).
- Fines for Non-Compliance: Failing to clean up after your dog can result in fines or citations issued by local animal control officers or law enforcement.
- Poop Bag Dispensers in Public Areas: Many parks and public spaces in Wisconsin provide poop bag dispensers as a courtesy for dog owners. However, it’s always a good idea to bring your own bags in case dispensers are empty.
The Ethics of Responsible Pet Waste Management
Responsible pet ownership extends beyond legal requirements. Here’s why scooping the poop is the right thing to do:
- Respect for Your Community: Cleaning up after your dog shows respect for your neighbors and fellow dog owners, fostering a cleaner and more pleasant environment for everyone.
- Protecting Public Health: Proper pet waste disposal minimizes the risk of disease transmission and safeguards public health.
- Environmental Stewardship: Responsible pet waste management helps protect our waterways and ecosystems from harmful contaminants.
How to Dispose of Dog Poop Responsibly
Here are the best practices for responsible dog poop disposal in Wisconsin:
- Always Carry Poop Bags: Make it a habit to carry poop bags with you whenever you’re out with your dog.
- Double-Bag It: For extra security and odor control, double-bag your dog’s waste.
- Tie it Tight and Dispose: Securely tie the bag closed and dispose of it in a designated waste bin.
- Not in Trash Cans: Unless specifically marked for pet waste, avoid disposing of dog poop in regular trash cans. Some parks might have designated pet waste disposal bins.
- Composting Considerations: While some areas allow composting dog waste under specific guidelines, it’s generally not recommended in Wisconsin due to potential parasite concerns. Check with your local waste management provider for clarification.
Additional Considerations
- Leaving Poop in Wooded Areas: Avoid leaving dog poop even in wooded areas, as it can still contaminate waterways through rain runoff.
- Biodegradable Bags: Consider using biodegradable poop bags to minimize your environmental footprint.
- Educate Others: Encourage other dog owners to practice responsible pet waste disposal by setting a positive example and sharing information.
Resources
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR): The WDNR website provides resources on responsible pet ownership and environmental stewardship practices.
- Your Local Animal Shelter or Rescue: Shelters and rescues might offer resources and educational materials on responsible pet waste management.
- Keep America Beautiful: This national non-profit promotes responsible pet ownership and provides resources on dog waste disposal.
Dog Licensing Laws in Wisconsin
Owning a dog in Wisconsin brings immense joy and companionship. However, with the privilege of pet ownership comes the responsibility to ensure your furry friend is properly licensed. Dog licensing laws in Wisconsin serve several crucial purposes, promoting public safety, animal welfare, and responsible pet ownership.

The Importance of Dog Licensing
Dog licensing in Wisconsin offers a multitude of benefits:
- Public Safety: Licensing helps track and identify dogs, facilitating the swift return of lost pets to their owners.
- Vaccination Verification: Licensing often requires proof of rabies vaccination, promoting public health and preventing the spread of rabies.
- Funding for Animal Services: Licensing fees contribute to funding animal control services, shelters, and other programs that benefit animal welfare.
- Responsible Pet Ownership: Licensing demonstrates a commitment to responsible pet ownership and helps enforce animal control ordinances.
Wisconsin’s Dog Licensing Laws
Here’s a breakdown of key points regarding dog licensing in Wisconsin:
- Statewide Mandate: Wisconsin State Statute 174.06(1)(a) mandates that all dogs over five months old must be licensed annually.
- Responsibility of Owners: The responsibility for obtaining and renewing dog licenses falls on the dog owner.
- Licensing Location: Dog licenses are typically obtained from the municipal clerk’s office in the city, town, or village where the dog is kept.
- Licensing Fees: Licensing fees vary depending on the municipality and whether the dog is spayed/neutered. Generally, fees range from $10 to $20 for a spayed/neutered dog and $20 to $30 for an intact dog.
Additional Considerations
- Proof of Rabies Vaccination: When obtaining a license, you’ll typically need to provide proof of current rabies vaccination for your dog.
- Multiple Dog Licenses: If you own multiple dogs, you’ll need to obtain a separate license for each one.
- License Tags: Upon licensing, your dog will receive a tag to be worn on its collar for identification purposes.
- Renewing Your Dog’s License: Dog licenses typically expire annually, and renewal is required to maintain compliance with the law.
Benefits of Licensing Your Dog
While staying compliant with the law is essential, dog licensing offers additional benefits for your furry friend:
- Increased Chance of Recovery: A licensed dog with a collar and tag is much easier to identify and return if it gets lost, offering peace of mind for pet owners.
- Reduced Risk of Fines: Neglected licensing can result in fines and penalties.
- Supporting Animal Welfare: Licensing fees contribute to programs that benefit animal shelters, lost pet recovery initiatives, and other animal welfare efforts.
The Process of Obtaining a Dog License
Here’s a general overview of the dog licensing process in Wisconsin:
- Gather Information: Have proof of your dog’s rabies vaccination and any other documentation required by your municipality readily available.
- Contact Your Local Municipal Clerk’s Office: Locate the clerk’s office in the city, town, or village where you reside. Their website or phone number can be found through a quick internet search.
- Complete the Licensing Application: The application form can usually be obtained online or directly from the clerk’s office.
- Pay the Licensing Fee: Fees can be paid by cash, check, or credit card depending on the municipality’s policy.
- Receive Your Dog’s License Tag: Once your application is processed and payment is received, you’ll receive a tag for your dog’s collar.
Resources
- Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP): The DATCP website provides information on dog licensing requirements and links to relevant resources.
- Wisconsin Towns Association: This association website offers resources for finding contact information for local municipal clerks’ offices.
- Your Local Municipal Website: Most city, town, and village websites provide information on dog licensing procedures and fees specific to their jurisdiction.
Dog Leash Laws in Wisconsin
Exploring the outdoors with your canine companion is a cherished pastime for countless dog owners in Wisconsin. However, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone requires responsible pet ownership, and leash laws play a crucial role in achieving this.

The Importance of Dog Leash Laws
Dog leash laws serve several critical purposes:
- Public Safety: Leashes offer greater control over dogs, minimizing the risk of bites, injuries, or altercations with other animals and people.
- Protecting Wildlife: Unleashed dogs can disrupt wildlife habitats and pose a threat to native species.
- Preventing Nuisances: Leashes help ensure dogs don’t damage property or disrupt activities in public spaces.
- Promoting Responsible Ownership: Leash laws encourage dog owners to be mindful of their pet’s behavior and the well-being of others.
Dog Leash Laws in Wisconsin
While Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, statewide leash law, most cities and municipalities have their own ordinances mandating leash use in public spaces. Here’s a breakdown of key points to remember:
- Local Leash Ordinances: These ordinances typically define public spaces where leashes are required and outline acceptable leash lengths. Common areas subject to leash laws include parks, streets, sidewalks, trails, and public beaches.
- Focus on Control: The primary objective of leash laws is to maintain control over your dog. Even in off-leash areas designated by the municipality, you must be able to effectively control your dog by voice command or a retractable leash.
- Exceptions for Service Animals: Federal law protects the rights of individuals with disabilities to use service animals in public spaces. Service animals are typically exempt from leash laws, although they must remain under their handler’s control at all times.
Responsible Leash Use
Following leash laws is essential, but responsible leash use goes beyond mere compliance. Here are some tips for safe and enjoyable walks with your dog:
- Choose the Right Leash: Select a leash of appropriate length and strength for your dog’s size and temperament.
- Maintain Control: Always maintain slack-free leash control to prevent your dog from lunging or pulling.
- Be Mindful of Others: Give ample space to people and other dogs, especially if your dog exhibits signs of nervousness or aggression.
- Respect Designated Off-Leash Areas: If utilizing an off-leash area, ensure your dog is well-trained, socialized, and can be recalled reliably before letting them off-leash.
Additional Considerations
- Retractable Leashes: While convenient, use retractable leashes cautiously in crowded areas to avoid accidental tangles or injuries.
- Cleaning Up Waste: Always carry poop bags and dispose of your dog’s waste properly, regardless of leash status.
- Leashing Requirements at Dog Parks: Many dog parks require dogs to be leashed until they enter the designated off-leash area.
- Educating Others: Lead by example and encourage fellow dog owners to practice responsible leash etiquette.
Resources
- Wisconsin Towns Association: This association website offers resources for locating contact information for local municipal clerk’s offices.
- Your Local Municipal Website: Most city, town, and village websites provide information on leash laws and other animal control ordinances specific to their jurisdiction.
- Wisconsin State Bar Association: The State Bar website can help you find a lawyer specializing in animal law if you have questions about specific leash law interpretations.
The Benefits of Responsible Leash Use
Responsible leash use benefits not only public safety but also contributes to a more positive experience for everyone:
- Reduced Stress for Dogs: Leashed dogs often feel more secure in unfamiliar environments.
- Peace of Mind for Owners: Maintaining control over your dog provides peace of mind and minimizes the risk of unexpected incidents.
- Creating a Welcoming Environment: Responsible leash use helps ensure public spaces are enjoyable for everyone, including those who might be fearful of dogs.
Dangerous Dog Laws in Wisconsin
Owning a dog is a rewarding experience, but ensuring public safety is paramount. Wisconsin, like many states, has laws in place to address dangerous dogs and potential bite risks.

Dangerous Dog Classifications
While Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, specific definition of a “dangerous dog,” most municipalities have ordinances outlining criteria for classifying a dog as potentially dangerous or vicious. Here are some common factors considered:
- History of Bites: A dog with a documented history of inflicting serious bites on humans or other animals is more likely to be deemed dangerous.
- Aggressive Behavior: Documented incidents of threatening behavior, such as growling, lunging, or snapping without provocation, can raise concerns.
- Breed Restrictions: Some municipalities might have breed-specific restrictions, but these are uncommon in Wisconsin. The focus is typically on behavior rather than breed.
The Role of Local Animal Control
Local animal control officers play a crucial role in dangerous dog cases. Here’s how they might become involved:
- Investigating Bite Incidents: Animal control officers investigate reported dog bite incidents to assess the severity, gather evidence, and determine if the dog poses a potential threat.
- Quarantine Orders: If a dog is suspected of rabies or has bitten someone, the animal control officer might issue a quarantine order to ensure proper observation and public health protection.
- Dangerous Dog Declarations: Based on the investigation, animal control might declare a dog potentially dangerous or vicious, triggering specific regulations for the owner.
Potential Consequences of Having a Dangerous Dog Designation
If your dog is classified as dangerous or vicious, here are some potential consequences you might face:
- Muzzle and Leash Requirements: Your dog might be required to be muzzled and leashed at all times in public spaces, with a leash of a specific length for better control.
- Secure Fencing Requirements: Your property might need secure fencing to prevent your dog from escaping and posing a threat to others.
- Liability Insurance: You might be required to carry additional liability insurance coverage for your dog in case of future incidents.
- Financial Penalties: Fines or penalties might be imposed depending on the severity of the case and your compliance with regulations.
- Potential Removal: In extreme cases, if the risk is deemed too high, the court might order the dog’s removal from your home or even euthanasia.
Preventing Dangerous Dog Situations
The best approach to dangerous dog situations is prevention. Here are some proactive measures dog owners can take:
- Responsible Training and Socialization: Proper training and socialization from a young age can significantly reduce the risk of aggressive behavior.
- Understanding Dog Body Language: Learn to recognize canine stress signals and avoid situations that might trigger aggression.
- Spay/Neutering Your Dog: Spaying or neutering your dog can contribute to a calmer temperament and potentially reduce the risk of certain types of aggression.
- Obedience Training Classes: Investing in obedience training classes can equip you with the skills to manage your dog’s behavior effectively.
Resources dog bite incident, here are some resources to help:
- Your Local Animal Control Department: Animal control officers can investigate the situation, advise you on regulations, and potentially enforce dangerous dog designations.
- Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP): The DATCP website provides information on animal control resources and responsible pet ownership practices.
- Wisconsin State Bar Association: The State Bar website can help you find a lawyer specializing in animal law if you need legal advice regarding a dangerous dog situation.
The Importance of Responsible Dog Ownership
Every dog has the potential to bite, but responsible ownership plays a crucial role in minimizing risks. By understanding dangerous dog laws, prioritizing proper training and socialization, and taking proactive measures to ensure your dog’s safety and the safety of others, we can build a more harmonious and secure environment for everyone who shares our communities. Remember, responsible dog ownership is not just about following regulations; it’s about fostering good canine citizenship and ensuring the well-being of all.
Dog Health and Welfare Laws in Wisconsin
Owning a dog is a privilege, and Wisconsin, like many states, recognizes the importance of responsible pet ownership. This includes ensuring your dog’s health and well-being through proper care and adherence to relevant laws.
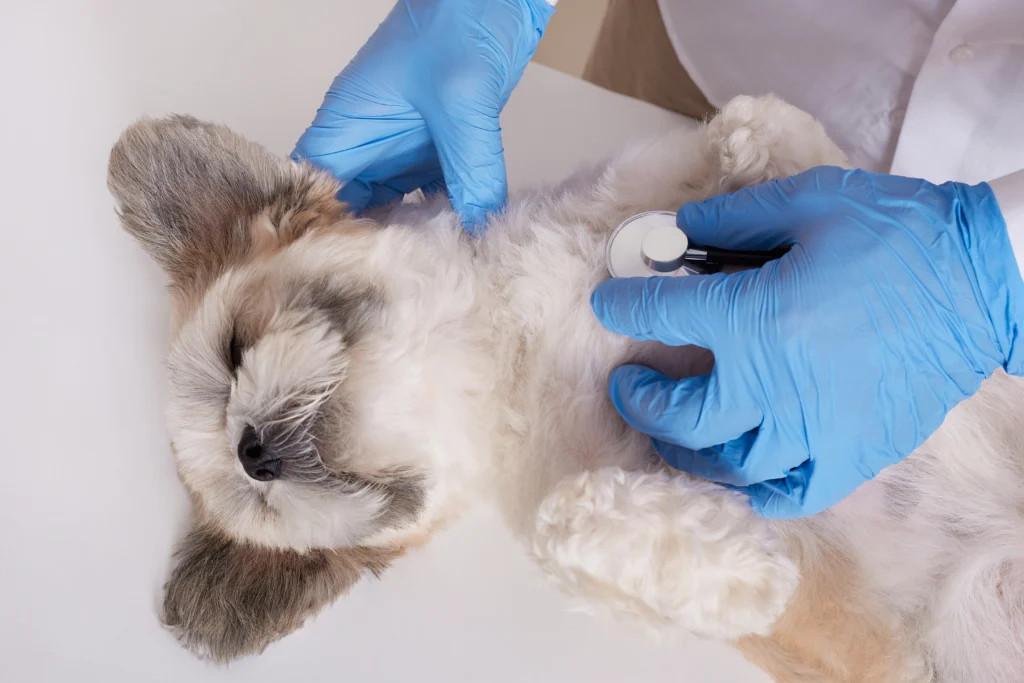
Wisconsin’s Animal Welfare Laws
Wisconsin primarily addresses animal welfare through Chapter 951 of the Wisconsin Statutes, which applies to all animals, including dogs. Here are some key points to remember:
- Prevention of Cruelty: The law prohibits any person from treating an animal, including a dog, in a cruel manner. This includes neglect, starvation, dehydration, inadequate shelter, or inflicting unnecessary pain or suffering.
- Veterinary Care: While not explicitly mandated by law, ensuring your dog receives necessary veterinary care is considered a core aspect of responsible ownership.
- Transporting Dogs: The law prohibits transporting animals in a cruel manner, requiring proper ventilation, space, and protection from extreme temperatures.
Essential Elements of Dog Health and Welfare
Legal compliance is crucial, but responsible pet ownership goes beyond the minimum requirements. Here are some essential elements for your dog’s health and well-being:
- Proper Nutrition: Provide your dog with a balanced and age-appropriate diet to meet their nutritional needs.
- Fresh Water Access: Ensure your dog has constant access to clean, fresh water at all times.
- Adequate Shelter: Provide your dog with a safe and comfortable shelter that protects them from the elements.
- Regular Exercise: Dogs require daily exercise to maintain physical and mental health.
- Mental Stimulation: Engage your dog with mental stimulation activities like playtime, training, or puzzle toys to prevent boredom and destructive behaviors.
- Preventative Veterinary Care: Schedule regular checkups with your veterinarian, maintain vaccinations, and address any health concerns promptly.
- Socialization: Socialize your dog from a young age to ensure they are comfortable interacting with other dogs and people.
Additional Considerations
- Tethering Restrictions: Some municipalities might have ordinances restricting how long a dog can be tethered outdoors.
- Hot Weather Safety: Never leave your dog unattended in a hot car or outside without adequate shade and water access during hot weather.
- Breeding Regulations: While not a statewide law, some municipalities might have regulations regarding commercial dog breeding operations.
- Microchipping: Consider microchipping your dog for easier identification if they get lost.
Resources
- Wisconsin Humane Society: The WHS website provides resources on responsible pet ownership, adoption, and animal welfare advocacy.
- Wisconsin Veterinary Medical Association (WVMA): The WVMA website offers information on finding a veterinarian in your area and the importance of preventative veterinary care.
- American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA): The ASPCA website provides a wealth of resources on dog health, training, and responsible pet ownership practices.
The Importance of Responsible Pet Ownership
Dog ownership brings immense joy, but it also comes with significant responsibility. By understanding and adhering to dog health and welfare laws, prioritizing proper care, and making your dog’s well-being a priority, you can contribute to a happier, healthier, and more fulfilling life for your furry friend. Remember, responsible pet ownership fosters a positive human-animal bond and strengthens the well-being of our communities as a whole.
Enhancing Dog Health and Welfare Through Advocacy
Beyond individual responsibility, pet owners can contribute to broader improvements in dog health and welfare:
- Supporting Animal Welfare Organizations: Donate or volunteer your time to organizations advocating for better animal welfare practices.
- Spreading Awareness: Educate others about responsible pet ownership and the importance of dog health and well-being.
- Advocating for Change: Support legislation that promotes responsible pet ownership and stricter animal cruelty laws.
The Human-Animal Bond and Building a Compassionate Community
Dogs enrich our lives with unconditional love, loyalty, and companionship. By prioritizing their health and well-being through responsible ownership, legal compliance, and advocacy efforts, we can build a more compassionate community where both humans and animals can thrive.
Dog Public Access Laws in Wisconsin
For many dog owners in Wisconsin, venturing out with their canine companions is a cherished part of daily life. However, navigating public spaces with your furry friend requires an understanding of dog public access laws.

Public Access Laws for Dogs
Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, comprehensive public access law for dogs. Instead, the legal landscape is shaped by a combination of factors:
- State Statutes: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 174 outlines general dog licensing requirements but doesn’t address public access specifically.
- Municipal Ordinances: Most cities, towns, and villages in Wisconsin have their own ordinances governing dog access in public spaces. These ordinances can vary considerably depending on the location.
- Private Businesses: Private businesses have the right to establish their own policies regarding dogs on their premises.
Finding Dog-Friendly Public Spaces
While there isn’t a centralized database listing all dog-friendly public spaces in Wisconsin, here are some resources to help you navigate:
- Municipal Websites: Most city, town, and village websites provide information on leash laws, park regulations, and designated dog parks within their jurisdiction.
- Dog-Friendly Apps: Mobile apps like BringFido or Sniffspot can help you locate dog-friendly parks, restaurants, and businesses in your area.
- Local Parks and Recreation Departments: Contact your local parks and recreation department for information on leash laws and designated dog parks in your area.
Common Public Access Considerations for Dogs
Here are some general considerations to keep in mind when venturing into public spaces with your dog in Wisconsin:
- Leash Laws: Most public spaces, like sidewalks, streets, and trails, require dogs to be leashed. Leash lengths might also be specified in local ordinances.
- Designated Dog Parks: Many communities have designated off-leash dog parks where dogs can socialize and exercise freely under owner supervision.
- Dog-Friendly Businesses: Some businesses, like restaurants with outdoor patios or pet stores, might welcome leashed dogs. Always check signage or inquire with the staff before entering.
- Restrictions on Certain Dog Breeds: While uncommon, some municipalities might have breed-specific restrictions in certain public areas. It’s always best to check local ordinances for any breed-related regulations.
- Service Animals: Federal law protects the rights of individuals with disabilities to use service animals in public spaces. Service animals are exempt from leash laws but must remain under their handler’s control at all times.
Responsible Dog Ownership
Public access for dogs hinges on responsible ownership. Here’s how to be a good dog park citizen and maintain positive public perception:
- Vaccinations and Licensing: Ensure your dog is up-to-date on vaccinations and properly licensed, as required by state law.
- Clean Up After Your Dog: Always carry poop bags and dispose of your dog’s waste properly, regardless of the location.
- Respectful Socialization: Train your dog to interact appropriately with other dogs and people to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone.
- Voice Control and Leash Management: Even in off-leash areas, maintain good voice control over your dog and have a leash readily available for situations when control is necessary.
- Respecting Boundaries: Be mindful of posted signs or areas designated as off-limits to dogs.
Advocating for Dog-Friendly Public Access
If you’re passionate about expanding dog-friendly access in your community, here are some ways to get involved:
- Support Businesses Welcoming Dogs: Patronize dog-friendly businesses to show support and encourage others to do the same.
- Advocate for Off-Leash Areas: Contact your local parks and recreation department or city council to express your interest in creating designated off-leash areas.
- Promote Responsible Dog Ownership: Educate others on the importance of responsible pet ownership to foster positive public perception of dogs in public spaces.
The Benefits of Dog-Friendly Public Access
Expanding dog-friendly public access offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Human-Animal Bond: Spending time outdoors strengthens the bond between owners and their dogs.
- Improved Dog Health and Well-being: Exercise in dog-friendly parks helps dogs stay physically and mentally stimulated.
- Increased Socialization: Off-leash areas provide opportunities for safe and positive social interactions for dogs.
- Community Building: Dog-friendly spaces encourage interaction between dog owners and foster a sense of community.
Dog Travel and Transportation Laws in Wisconsin
For many dog owners in Wisconsin, venturing out with their furry companions isn’t just about walks in the park. Road trips, camping adventures, and even air travel can be exciting bonding experiences. However, ensuring your dog travels safely and legally requires knowledge of specific regulations.

Dog Travel Regulations
While Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, comprehensive law governing dog travel within the state, there are a few key considerations to remember:
- Animal Health Requirements: There are no specific health certificate requirements for moving dogs within Wisconsin. However, if you’re traveling to another state or country, rabies vaccination and health certificates might be necessary. Always check the regulations of your destination beforehand.
- Transporting Dogs Securely: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 347 addresses securing loads in vehicles. While not explicitly mentioning dogs, it emphasizes the importance of transporting cargo safely to prevent hazards. This translates to ensuring your dog is properly restrained during travel to avoid them becoming projectiles in case of sudden stops or accidents.
- Temperature Considerations: Never leave your dog unattended in a parked car, especially during hot weather. This can be life-threatening and might violate animal cruelty laws.
Safe and Humane Dog Travel Practices
Legal compliance is crucial, but prioritizing your dog’s safety and comfort during travel goes beyond the minimum requirements. Here are some essential practices:
- Vehicle Restraint: Invest in a dog harness or crate specifically designed for car travel. Secure the harness to a seatbelt anchor or the crate to a tie-down point in the vehicle.
- Travel Crate Acclimation: If using a crate, gradually introduce your dog to it before travel to ensure they feel comfortable and secure.
- Travel Essentials: Pack plenty of fresh water, food for the journey, bowls, waste bags, and any medications your dog might require.
- Frequent Rest Stops: Plan for regular breaks to allow your dog to eliminate, stretch their legs, and rehydrate, especially on long journeys.
- Motion Sickness Prevention: Consult your veterinarian about medication or natural remedies if your dog suffers from motion sickness.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a comfortable temperature in the car by using air conditioning during hot weather and avoiding leaving your dog unattended in a parked vehicle.
- Microchipping: Microchipping your dog significantly increases the chances of a safe reunion if they get lost while traveling.
Traveling with Your Dog on Public Transportation
Public transportation options for dogs in Wisconsin vary depending on the specific mode of transport:
- Buses: Most intercity bus services in Wisconsin do not allow dogs as passengers, with the exception of service animals.
- Trains: Amtrak allows service animals on board, but pet policies for non-service animals are limited. Always check with Amtrak directly for current regulations.
- Ride Sharing Services: Some ride-sharing services, like Uber or Lyft, might allow dogs at the driver’s discretion. It’s essential to check their pet policies and request a driver who is comfortable transporting animals.
Traveling with Your Dog by Air
When flying with your dog, airline policies are paramount. Here’s a general overview:
- Airline Requirements: Each airline has specific regulations regarding pet travel, including size restrictions, breed restrictions, documentation requirements, and fees.
- Booking Considerations: Not all flights accept pets, and those that do might have limitations on the number of pets allowed per flight. Book your flight well in advance, especially if traveling during peak seasons.
- Pet Carriers: Airlines typically require your dog to travel in a specific size and type of airline-approved pet carrier that fits comfortably under the seat in front of you.
- Health Certificates: For international travel, a health certificate from a licensed veterinarian is typically required.
Dog Housing and Accommodation Laws in Wisconsin
For many Wisconsin residents, dogs are cherished members of the family. Finding suitable housing becomes a shared journey where both human and canine needs must be met.

Dog Housing Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, statewide law governing dog-friendly housing. Instead, the legal landscape is shaped by a combination of factors:
- Fair Housing Act (FHA): This federal law protects individuals with disabilities from discrimination based on their disability in housing. While not specific to dogs, it can apply to situations where a person with a disability requires a service animal for their well-being.
- Local Fair Housing Ordinances: Some municipalities might have their own fair housing ordinances that might offer additional protections for tenants with pets, including emotional support animals.
- Landlord-Tenant Laws: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 704 outlines general landlord-tenant rights and responsibilities. While it doesn’t explicitly address pets, it establishes the framework for pet policies in rental agreements.
- Landlord Policies: Ultimately, landlords have the right to establish their own pet policies, as long as these policies comply with federal and state fair housing laws.
Key Considerations for Dog-Friendly Housing
Here are some crucial aspects to consider when searching for dog-friendly housing in Wisconsin:
- Pet Policies: Carefully review the lease agreement or inquire about the landlord’s pet policy. This will typically outline breed restrictions, size limitations, the number of pets allowed, and any associated fees.
- Reasonable Accommodations: If you have a disability and require a service animal, you are entitled to reasonable accommodation under the FHA. This means the landlord cannot deny your housing application solely due to your service animal.
- Documentation for Service Animals: Landlords can request documentation verifying your disability and the necessity of the service animal for your well-being. However, they cannot request specific medical information or ask about the service animal’s training.
- Emotional Support Animals (ESAs): ESAs are not protected by the FHA in the same way as service animals. Landlords can have stricter policies regarding ESAs, such as requiring a letter from a mental health professional documenting the need for the ESA.
- Pet Deposits and Fees: Many landlords charge pet deposits or monthly pet fees to cover potential damage from pets. Be sure to understand these fees and their limitations according to Wisconsin law.
Finding Dog-Friendly Housing Resources
- Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP): The DATCP website provides information on general landlord-tenant rights and resources for pet owners.
- Wisconsin Legal Aid: This organization offers legal assistance to tenants facing housing discrimination, including issues related to pets.
- Fair Housing Council of Greater Milwaukee: This organization provides resources and assistance to renters facing housing discrimination throughout Wisconsin.
- Apartment Search Websites: Many apartment search websites allow you to filter listings based on pet-friendliness, breed restrictions, and size limitations.
Responsible Dog Ownership
Responsible dog ownership is crucial for advocating for and maintaining access to dog-friendly housing. Here are some ways to be a good dog tenant:
- Compliance with Pet Policies: Adhere to the terms outlined in your lease agreement regarding pets.
- Proper Training and Socialization: Ensure your dog is well-trained, socialized, and doesn’t exhibit destructive behaviors.
- Cleanliness and Maintenance: Be a responsible pet owner and promptly clean up after your dog to avoid damage to the property.
- Consideration for Neighbors: Minimize barking and ensure your dog doesn’t disrupt the peace and quiet of other tenants.
Building a More Dog-Friendly Housing Market
While challenges exist, there are ways to advocate for a more dog-friendly housing landscape in Wisconsin:
- Supporting Dog-Friendly Landlords: Patronize landlords who offer pet-friendly policies and responsible pet ownership initiatives.
- Working with Local Advocacy Groups: Connect with organizations working to promote fair housing policies for tenants with pets.
- Educating Landlords: Promote responsible pet ownership and the benefits of dog-friendly housing for responsible tenants.
Dog Adoption and Sale Laws in Wisconsin
For many Wisconsin residents, welcoming a dog into their lives isn’t just about acquiring a pet; it’s about forging a lifelong bond with a furry companion. Whether you choose adoption or purchase, understanding Wisconsin’s dog adoption and sale laws empowers you to make informed decisions and ensure a responsible, ethical experience.

Understanding Dog Adoption Laws
Wisconsin offers numerous options for adopting a dog, each with its own regulations:
- Animal Shelters and Rescue Organizations: Many shelters and rescues in Wisconsin care for homeless dogs. These organizations typically have adoption fees that cover the cost of vaccinations, spaying/neutering, and microchipping.
- Private Adoptions: Individuals might rehome their dogs directly through online platforms or personal connections. While not regulated by the state, responsible rehoming practices include full disclosure of the dog’s health and temperament.
Key Considerations for Dog Adoption
Here are some crucial aspects to keep in mind when adopting a dog in Wisconsin:
- Adoption Process: Shelters and rescues typically have an adoption process that might involve an application, reference checks, and a meet-and-greet with the dog.
- Adoption Fees: Adoption fees vary but usually cover essential care received by the dog at the shelter or rescue.
- Health Considerations: Reputable shelters and rescues disclose known health issues with the dog before adoption. Ask for their medical records and consider scheduling a veterinary checkup after adoption.
- Breed Considerations: Research different dog breeds and choose one that aligns with your lifestyle and living situation.
- Matching Personalities: Consider your personality and activity level when choosing a dog to ensure compatibility and a fulfilling life together.
Resources for Dog Adoption
- Wisconsin Humane Society (WHS): The WHS website lists dogs available for adoption at their shelters and rescue partners across the state.
- Adopt-a-Pet.com: This website allows you to search for adoptable dogs in your area from shelters, rescues, and private individuals.
- Petfinder: Similar to Adopt-a-Pet.com, Petfinder allows you to search for adoptable dogs by breed, location, and other criteria.
Understanding Dog Sale Laws
Wisconsin regulates dog sales through a tiered licensing system:
- No License Required: If you’re occasionally selling a litter of puppies born to your pet dog and selling them within Wisconsin, you likely don’t need a license. However, there are limitations:
- You can only sell dogs eight weeks of age or older.
- You cannot sell more than 24 dogs per year.
- Out-of-State Dealer License: If you’re a dog breeder or dealer bringing dogs from another state to sell in Wisconsin, you need an out-of-state dealer license from the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP).
- Wisconsin Dog Seller/Dealer License: This license is required for:
- Dog breeders selling 25 or more dogs per year from at least four litters.
- Dog dealers or retailers selling 25 or more dogs per year in Wisconsin.
- Non-profit animal shelters sheltering 25 or more dogs per year.
Additional Considerations
Here are some crucial aspects to keep in mind when purchasing a dog in Wisconsin:
- Licensing Verification: Ensure the breeder or seller has the proper license required by Wisconsin law.
- Certificate of Veterinary Inspection (CVI): Reputable sellers provide a CVI for each dog sold, documenting a recent veterinary exam and overall health.
- Breed Reputable Breeders: If choosing a specific breed, research reputable breeders who prioritize ethical breeding practices and healthy bloodlines.
- Contract Review: Carefully review any purchase contracts outlining the terms of the sale, health guarantees (if offered), and return policies (if applicable).
Dog Park and Recreation Laws in Wisconsin
Wisconsin boasts stunning landscapes and vibrant communities, making it a great place to live with your canine companion. Exploring these spaces with your dog can be a source of joy and exercise, but navigating dog park and recreation laws is crucial for a safe and enjoyable experience.

Dog Park and Recreation Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, all-encompassing dog park and recreation law. Instead, access and regulations are determined by a combination of factors:
- State Statutes: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 174 outlines general dog licensing requirements but doesn’t address dog parks or recreation areas specifically.
- Municipal Ordinances: Most cities, towns, and villages in Wisconsin have their own ordinances governing dog access in parks and recreational areas. These ordinances can vary considerably depending on the location.
- Dog Park Rules: Many communities have designated dog parks with their own specific set of rules posted at the park entrance.
Finding Dog Parks and Recreation Areas
While there isn’t a centralized database listing all dog parks and recreation areas in Wisconsin, here are some resources to help you navigate:
- Municipal Websites: Most city, town, and village websites provide information on leash laws, park regulations, and designated dog parks within their jurisdiction.
- Dog Park Apps: Mobile apps like BringFido or Sniffspot can help you locate dog parks, dog-friendly trails, and other recreational areas in your area.
- Local Parks and Recreation Departments: Contact your local parks and recreation department for information on leash laws, designated dog parks, and dog-friendly trails in your area.
General Considerations for Dog Parks and Recreation
Here are some general considerations to keep in mind when venturing into dog parks and recreation areas with your dog in Wisconsin:
- Leash Laws: Most public parks and trails require dogs to be leashed, with leash lengths often specified in local ordinances. Designated off-leash dog parks are exceptions where dogs can socialize and exercise freely under responsible owner supervision.
- Dog Park Rules: Always adhere to the posted rules at the dog park you visit. These rules might address vaccination requirements, waste disposal procedures, size limitations, and proper dog park etiquette.
- Responsible Ownership: Maintain control of your dog at all times, even in off-leash areas. Ensure your dog is well-socialized and doesn’t exhibit aggressive behavior.
- Cleaning Up After Your Dog: Always carry poop bags and dispose of your dog’s waste properly in designated waste disposal bins.
- Respecting On-Leash Areas: When visiting parks with on-leash restrictions, respect these regulations to ensure the safety and enjoyment of all park users.
Building a Positive Dog Park Experience
Dog parks offer a stimulating environment for dogs to socialize and exercise. Here’s how to be a good dog park citizen and contribute to a positive experience:
- Vaccinations and Licensing: Ensure your dog is up-to-date on vaccinations and properly licensed, as required by state law.
- Proper Equipment: Use a well-fitting harness and a sturdy leash when entering on-leash areas and exiting dog parks.
- Dog Socialization: Gradually introduce your dog to the dog park environment to ensure they feel comfortable and integrate well with other dogs.
- Supervision and Voice Control: Never leave your dog unattended in a dog park. Maintain good voice control to manage your dog’s interactions with others.
- Respecting Boundaries: Be mindful of other dog owners and their dogs. Give space to those who might seem uncomfortable or have shy dogs.
Advocating for Dog-Friendly Parks and Recreation
Passionate about expanding dog-friendly access in your community? Here are some ways to make a difference:
- Supporting Parks and Recreation Departments: Volunteer at dog park clean-up events or participate in public forums to advocate for responsible dog park use.
- Contacting Local Officials: Express your interest in creating designated dog parks or expanding dog-friendly trail access in your area.
- Promoting Responsible Dog Ownership: Educate others on the importance of responsible pet ownership to foster positive public perception of dogs in parks and recreation areas.
Dog Food and Nutrition Laws in Wisconsin
For dog owners in Wisconsin, ensuring their furry companions receive safe and nutritious food is paramount. However, navigating the world of dog food regulations and understanding the legalities surrounding pet nutrition can be confusing.

Dog Food Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have specific state laws directly regulating dog food ingredients or labeling. The primary regulatory body overseeing pet food safety is:
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA establishes federal guidelines for pet food labeling and manufacturing practices to ensure the safety, wholesomeness, and proper labeling of pet food products sold across the state.
Key Considerations for Dog Food Safety
While there aren’t state-specific dog food laws, here are some crucial aspects to consider when choosing food for your dog:
- FDA Regulations: The FDA enforces good manufacturing practices for pet food companies and mandates specific labeling requirements. Look for the AAFCO (Association of American Feed Control Officials) feeding statement on the label, indicating the food meets the nutritional requirements for your dog’s life stage.
- Ingredients and Sourcing: Research the ingredients listed on the dog food label. High-quality foods prioritize real meat sources, whole grains, and essential vitamins and minerals.
- Breed and Age Considerations: Different dog breeds and life stages have varying nutritional needs. Choose a food formulated for your dog’s specific requirements.
- Veterinary Consultation: Consult your veterinarian for personalized recommendations on dog food based on your dog’s breed, health status, and activity level.
Finding Reliable Resources on Dog Food Safety
Here are some resources to help you make informed decisions about your dog’s food:
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Center for Veterinary Medicine: Provides information on pet food safety, labeling regulations, and recalls.
- Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO): Offers information on pet food labeling guidelines and nutritional requirements.
- World Small Animal Veterinary Association (WSAVA): Provides resources on pet nutrition and choosing a healthy diet for your dog.
Promoting Optimal Dog Nutrition
While legal regulations set a baseline for dog food safety, optimizing your dog’s nutrition goes beyond following the law. Here are some additional tips:
- Read Labels Carefully: Understand the ingredients list and guaranteed analysis on the dog food label.
- Portion Control: Feed your dog the appropriate amount of food based on their age, weight, and activity level to avoid overfeeding and obesity.
- Fresh Water Access: Ensure your dog has constant access to clean, fresh water to stay hydrated.
- Treats in Moderation: Use treats for training or rewards, but limit them to avoid disrupting your dog’s balanced diet.
- Monitoring Your Dog’s Health: Pay attention to your dog’s weight, energy levels, and coat condition. Consult your veterinarian if you notice any concerning changes that might be diet-related.
Addressing Home Cooked Diets and Raw Feeding
While commercially prepared dog food is the most common option, some dog owners choose alternative feeding methods:
- Home-Cooked Diets: If considering a home-cooked diet, consult a veterinary nutritionist to ensure your dog receives all the essential nutrients they need.
- Raw Feeding: Raw feeding carries a higher risk of bacterial contamination for both you and your dog. Thorough research and veterinary guidance are crucial if considering this approach.
The Importance of Responsible Dog Ownership
Choosing a healthy and safe diet is a crucial aspect of responsible dog ownership. By prioritizing your dog’s nutritional needs, you contribute to their overall health and well-being.
Dog Health and Veterinary Care Laws in Wisconsin
For dog owners in Wisconsin, ensuring their furry friend’s well-being is a top priority. Understanding the legal landscape surrounding dog health and veterinary care empowers you to make informed decisions and navigate potential situations with confidence.

Dog Health and Veterinary Care Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, all-encompassing law governing dog health and veterinary care. However, several key aspects influence responsible dog ownership and veterinary care:
- Rabies Vaccination: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 95.21 mandates rabies vaccination for all dogs five months of age or older. Rabies vaccination certificates are typically required for dog licensing, travel, and boarding facilities.
- Animal Cruelty Laws: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950.48 outlines animal cruelty statutes. These laws prohibit neglecting, abandoning, or inflicting unnecessary suffering on animals, including dogs.
- Veterinary Practice Acts: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 453 regulates veterinary practice within the state. These regulations ensure veterinarians are licensed and qualified to provide veterinary care.
Key Considerations for Responsible Dog Ownership
Beyond legal mandates, responsible dog ownership encompasses a range of practices that promote your dog’s health and well-being:
- Regular Veterinary Checkups: Schedule regular veterinary checkups for your dog, even if they seem healthy. These checkups allow early detection and treatment of potential health issues.
- Parasite Prevention: Implement a parasite prevention plan recommended by your veterinarian to protect your dog from fleas, ticks, heartworms, and other internal parasites.
- Proper Nutrition: Feed your dog a high-quality diet appropriate for their breed, age, and activity level. Consult your veterinarian for personalized recommendations.
- Exercise and Enrichment: Provide your dog with regular exercise and mental stimulation through walks, playtime, and interactive toys.
- Vaccinations: Maintain your dog’s vaccinations according to your veterinarian’s recommendations, including rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and other core vaccines.
Finding a Reputable Veterinarian
Choosing a veterinarian who prioritizes your dog’s well-being is crucial. Here are some resources to help you find a qualified vet:
- Wisconsin Veterinary Medical Association (WVMA): The WVMA website provides a directory of licensed veterinarians in Wisconsin.
- American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA): The AVMA website offers a search tool to locate veterinarians across the country.
- Online Reviews and Recommendations: Read online reviews from other pet owners and seek recommendations from friends, family, or animal shelters.
Your Rights and Responsibilities Regarding Veterinary Care
Understanding your rights and responsibilities regarding veterinary care empowers you to advocate for your dog’s health:
- Informed Consent: Veterinarians are required to obtain your informed consent before performing any medical procedures on your dog.
- Estimated Costs: Ask for an estimated cost of treatment before any procedures are performed. You have the right to choose or decline treatments based on cost considerations.
- Medical Records: Your dog’s medical records belong to you. You have the right to request copies of these records for transfer to another veterinarian if needed.
When Legal Issues Arise in Veterinary Care
While uncommon, situations might arise where legal guidance is necessary:
- Veterinary Malpractice: If you suspect your veterinarian acted negligently, causing harm to your dog, consult with an animal law attorney to explore your options.
- Disputes Over Billing: If you have a disagreement with a veterinary bill, discuss it with the clinic directly. If unresolved, consider filing a complaint with the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP).
Resources
Several resources can assist pet owners facing challenges with veterinary care:
- Wisconsin Veterinary Medical Association (WVMA): The WVMA offers resources and information on pet health and veterinary care.
- Wisconsin Humane Society (WHS): The WHS provides financial assistance programs to help low-income pet owners afford essential veterinary care for their dogs.
- Non-Profit Veterinary Organizations: Organizations like the American Animal Hospital Association’s AAHA Helping Pets Fund offer financial assistance for veterinary care in specific cases.
Dog Identification and Microchipping Laws in Wisconsin
For dog owners in Wisconsin, ensuring their furry companions wear proper identification is crucial. Not only does it comply with legal requirements, but it also significantly increases the chances of a safe reunion if your dog gets lost.

Dog Identification Laws
Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 174 outlines dog licensing and identification requirements:
- Dog Licensing: All dogs five months of age or older must be licensed annually with their municipality (city, town, or village). Licenses typically include a rabies vaccination tag.
- Identification Tag: Along with a license tag, dogs must wear a collar with an identification tag bearing the owner’s name, address, and phone number.
Key Considerations for Dog Identification
While the law mandates a basic level of identification, responsible dog owners can go beyond the minimum requirements:
- Durability: Choose a collar and identification tag made of durable materials that can withstand daily wear and tear.
- Visibility: Opt for brightly colored collars or reflective tags for better visibility during nighttime walks.
- Up-to-Date Information: Ensure the information on your dog’s identification tag is current, reflecting your latest address and phone number.
- Multiple Tags: Consider attaching a secondary tag with emergency contact information in case the primary tag gets lost.
The Benefits of Microchipping Your Dog
Microchipping adds another layer of security to your dog’s identification:
- Permanent Identification: A microchip is a tiny chip implanted under your dog’s skin, containing a unique identification number linked to your contact information in a national pet recovery database.
- Increased Recovery Rates: Microchips are a reliable way to identify lost dogs, even if their collar and tags are missing. This significantly increases the chances of a successful reunion.
- Travel Considerations: Some states or countries might require microchipping for traveling with your dog.
Microchipping Laws and Resources
While Wisconsin doesn’t mandate microchipping for all dogs, there are situations where it might be required:
- Breed-Specific Ordinances: Some municipalities in Wisconsin might have ordinances requiring microchipping for specific dog breeds. Check with your local animal control department for details.
- Travel Regulations: Some states or countries have microchipping requirements for dogs entering their borders. Always research regulations for your destination before traveling.
Resources
Here are some resources to help you get your dog microchipped in Wisconsin:
- Veterinarians: Most veterinary clinics in Wisconsin offer microchipping services.
- Animal Shelters and Rescue Organizations: Many shelters and rescues microchip dogs before adoption.
- Low-Cost Microchipping Events: Non-profit organizations or animal welfare groups might hold low-cost microchipping events in your area.
Promoting Responsible Dog Ownership
Responsible dog ownership goes beyond legal compliance. Here are some additional tips:
- Microchip Early: Consider microchipping your dog at a young age, ideally before their first vaccinations.
- Keep Contact Information Updated: Ensure the information linked to your dog’s microchip is current, reflecting your latest address and phone number.
- Spread the Word: Educate friends, family, and dog walkers about the importance of proper identification and microchipping.
The Emotional and Practical Value of Identification
Equipping your dog with proper identification and a microchip offers peace of mind and significantly increases the chances of a happy reunion if they get lost. It’s a small investment with a potentially life-changing outcome.
Dog Breeding and Genetics Laws in Wisconsin
For passionate dog breeders in Wisconsin, ensuring ethical breeding practices and healthy bloodlines is paramount. However, navigating the legal landscape surrounding dog breeding and genetics can be complex.

Dog Breeding and Genetics Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, comprehensive law governing dog breeding and genetics. Instead, regulations are established through a tiered licensing system:
- No License Required: If you occasionally sell a litter of puppies born to your pet dog within Wisconsin, you likely don’t need a license. However, there are limitations:
- You can only sell dogs eight weeks of age or older.
- You cannot sell more than 24 dogs per year.
- Out-of-State Dealer License: If you’re a dog breeder or dealer bringing dogs from another state to sell in Wisconsin, you need an out-of-state dealer license from the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP).
- Wisconsin Dog Seller/Dealer License: This license is required for:
- Dog breeders selling 25 or more dogs per year from at least four litters.
- Dog dealers or retailers selling 25 or more dogs per year in Wisconsin.
- Non-profit animal shelters sheltering 25 or more dogs per year.
Key Considerations for Responsible Dog Breeding in Wisconsin
Beyond licensing requirements, responsible dog breeders in Wisconsin prioritize ethical breeding practices and animal welfare:
- Breed Club Standards: Adhere to breed club standards established by reputable organizations like the American Kennel Club (AKC) to ensure breed purity and maintain desirable physical and temperamental characteristics.
- Genetic Testing: Utilize genetic testing to identify potential hereditary diseases in breeding stock and avoid passing them onto future generations.
- Health Screenings: Perform appropriate health screenings on breeding dogs before breeding to minimize the risk of passing on health issues to puppies.
- Pregnant and Nursing Dam Care: Provide proper nutrition, veterinary care, and a comfortable environment for pregnant and nursing dams to promote the health of both mother and puppies.
- Puppy Socialization: Socialize puppies from a young age to prepare them for life in their forever homes.
Resources
Here are some resources to help responsible dog breeders in Wisconsin thrive:
- Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP): The DATCP website provides information on dog seller/dealer licensing requirements and best practices for animal welfare.
- American Kennel Club (AKC): The AKC offers resources on ethical breeding practices, breeder education, and responsible dog ownership.
- National Alliance of Dog Breeders (NADB): The NADB provides information on responsible breeding practices, breed standards, and breeder networking.
Animal Cruelty Laws and Responsible Breeding
Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950.48 outlines animal cruelty statutes. Breeders must ensure breeding practices adhere to these laws and prioritize the well-being of their dogs:
- Adequate Shelter and Food: Provide breeding dogs with clean, comfortable shelter, access to fresh water, and a nutritious diet.
- Veterinary Care: Provide necessary veterinary care to breeding dogs, including vaccinations, parasite prevention, and treatment for any illnesses.
- Humane Treatment: Avoid any practices that cause unnecessary pain, suffering, or distress to breeding dogs.
The Ethical Considerations
The breeding of mixed-breed dogs, often called “designer dogs,” is a growing trend. While not illegal, responsible breeders carefully consider these factors:
- Unpredictable Traits: Mixed breeds can have unpredictable physical and temperamental traits, potentially leading to health concerns or behavioral issues.
- Overcrowding Shelters: Mixed-breed dogs already make up a large percentage of dogs in shelters. Responsible breeders strive to place their puppies in loving homes, not contribute to shelter overcrowding.
Dog Environmental Impact Laws in Wisconsin
For dog-loving Wisconsin residents, enjoying the outdoors with your canine companion is a cherished pastime. However, responsible dog ownership extends beyond leash laws and waste disposal. Understanding the environmental impact of dogs and relevant regulations empowers you to minimize your dog’s footprint and ensure a healthy environment for everyone.

The Environmental Impact of Dogs
While dogs bring immense joy, their presence can have unintended consequences for the environment:
- Waste Management: Improperly disposed-of dog waste can contaminate waterways, harm wildlife, and contribute to unpleasant odors.
- Habitat Disruption: Off-leash dogs roaming natural areas can disrupt wildlife habitats, scare away native species, and damage sensitive ecosystems.
- Erosion: Dog paws and digging can contribute to soil erosion, especially on trails and natural surfaces.
- Nutrient Pollution: Dog waste introduces excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus into waterways, fostering algae blooms that disrupt aquatic ecosystems.
Dog Waste Disposal Regulations
Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 88 outlines general waste disposal regulations, but doesn’t have specific laws solely targeting dog waste. However, municipalities (cities, towns, and villages) often have ordinances addressing dog waste disposal:
- Leash Laws and Poop-and-Scoop Requirements: Most municipalities require dogs to be leashed in public spaces and mandate owners to pick up and dispose of their dog’s waste properly.
- Designated Waste Disposal Bins: Some parks and recreation areas provide designated dog waste disposal bins to facilitate responsible waste management.
Responsible Dog Ownership
Beyond legal requirements, responsible dog owners can significantly minimize their dog’s environmental impact:
- Always Carry Poop Bags: Make carrying poop bags a regular habit on walks and hikes. Choose biodegradable bags whenever possible.
- Double-Bagging and Proper Disposal: Double bag your dog’s waste and dispose of it in designated waste bins or trash receptacles. Never leave waste behind.
- Leash Laws and Trail Etiquette: Respect leash laws in public spaces. On trails, stay on designated paths and avoid letting your dog wander off-leash to minimize disruption to wildlife and vegetation.
- Educating Others: Lead by example and educate other dog owners about responsible waste disposal practices and respecting leash laws in natural areas.
Minimizing Your Dog’s Environmental Footprint
Responsible dog ownership extends beyond waste management:
- Sustainable Food Choices: Consider eco-friendly dog food options made with responsibly sourced ingredients and minimal packaging.
- Water Conservation: Use a portable water bowl and collect excess water after walks to avoid unnecessary water waste.
- Eco-Friendly Grooming Products: Opt for biodegradable and natural grooming products that minimize environmental impact.
- Supporting Sustainable Businesses: Choose dog toys, accessories, and other supplies made from recycled materials or supporting companies with sustainable practices.
Advocating for Dog-Friendly
Want to make a bigger difference? Consider these actions:
- Supporting Dog Parks with Eco-Friendly Features: Advocate for dog parks with features like waste disposal stations, composting toilets, and native plant landscaping.
- Volunteering for Trail Maintenance: Volunteer your time with organizations dedicated to maintaining hiking and nature trails, mitigating the impact of dog traffic on natural areas.
- Promoting Responsible Dog Ownership: Educate others about the importance of responsible dog ownership and minimizing environmental impact.
Dog Behavioural Training Laws in Wisconsin
For dog owners in Wisconsin, fostering well-behaved canine companions is a top priority. While dog training methods and philosophies vary, understanding the legal landscape surrounding behavioral training empowers you to make informed choices and navigate potential situations with confidence.

Dog Behavioral Training Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have specific laws directly regulating dog behavioral training practices or qualifications for dog trainers. However, several key aspects influence responsible dog ownership and training approaches:
- Animal Cruelty Laws: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950.48 outlines animal cruelty statutes. These laws prohibit using training methods that inflict unnecessary pain, suffering, or distress on dogs. This includes harsh physical corrections, punishment-based training, or the use of aversive tools like choke chains or prong collars in a cruel manner.
- Municipal Leash Laws and Ordinances: Many municipalities in Wisconsin have leash laws and ordinances mandating leash use in public spaces. Training your dog to walk politely on a leash is crucial for responsible ownership and respecting leash laws.
- Veterinarian Recommendations: Consult your veterinarian for personalized advice on dog training and behavior modification. They can identify potential underlying medical reasons contributing to behavioral issues and recommend appropriate training approaches.
Considerations for Choosing a Dog Trainer
While there are no licensing requirements for dog trainers in Wisconsin, responsible dog owners prioritize qualified professionals:
- Positive Reinforcement Methods: Seek trainers who utilize positive reinforcement methods that reward good behavior and encourage desired outcomes without resorting to punishment or dominance techniques.
- Experience and References: Choose trainers with experience in addressing your dog’s specific behavioral concerns. Request references and read online reviews to gauge their effectiveness.
- Certifications: While not mandatory, some trainers hold certifications from reputable organizations like the Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers (CCPDT).
Resources
Here are some resources to help you find a qualified dog trainer in Wisconsin:
- Association of Professional Dog Trainers (APDT): The APDT website provides a searchable directory of professional dog trainers across the US, including Wisconsin.
- Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers (CCPDT): The CCPDT website offers a search tool to locate certified professional dog trainers in your area.
- Local Animal Shelters and Rescue Organizations: Many shelters and rescues have connections with qualified dog trainers or offer their own training programs for adopted dogs.
Responsible Dog Training Practices
Responsible dog training goes beyond legal compliance:
- Positive Reinforcement: Focus on positive reinforcement methods that reward good behavior and encourage desired outcomes. These methods are not only effective but also strengthen the bond between you and your dog.
- Patience and Consistency: Effective dog training requires patience and consistency. Utilize positive reinforcement techniques consistently during training sessions and real-world situations.
- Socialization: Socialize your dog from a young age to ensure they are comfortable interacting with other dogs, people, and various environments.
- Addressing Underlying Issues: If your dog exhibits behavioral problems like aggression, anxiety, or excessive barking, consult a veterinarian and a qualified dog trainer to address potential underlying medical or behavioral causes.
When Legal Issues Arise in Dog Training
While uncommon, situations might arise where legal guidance is necessary:
- Animal Cruelty Allegations: If you suspect a dog trainer is using cruel or abusive methods, report your concerns to your local animal control agency or the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP).
- Dog Bite Injuries: If your dog bites someone due to inadequate training, you might face legal liability. Working with a qualified dog trainer can help prevent such incidents.
Dog Protection and Rescue Laws in Wisconsin
For animal lovers in Wisconsin, ensuring the well-being of vulnerable dogs is a priority. Understanding the legal framework surrounding dog protection and rescue empowers you to take action and advocate for those in need.

Dog Protection Laws
Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950 outlines animal cruelty statutes that offer legal protection for dogs:
- Prohibition of Cruelty: These laws prohibit inflicting unnecessary pain, suffering, or death on animals, including dogs. Examples include neglecting to provide food, water, shelter, or veterinary care, or using cruel training methods.
- Reporting Requirements: Anyone who suspects animal cruelty has a legal responsibility to report it to their local animal control agency or a law enforcement officer. Anonymous reporting is usually allowed.
- Confiscation of Animals: Authorities can confiscate animals suffering from neglect or abuse and place them in protective care.
Key Considerations for Protecting Vulnerable Dogs
Beyond legal mandates, responsible citizens can play a crucial role in protecting dogs:
- Identifying Signs of Neglect: Be aware of signs of neglect, such as excessive thinness, dehydration, visible injuries, lack of shelter, or being left unattended for extended periods.
- Reporting Concerns: If you suspect a dog is being neglected or abused, don’t hesitate to report it to the authorities.
- Supporting Animal Welfare Organizations: Support animal shelters, rescue organizations, and advocacy groups working to protect dogs and find them loving homes.
The Role of Animal Control in Dog Protection
Animal control agencies play a vital role in enforcing animal cruelty laws and protecting dogs:
- Responding to Complaints: Animal control officers investigate reports of animal cruelty and take appropriate action.
- Confiscating Abused/Neglected Dogs: They can confiscate dogs found in abusive or neglectful situations and place them in protective care.
- Sheltering Lost and Abandoned Dogs: Animal control facilities provide temporary housing and care for lost and abandoned dogs until they are reunited with their owners or placed in adoptive homes.
Dog Rescue Laws and Resources
Wisconsin doesn’t have specific laws governing dog rescue activities. However, several regulations establish frameworks for animal shelters and rescue organizations:
- Licensing Requirements: Animal shelters sheltering 25 or more dogs per year require a Wisconsin Dog Seller/Dealer License from the Wisconsin Department of Agriculture, Trade and Consumer Protection (DATCP).
- Animal Welfare Standards: Licensed shelters and rescues must adhere to specific animal welfare standards set forth by the DATCP, ensuring proper care for dogs in their custody.
- Adoption Procedures: Shelters and rescues have established adoption procedures that might include screening potential adopters and ensuring a good fit between the dog and the new home.
Finding a Reputable Dog Rescue Organization
Here are some resources to help you find a reputable dog rescue organization in Wisconsin:
- Wisconsin Humane Society (WHS): The WHS is a statewide organization with shelters and rescue programs dedicated to finding loving homes for dogs in need.
- The Shelter Pet Project: This national initiative promotes pet adoption and provides a searchable directory of animal shelters and rescue organizations, including those in Wisconsin.
- National Network for Animals (NNA): The NNA website offers a directory of animal rescue organizations categorized by state and type.
Promoting Responsible Dog Ownership
Responsible dog ownership goes beyond legal compliance and helps prevent dogs from ending up in shelters or rescue organizations:
- Proper Pet Identification: Ensure your dog wears a collar with identification tags bearing your name, address, and phone number. Consider microchipping for added security.
- Spay/Neuter Your Dog: Spaying and neutering your dog helps control pet overpopulation and reduces the number of dogs entering shelters.
- Responsible Breeding Practices: If you choose to breed your dog, prioritize ethical breeding practices that prioritize animal welfare and responsible placement of puppies.
Dog Entertainment and Work Laws in Wisconsin
For Wisconsin residents with talented canine companions, the allure of the entertainment industry or utilizing their dogs for work purposes is undeniable. However, navigating the legal landscape surrounding dog entertainment and work in Wisconsin can be confusing.

Dog Entertainment and Work Laws
Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, all-encompassing law governing dog entertainment or work. Instead, regulations are established through a combination of:
- Federal Laws: The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Animal Welfare Act (AWA) sets forth minimum standards of care for animals used in exhibition, research, testing, transportation, or sale.
- State Regulations: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 951 outlines regulations for animal exhibition facilities, which might encompass some dog entertainment activities.
- Municipal Ordinances: Some municipalities within Wisconsin might have additional ordinances regarding animal performances or specific working dog regulations.
Key Considerations for Dog Entertainment
While there’s no single permit for dog entertainment in Wisconsin, responsible dog owners prioritize ethical practices:
- Animal Welfare Act (AWA) Compliance: Even if not explicitly required, ensure compliance with the AWA by providing proper housing, food, water, veterinary care, exercise, and enrichment for your dog.
- Humane Treatment: Dog entertainment activities should never involve cruelty, force, or coercion. Prioritize your dog’s well-being and comfort throughout training and performance.
- Appropriate Training: Ensure your dog is appropriately trained for the intended activity and enjoys participating. Avoid pushing your dog beyond their comfort level.
- Age and Health Considerations: Only involve dogs that are physically and mentally mature for the demands of entertainment activities.
Resources
Here are some resources to guide you in ethical dog entertainment:
- American Humane: This organization offers resources on animal welfare in entertainment, including guidelines for responsible training and handling.
- The American Federation of Television and Radio Artists (AFTRA): AFTRA represents animal actors and provides resources on animal welfare standards in film and television productions.
- Local Animal Training Professionals: Seek guidance from experienced and certified animal trainers who prioritize ethical and positive reinforcement methods.
Dog Work Laws
While some states have regulations regarding working dogs, Wisconsin lacks specific laws governing most working dog activities. However, some general areas have established regulations:
- Service Animals: The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) protects the rights of individuals with disabilities to be accompanied by service animals in public spaces. Wisconsin businesses and organizations must comply with the ADA.
- Therapy Animals: Therapy animals provide emotional or psychological support but are not legally protected under the ADA. Facilities inviting therapy animals might have specific requirements or limitations.
- Hunting and Herding Dogs: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) regulations govern hunting seasons and licensing requirements for hunting dogs. Specific regulations might apply to certain breeds used for herding livestock.
Resources
Here are some resources for navigating working dogs in Wisconsin:
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR): The WDNR website provides information on hunting regulations and licensing requirements for hunting dogs.
- National Association of Service Dogs (NASD): The NASD offers resources on service dog training and certification.
- Alliance of Therapy Dogs: This organization advocates for the responsible use of therapy dogs and provides information about getting involved.
The Importance of Responsible Dog Ownership
Whether for entertainment or work, responsible dog ownership is paramount:
- Prioritize Your Dog’s Well-Being: Always prioritize your dog’s health, comfort, and happiness above any performance or work demands.
- Breed and Temperament Suitability: Choose activities that suit your dog’s breed, temperament, and physical limitations.
- Proper Training and Conditioning: Ensure your dog receives proper training and physical conditioning for the demands of the specific work or entertainment role.
- Regular Veterinary Care: Maintain regular veterinary checkups and address any health concerns that might impact your dog’s ability to participate in activities.
Dog Technology and Innovation Laws in Wisconsin
The world of pet technology is booming, offering innovative solutions for dog owners in Wisconsin. From smart feeders to wearable health trackers, these advancements raise questions about legal frameworks and responsible use.

Dog Technology and Innovation Laws
Currently, Wisconsin doesn’t have specific laws directly regulating pet tech products or dog health technology innovations. However, several existing regulations influence responsible use and potential future legal developments:
- Federal Laws: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the safety and effectiveness of medical devices, including those potentially impacting animal health. Some dog health technology products might fall under FDA regulations.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Wisconsin consumer protection laws apply to pet tech products. These laws ensure products are safe, as advertised, and not misleading to consumers.
- Data Privacy Concerns: As dog technology often collects data, it’s crucial to be aware of data privacy considerations. Federal and state laws might address data collection and usage practices.
Key Considerations
While dog technology offers exciting possibilities, responsible pet ownership comes first:
- Prioritize Your Dog’s Needs: Don’t replace human interaction, playtime, and proper training with tech solutions. Technology should complement responsible ownership, not replace it.
- Research Products Thoroughly: Research pet tech products carefully, understanding their intended purpose, functionalities, and potential limitations.
- Data Privacy and Security: Be mindful of data collection practices employed by dog tech products. Choose products with strong data security measures and understand how your dog’s data is used.
- Veterinarian Consultation: Consult your veterinarian before using any dog health technology product, especially those claiming to diagnose or treat medical conditions.
Legal Considerations
The pet tech industry is constantly evolving, but here are some examples with potential legal considerations:
- Wearable Health Trackers: These devices monitor vital signs and activity levels. While not currently regulated, FDA oversight might evolve as technology advances.
- Remote Training Devices: Devices using electronic stimulation for training raise concerns about animal welfare. Wisconsin adheres to animal cruelty statutes, so any device causing unnecessary discomfort would be illegal.
- Automated Feeding Systems: These systems dispense food on a schedule. While convenient, ensure portion control features are accurate and reliable to avoid overfeeding.
- Smart Toys and Interactive Games: These can be enriching for dogs, but prioritize real-world interaction and avoid relying solely on tech for playtime.
The Future of Dog Technology and Innovation
The legal landscape surrounding dog technology is likely to evolve as advancements continue. Here are some potential future developments:
- FDA Regulations: As dog health technology becomes more sophisticated, the FDA might implement stricter regulations regarding safety and efficacy.
- Data Privacy Laws: Data privacy laws might become more specific regarding pet tech products, ensuring transparency and user control over data collection practices.
- Focus on Animal Welfare: Legislation might address animal welfare concerns surrounding certain dog technology applications, prioritizing responsible use and preventing cruelty.
Staying Informed and Making Responsible Choices
Staying informed and making responsible choices is crucial when navigating dog technology:
- Research Industry Trends: Follow reputable sources for news and updates on the pet tech industry.
- Consult Experts: Seek guidance from veterinarians, animal behaviorists, and pet tech professionals when evaluating specific products.
- Advocate for Responsible Innovation: Support initiatives that promote responsible development and use of dog technology, prioritizing animal welfare and ethical practices.
Human Coexistence Laws in Wisconsin
For dog lovers in Wisconsin, fostering a strong connection with your furry friend is paramount. While there aren’t specific laws solely promoting dog-human cohabitation, Wisconsin offers a legal framework that supports responsible dog ownership and facilitates positive interactions between humans and dogs.

Laws Supporting Responsible Dog Ownership
Wisconsin Statutes establish several regulations that indirectly promote responsible dog ownership, fostering a foundation for positive human-dog coexistence:
- Leash Laws and Public Space Ordinances: Most municipalities in Wisconsin have leash laws mandating dogs to be leashed in public spaces. This ensures public safety for both humans and dogs, allowing for enjoyable shared experiences.
- Waste Disposal Regulations: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 88 outlines general waste disposal regulations. While not solely targeting dog waste, most municipalities have ordinances requiring owners to pick up and dispose of their dog’s waste properly. This minimizes environmental impact and promotes responsible pet ownership in shared spaces.
- Animal Cruelty Laws: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950.48 outlines animal cruelty statutes. These laws prohibit inflicting unnecessary pain, suffering, or death on animals. Following these laws ensures basic animal welfare and fosters a foundation for a positive human-dog bond.
Promoting Positive Human-Dog Interactions
Responsible dog ownership and positive training methods go far beyond legal compliance, promoting happy and well-adjusted dogs that are enjoyable companions:
- Socialization: Socialize your dog from a young age to ensure they are comfortable interacting with other dogs, people, and various environments. This socialization lays the groundwork for positive interactions in public spaces.
- Positive Reinforcement Training: Focus on positive reinforcement training methods that reward good behavior and encourage desired outcomes. This builds trust and fosters a strong bond between you and your dog.
- Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary checkups ensure your dog’s physical and mental health. A healthy dog is more likely to be a happy and well-behaved companion.
- Understanding Dog Behavior: Learn about basic dog behavior and communication. This helps you understand your dog’s needs and respond appropriately, strengthening your bond.
Resources
Here are some resources to help you build a strong connection with your dog:
- American Kennel Club (AKC): The AKC website offers resources on dog training, socialization, and behavior.
- Association of Professional Dog Trainers (APDT): The APDT website provides a searchable directory of professional dog trainers across the US, including Wisconsin.
- Local Animal Shelters and Rescue Organizations: Many shelters and rescues offer educational programs on dog training, behavior, and responsible ownership.
- Veterinarians: Consult your veterinarian for personalized advice on training, behavior, and building a positive relationship with your dog.
Public Spaces and Dog-Friendly Establishments
Wisconsin offers a growing number of dog-friendly establishments and public spaces:
- Dog Parks: Many communities have designated dog parks where dogs can run leash-free in a safe and controlled environment. These spaces allow dogs to socialize and exercise, contributing to their overall well-being and enjoyment.
- Dog-Friendly Restaurants and Businesses: An increasing number of restaurants, cafes, and businesses welcome well-behaved dogs on leashes. Enjoying outings with your furry friend can strengthen your bond and create positive shared experiences.
- Hiking and Outdoor Activities: Many trails and natural areas in Wisconsin allow dogs, with leash regulations in place. Exploring the outdoors together can be a fun and enriching activity for both you and your dog.
Advocating for Dog-Friendly Initiatives
Want to make a difference? Consider these ways to promote dog-friendly environments:
- Supporting Dog Parks and Off-Leash Areas: Advocate for the creation and maintenance of dog parks and off-leash areas in your community.
- Educating Others on Responsible Dog Ownership: Educate others on responsible dog ownership practices like leash etiquette and proper waste disposal. This promotes positive interactions between dogs and humans in public spaces.
- Supporting Dog-Friendly Businesses: Patronize businesses that welcome well-behaved dogs. This encourages other businesses to consider becoming dog-friendly as well.
Other Relevant Dog Laws in Wisconsin
Canine Good Citizen (CGC) Programs and Legal Benefits
- CGC Programs: The American Kennel Club (AKC) offers Canine Good Citizen (CGC) programs, certifying dogs that demonstrate basic obedience and good manners in public settings.
- Legal Benefits (Limited): While CGC certification doesn’t hold legal weight in Wisconsin, some municipalities might offer benefits like reduced dog licensing fees for CGC-certified dogs.
- Focus on Training: The primary benefit of CGC programs lies in demonstrating your dog’s good behavior and responsible ownership, fostering positive human-dog interactions.
Dog Insurance and Coverage Laws
- Regulation: Wisconsin doesn’t mandate dog insurance.
- Coverage Options: Pet insurance companies offer various coverage options, including accident and illness, liability (for bites or injuries), and wellness plans.
- Choosing a Plan: Consider your dog’s breed, age, health, and lifestyle when selecting a pet insurance policy.
Laws Regarding Dogs in Hot Cars and Animal Endangerment
- Animal Cruelty Laws: Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950.48 outlines animal cruelty statutes, prohibiting leaving an animal in a confined space without adequate ventilation or protection from extreme temperatures, which can be deadly for dogs.
- Reporting Concerns: If you see a dog left in a hot car, contact animal control immediately.
- Preventive Measures: Never leave your dog unattended in a hot car, even for short periods.
Legal Aspects of Dog Parks and Shared Spaces
- Leash Laws and Ordinances: Most municipalities in Wisconsin have leash laws requiring dogs to be leashed in public spaces, with designated off-leash areas like dog parks being exceptions.
- Park Rules and Regulations: Individual dog parks might have specific rules regarding size requirements, vaccination status, and responsible owner behavior.
- Shared Responsibility: Dog park users share responsibility for ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone. Respect leash laws, pick up after your dog, and maintain control of your canine companion.
Dog-Related Property Damage and Homeowner’s Insurance
- Homeowner’s Insurance: Most homeowner’s insurance policies cover dog-related property damage to others’ property with limitations. Check your specific policy details.
- Liability Coverage: Consider additional liability coverage if you’re concerned about potential dog-related damage claims.
- Responsible Ownership: Training your dog with good manners and preventing destructive behavior minimizes the risk of property damage.
Service and Working Dog Laws in Employment and Public Access
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): The ADA protects the rights of individuals with disabilities to be accompanied by trained service animals in public spaces. Wisconsin businesses and organizations must comply with the ADA.
- Working Dogs: Therapy animals and emotional support animals are not service animals under the ADA and may have limitations on public access.
- Verification of Service Status: Businesses cannot require proof of disability but can ask if the dog is a service animal and what work or task it performs.
Animal Welfare and Protection Laws Against Neglect and Abandonment
- Wisconsin Statutes Chapter 950: This chapter outlines animal cruelty and neglect statutes.
- Reporting Requirements: Anyone suspecting animal neglect or abuse has a legal obligation to report it to animal control or law enforcement.
- Abandonment: Abandoning a dog is illegal. If you can no longer care for your dog, surrender them to a shelter or rescue organization.
This comprehensive guide explored various aspects of dog ownership in Wisconsin. We delved into laws regarding training, protection, entertainment, work, technology, and human-dog coexistence. While Wisconsin doesn’t have a single, overarching dog law, a framework of regulations and responsible ownership practices paves the way for a harmonious relationship between humans and canines.
Understanding and complying with these laws is not just about legal repercussions; it’s about ensuring the well-being of our furry companions and fostering a safe and enjoyable environment for everyone in Wisconsin. By prioritizing responsible ownership, we create a win-win situation for dogs, owners, and society as a whole.
FAQs
Can I take my dog swimming in public lakes and rivers?
Wisconsin generally allows dogs in public waterways, but leash laws might still apply on beaches or shorelines. Always check with local authorities for specific regulations regarding swimming areas and leash requirements.
Are there any breed restrictions in Wisconsin?
There’s no statewide ban on specific dog breeds in Wisconsin. However, some municipalities might have breed-specific ordinances. It’s crucial to check with your local animal control or municipality to understand any breed restrictions in your area.
What are the regulations for traveling with my dog in Wisconsin?
There are no specific state-wide regulations for traveling with your dog within Wisconsin. However, some public spaces like parks or trails might have restrictions on dog access. Always check with the specific location you plan to visit. When traveling across state lines, be aware of rabies vaccination requirements and potential health certificates needed.
What are the rules for microchipping my dog in Wisconsin?
Microchipping your dog is not mandatory in Wisconsin, but highly recommended. There are no specific regulations regarding microchip registration, but most microchip companies offer online registration options. Ensure you keep your contact information updated with the microchip company.
Can I bring my dog to work in Wisconsin?
Whether you can bring your dog to work depends on your employer’s policies and workplace regulations. Some workplaces might have pet-friendly policies, while others might not allow dogs due to safety concerns or potential disruptions. Always check with your employer’s HR department for their specific policies regarding dogs in the workplace.







