Dog Laws in New York
As a dog owner in the United States, where millions of us consider our canine companions cherished family members, understanding dog laws is crucial. With an estimated 85 million dogs gracing American households, it’s no surprise there’s a complex web of regulations to ensure the safety and well-being of both our furry friends and the communities we share.
These laws delve into various areas, from licensing and leash requirements to responsible ownership practices and even innovative dog tech regulations. By familiarizing myself with dog laws in my state, New York, I can ensure I’m providing the best possible care for my dog while fostering a harmonious relationship with my fellow New Yorkers.
Table of Contents
Dog Bite Laws in New York
New York, a state brimming with vibrant cities and stunning landscapes, is also home to millions of cherished canine companions. Ensuring responsible dog ownership and promoting harmonious coexistence between humans and dogs requires a clear understanding of dog bite laws. While New York doesn’t have a single, all-encompassing dog bite statute, a combination of laws and legal precedents shapes how dog bite incidents are handled.

Strict Liability and Negligence
New York’s dog bite laws function under a “mixed-bailable” system, meaning liability depends on the dog’s history and the circumstances of the bite:
- Strict Liability for Previously Dangerous Dogs: If a dog has a documented history of biting or displaying aggressive tendencies, the owner is held strictly liable for any injuries it causes, regardless of provocation. This emphasizes responsible ownership and the importance of addressing prior aggression.
- Negligence for First-Time Bites: For dog bites with no prior history of aggression, the concept of negligence comes into play. The victim must prove the dog owner acted negligently, meaning they failed to take reasonable precautions to prevent the bite. This could include failing to leash the dog, not properly securing it in a fenced yard, or ignoring signs of potential aggression.
“Negligence” in Dog Bite Cases
The concept of negligence is central to dog bite cases where strict liability doesn’t apply. Here’s what it entails:
- Duty of Care: Dog owners have a legal duty to take reasonable steps to ensure their dog doesn’t cause harm to others. This includes proper training, leashing in public spaces, and secure containment on private property.
- Breach of Duty: If an owner fails to fulfill their duty of care (e.g., not leashing their dog), they have breached their legal responsibility.
- Causation: The owner’s negligence must be the direct cause of the bite.
- Damages: The victim must have suffered physical or emotional injuries as a result of the bite.
The “One-Bite Rule”
While not a formal law in New York, the concept of the “one-bite rule” sometimes factors into dog bite cases, particularly those involving first-time bites with no prior aggression. This informal rule suggests that owners might not be held liable if their dog bites for the first time, under the assumption the owner couldn’t have predicted the behavior. However, courts often consider various factors, and the one-bite rule doesn’t guarantee immunity for owners in first-time bite scenarios.
Consequences for Dog Owners
Dog bite incidents can have legal and financial repercussions for owners, even beyond potential lawsuits from the victim:
- Fines and Penalties: Depending on the severity of the bite and the dog’s history, owners might face fines or even criminal charges.
- Quarantine and Muzzle Requirements: Biting dogs might be mandated to undergo quarantine and wear muzzles in public spaces.
- Increased Insurance Rates: Dog bite incidents can lead to higher homeowner’s insurance premiums.
Preventing Dog Bites
The best approach to dog bites is prevention:
- Proper Training and Socialization: Investing in professional training and social interaction for your dog from a young age helps them develop good behavior and reduces the risk of aggression.
- Responsible Leash Use: Always leash your dog in public spaces, even if they seem friendly. Leashes provide control and prevent unforeseen encounters.
- Understanding Dog Body Language: Learn to recognize canine body language that might signal fear or anxiety, allowing you to intervene and de-escalate potentially tense situations.
- Secure Containment at Home: Ensure your property is properly fenced and secure to prevent your dog from escaping and potentially harming others.
New York’s Role in Promoting Responsible Ownership
While there aren’t breed-specific dog bite laws in New York, the state promotes responsible ownership through various initiatives:
- Dog Licensing: Most municipalities in New York require dog licensing, which helps track dog ownership and potentially identify repeat offenders.
- Animal Cruelty Laws: New York has animal cruelty laws that prohibit neglect and abuse, promoting the well-being of all dogs and reducing the risk of aggressive behavior.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Some New York communities run public awareness campaigns educating dog owners on responsible pet care and bite prevention strategies.
Dog Barking and Noise Laws in New York
New York, a state known for its vibrant cities and diverse communities, also boasts a significant dog population. While our furry companions bring joy and companionship, excessive barking can disrupt the peace for neighbors and raise concerns about animal welfare. Fortunately, New York has established regulations to address dog barking and noise complaints, fostering a balance between responsible dog ownership and peaceful coexistence.

Understanding Noise Ordinances
Unlike some states with centralized noise ordinances, New York follows a decentralized approach:
- Local Regulations: Most municipalities have their own noise control ordinances, including specific regulations regarding animal noise, particularly dog barking. These ordinances might outline acceptable noise levels, permissible durations of barking, and designated quiet hours.
- Contact Your Local Authority: The best way to understand the specific dog barking and noise laws in your area is to contact your local animal control department or access the noise control ordinances on your municipality’s website. These resources can provide details regarding:
- Acceptable noise levels in decibels (dB)
- Limitation on barking duration (e.g., continuous barking for more than 10 minutes, or repeated barking throughout the day)
- Designated quiet hours during which stricter noise regulations apply
Considering “Reasonableness”
While specific decibel levels and durations might be outlined in local ordinances, the concept of “reasonableness” plays a crucial role in dog barking complaints:
- Context Matters: Factors like the dog’s breed, the circumstances triggering the barking (e.g., unfamiliar sounds, feeling threatened), and the overall duration and frequency of barking are considered. Occasional barking in response to external stimuli is generally seen as acceptable.
- Chronic Barking vs. Occasional Vocalizations: Chronic, excessive barking that disrupts the peace and tranquility of the neighborhood is the primary concern addressed by noise ordinances.
Addressing Dog Barking Complaints
If you’re experiencing excessive dog barking from a neighbor’s property, here’s a recommended approach:
- Direct Communication: Consider a friendly conversation with your neighbor about the barking. Sometimes, owners might be unaware of the extent of the noise or could be open to solutions.
- Mediation Services: Some municipalities offer mediation services to help neighbors resolve noise complaints constructively and amicably.
- Filing a Noise Complaint: If communication efforts fail, you can file a noise complaint with your local animal control department or relevant authority. Be prepared to provide details about the barking frequency, duration, and any attempts you’ve made to communicate with the owner.
Preventing Excessive Barking
The best approach to dog barking issues is prevention through responsible ownership:
- Proper Training and Socialization: Providing your dog with training and socialization from a young age can help them become less reactive to external stimuli, reducing unnecessary barking.
- Addressing Underlying Causes: Excessive barking can sometimes be a sign of anxiety, boredom, or separation anxiety. Consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist to identify potential triggers and develop a plan to address them.
- Providing Enrichment Activities: Regular exercise, mental stimulation, and interactive playtime can help tire your dog out and reduce boredom-induced barking.
- Creating a Safe and Secure Environment: Ensure your dog’s yard is properly fenced to prevent them from feeling threatened by external stimuli that might trigger barking.
Statewide Animal Welfare Laws and Considerations
While dog barking laws are primarily at the municipal level, New York has statewide animal cruelty laws that indirectly impact barking issues:
- Adequate Shelter and Care: These laws require owners to provide their dogs with adequate shelter, food, water, and veterinary care. Neglecting these basic needs can lead to anxiety and excessive barking in dogs.
- Addressing Distress: Animal cruelty laws prohibit owners from allowing their dogs to suffer unreasonable distress. Excessive barking can be a sign of distress, and failing to address the underlying cause might be considered a violation of these laws.
Building a More Peaceful Community
By understanding dog barking laws, practicing responsible pet ownership, and utilizing communication channels, we can create a more peaceful and harmonious environment for both dog owners and their neighbors in New York. Remember, prevention through training, enrichment, and addressing underlying causes goes a long way in minimizing excessive barking. If issues arise, consider communication, mediation, and following established noise complaint processes. Working together, we can ensure New York remains a vibrant and enjoyable place for all residents, canine and human alike.
Dog Poop Disposal Laws in New York
New York, a state brimming with bustling cities, picturesque landscapes, and millions of cherished canine companions, prioritizes a clean and healthy environment for everyone. Dog waste disposal is an essential aspect of responsible pet ownership, and New York has established regulations to ensure dog owners do their part in keeping our communities sanitary. Understanding these dog poop disposal laws in New York is crucial for responsible dog ownership and fostering a positive public image for dog lovers.

A Statewide Mandate
New York has a statewide law, often referred to as the “Pooper Scooper Law,” mandating the proper disposal of dog waste by dog owners:
- Obligation to Clean Up: This law requires all dog owners to immediately remove and dispose of their dog’s waste from any public or private property (excluding their own fenced-in yard) where the dog is walked, exercised, or otherwise allowed to eliminate.
- Fines and Penalties: Failing to clean up after your dog can result in fines, typically ranging from $25 to $250, depending on the municipality and the frequency of offenses. Local animal control departments or law enforcement are responsible for enforcing these penalties.
Local Ordinances
While the Pooper Scooper Law provides a statewide framework, many municipalities in New York have additional ordinances regarding dog waste disposal:
- Leash Laws and Designated Areas: Most municipalities require dogs to be leashed in public spaces. Some might designate specific areas, such as dog parks, where dog waste disposal bags are provided, encouraging responsible cleanup.
- Signage and Public Awareness Campaigns: Many communities utilize signage in public spaces to remind dog owners of their waste disposal obligations. Public awareness campaigns can further educate dog owners about the importance of responsible pet ownership.
The Importance of Responsible Dog Poop Disposal
Beyond legal compliance, responsible dog waste disposal is crucial for several reasons:
- Public Health: Dog waste can harbor harmful bacteria and parasites that pose health risks to humans, especially children. Proper disposal minimizes these risks.
- Environmental Protection: Dog waste left on the ground can contaminate waterways and contribute to water pollution. Scooping and disposing of waste properly protects our environment.
- Community Harmony: Uncollected dog waste creates an unpleasant and unsanitary environment for everyone, fostering negativity towards dog owners. Responsible waste disposal promotes a cleaner and more enjoyable community for all.
Proper Disposal Practices
Knowing how to properly dispose of dog waste is essential for responsible dog ownership:
- Carrying Waste Disposal Bags: Always carry disposable bags with you whenever walking your dog. Many municipalities provide free or low-cost waste disposal bags in parks or through community programs.
- Double Bagging: Use double bags for extra security to prevent leaks and unpleasant odors. Biodegradable bags are an eco-friendly option.
- Tying Bags Securely: Tie the bags securely after use to prevent spills and ensure proper containment.
- Trash Disposal: Dispose of the sealed waste bags in designated trash receptacles or bins provided in public spaces. Never leave waste bags on the ground, even if hidden in bushes.
- Composting Restrictions: While some areas might have pet waste composting programs, dog waste typically isn’t suitable for traditional composting due to parasite concerns. Always check local regulations before composting dog waste.
Building a More Responsible Dog-Owning Community
By understanding and adhering to dog poop disposal laws, we can create a cleaner, healthier, and more enjoyable environment for everyone in New York. Here’s how you can contribute:
- Be a Vorbild (German for role model): Lead by example by always picking up after your dog. This sets a positive precedent for other dog owners in the community.
- Educate Others: Spread awareness about responsible dog ownership by gently reminding others to pick up after their dogs.
- Advocate for Dog-Friendly Initiatives: Support initiatives that provide dog waste disposal bags in public spaces or community programs promoting responsible pet ownership.
Dog Licensing Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and millions of cherished canine companions, prioritizes responsible pet ownership. Dog licensing is a cornerstone of this commitment, ensuring dogs are properly identified, promoting public health, and contributing to animal welfare initiatives. Let’s delve into the intricacies of dog licensing laws in New York, empowering you to be a responsible dog owner and navigate this essential regulation.

The Importance of Dog Licensing
Dog licensing in New York serves several crucial purposes:
- Identification: A dog license serves as an official identification tag, allowing authorities to reunite lost dogs with their owners quickly and efficiently. This not only brings peace of mind to owners but also reduces the strain on animal shelters by minimizing the number of unclaimed animals.
- Vaccination Verification: Dog licensing often coincides with rabies vaccination verification. Up-to-date rabies vaccinations are essential for public health, protecting both humans and animals from this deadly disease. Licensing helps ensure vaccination compliance.
- Funding Animal Welfare Programs: Licensing fees contribute to vital animal welfare programs in New York. These funds might support animal control operations, shelter services, spay/neuter initiatives, and public education campaigns promoting responsible pet ownership.
Understanding Municipal Regulations
Unlike some states with a centralized dog licensing system, New York follows a decentralized approach:
- Local Regulations: Most municipalities in New York have their own dog licensing ordinances. These ordinances outline specific requirements, including:
- Eligibility: The age at which a dog needs to be licensed (typically four months old)
- Licensing Fees: The cost of obtaining a dog license, which can vary depending on the municipality and whether the dog is spayed/neutered (often offering a discount for sterilized pets)
- Renewal Process: The timeframe for license renewal (usually annually)
- Exemptions: Potential exemptions for certain categories of dogs, such as working dogs or service animals (although some form of identification might still be required)
- Contact Your Local Authority: The best way to understand the specific dog licensing laws in your area is to contact your local animal control department or access the information on your municipality’s website. These resources can provide details regarding:
- Online or in-person licensing options
- Required documentation (e.g., proof of rabies vaccination)
- Fines for non-compliance
The Benefits of Dog Licensing
Beyond legal compliance, dog licensing offers several benefits for both pet owners and the community:
- Peace of Mind: A licensed dog with an identification tag allows for quicker reunification in case of a lost pet.
- Reduced Shelter Intake: Licensing promotes responsible pet ownership, potentially leading to fewer abandoned animals entering shelters.
- Support for Animal Welfare: Licensing fees contribute to programs that benefit all animals, not just your own.
The Licensing Process
Obtaining a dog license in New York is typically a straightforward process:
- Gather Required Documents: This might include proof of rabies vaccination and spay/neuter status (if applicable).
- Choose Your Method: Many municipalities offer online licensing options for your convenience. Alternatively, you can visit your local animal control office or authorized licensing agent.
- Complete the Application: Fill out the dog license application form, providing accurate information about your dog and contact details.
- Pay the Fee: Submit the completed application along with the required licensing fee.
- Receive Your License Tag: Upon approval, you’ll receive an official dog license tag to be attached to your dog’s collar.
Maintaining Compliance
Dog licenses typically expire annually. Here’s how to ensure your dog’s license stays up-to-date:
- Renewal Reminders: Many municipalities offer renewal reminders via email or mail.
- Renew on Time: Renew your dog’s license before the expiration date to avoid potential fines.
- Update Information: If your contact details or dog’s vaccination status changes, notify the licensing authority to maintain accurate records.
Fines and Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to license your dog in New York can result in fines, typically ranging from $25 to $250, depending on the municipality and the duration of non-compliance. It’s important to be aware of the specific penalties in your area and avoid unnecessary financial repercussions.
Dog Leash Laws in New York
New York, a state known for its bustling cities, picturesque landscapes, and millions of cherished canine companions, prioritizes responsible pet ownership and public safety. Dog leash laws play a vital role in ensuring a harmonious coexistence between humans and dogs in public spaces. This guide dives into the intricacies of dog leash laws in New York, empowering you to be a responsible dog owner and navigate these crucial regulations.

The Importance of Dog Leash Laws
Dog leash laws in New York serve several critical purposes:
- Public Safety: Leashes provide control over dogs, preventing them from running towards strangers, causing accidents (e.g., tripping pedestrians), or interacting with other animals unexpectedly. This minimizes the risk of injuries to both humans and animals.
- Protecting Wildlife: Unleashed dogs can disrupt wildlife habitats and harm native species. Leashes help ensure responsible interaction with natural environments.
- Preventing Dog Fights: Leashes help maintain control and prevent altercations between dogs, minimizing stress and potential injuries.
- Promoting Responsible Ownership: Leash laws encourage responsible pet owners to be mindful of their dogs’ behavior and respectful of others in public spaces.
Understanding Municipal Regulations
Unlike some states with a single, statewide leash law, New York follows a decentralized approach:
- Local Regulations: Most municipalities in New York have their own dog leash ordinances. These ordinances outline specific regulations regarding leash use, including:
- Required Leash Length: The maximum leash length permitted in public spaces (typically six feet).
- Designated Off-Leash Areas: Some municipalities might designate specific parks or dog runs as off-leash areas where dogs can play freely under certain guidelines (e.g., requiring proof of vaccination and responsible owner supervision).
- Exemptions: Potential exemptions for service animals or working dogs (although some form of control mechanism might still be required).
- Contact Your Local Authority: The best way to understand the specific dog leash laws in your area is to contact your local animal control department or access the information on your municipality’s website. These resources can provide details regarding:
- Fines for non-compliance
- Specific leash requirements (e.g., retractable leash restrictions)
- Designated off-leash areas and their regulations
Beyond the Basics: Responsible Leash Use
Responsible leash use goes beyond simply attaching a leash to your dog. Here are some additional considerations:
- Maintaining Control: Ensure your leash is the appropriate length and strength to control your dog effectively in various situations.
- Using Leash Manners: Train your dog to walk calmly and loosely on a leash, avoiding pulling or lunging.
- Maintaining Awareness: Stay alert and focused on your dog when walking on a leash, especially in crowded areas or near distractions.
- Picking Up After Your Dog: Leash laws don’t negate your responsibility to clean up after your dog’s waste.
- Respecting Others: Be mindful of others using the same space and avoid allowing your dog to jump on people or block their path.
Understanding Off-Leash Areas
While designated off-leash areas can provide a great opportunity for your dog to run and socialize, responsible behavior is still crucial:
- Know Your Dog: Only use off-leash areas if your dog has good recall and is comfortable around other dogs.
- Maintain Supervision: Never leave your dog unattended in an off-leash area. Remain close by and be prepared to intervene if necessary.
- Proof of Vaccination: Some off-leash areas might require your dog to have up-to-date vaccinations (e.g., rabies) for safety reasons.
- Respecting Others: Be considerate of other dog owners and their pets, ensuring your dog interacts appropriately with others in the area.
Fines and Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with dog leash laws in New York can result in fines, typically ranging from $25 to $250, depending on the municipality and the severity of the offense. Repeated violations might lead to increased fines or even court appearances.
Additional Regulations
While dog leash laws are a core component of responsible dog ownership in public spaces, some additional regulations might be in place:
- Muzzle Requirements: Certain breeds or dogs with a history of aggression might be required to wear muzzles in public spaces, even when leashed.
- Breed Restrictions: While uncommon, some municipalities might have breed-specific restrictions regarding public spaces (e.g., banning certain breeds from parks). Always check local regulations.
Dangerous Dog Laws in New York
New York, a state brimming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and millions of cherished canine companions, prioritizes the safety of both humans and animals. While most dogs are beloved members of our families, there are situations where specific canines pose a potential threat. New York’s “dangerous dog” laws establish a framework for addressing these situations and promoting responsible dog ownership. Understanding these laws empowers you to be a proactive owner and navigate potential legal issues.
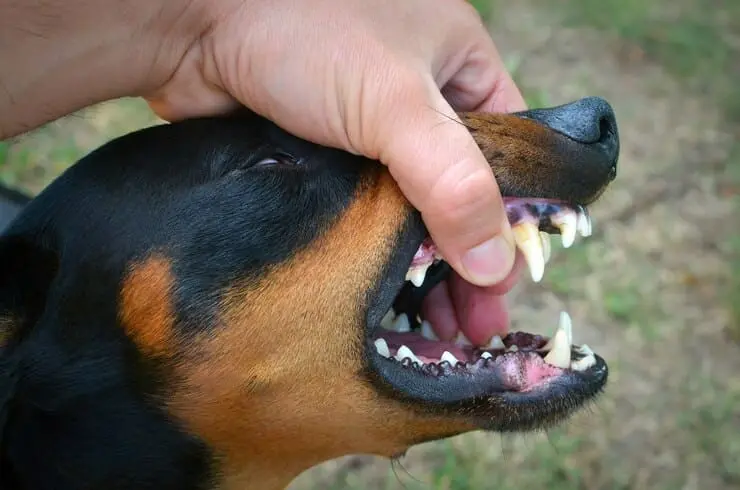
What Constitutes a “Dangerous Dog” in New York?
New York law defines a “dangerous dog” as any dog that exhibits specific aggressive behavior:
- Documented Attacks: If a dog has a documented history of attacking a person, companion animal (defined as a dog or cat kept for companionship), service animal, or guide dog without justification, it’s classified as dangerous.
- Threatening Behavior: A dog displaying threatening behavior towards a person, companion animal, service animal, or guide dog, even without causing injury, might be deemed dangerous if the behavior suggests a high likelihood of future attacks.
The Role of Animal Control
Following a reported incident, animal control officers will typically investigate:
- Evidence Gathering: Officers will gather evidence, including witness testimonies, medical records (if applicable), and potentially evaluations from animal behaviorists.
- Hearing Process: A hearing might be held to determine if the dog meets the criteria of a “dangerous dog.” The dog owner has the right to present evidence and arguments during this process.
- Potential Outcomes: Based on the hearing’s outcome, the court might:
- Dismiss the Case: If evidence doesn’t support the “dangerous dog” designation, the case might be dismissed.
- Impose Regulations: The court might order specific regulations for the dog, such as neutering/spaying, microchipping, muzzle requirements in public spaces, and secure confinement on private property.
- Euthanasia: In severe cases, particularly involving repeated attacks or a high risk of future harm, the court might order the dog’s euthanasia.
“Strict Liability” vs. “Negligence”
New York’s dangerous dog laws operate under a “mixed-bailable” system, with liability depending on the dog’s history and the circumstances of the incident:
- Strict Liability for Previously Declared Dangerous Dogs: If a dog has already been classified as dangerous through the legal process, the owner is held strictly liable for any injuries it inflicts, regardless of provocation. This emphasizes the importance of adhering to court-ordered regulations for dangerous dogs.
- Negligence for First-Time Bites: For dog bites with no prior “dangerous dog” designation, the concept of negligence comes into play. The victim must prove the dog owner acted negligently, meaning they failed to take reasonable precautions to prevent the bite. This could encompass neglecting to leash the dog in public spaces, not providing secure containment on private property, or ignoring signs of potential aggression.
Consequences for Owners
Being deemed the owner of a dangerous dog can have repercussions beyond potential lawsuits:
- Financial Penalties: Fines associated with the court case, potential ongoing costs for mandatory measures (e.g., muzzles), and increased insurance premiums are potential consequences.
- Restricted Ownership Rights: Owning a dangerous dog might come with limitations, such as restrictions on the number of dogs allowed in a household or specific requirements for public spaces.
- Impact on Pet Ownership: A “dangerous dog” designation can make it more challenging to find pet housing or secure services like boarding or grooming.
Preventing Dangerous Dog Situations
The best approach to dangerous dog situations is prevention:
- Responsible Training and Socialization: Investing in professional training and early socialization for your dog can significantly reduce the risk of aggressive behavior.
- Understanding Dog Body Language: Learning to recognize canine body language that signals fear, anxiety, or potential aggression allows you to intervene and de-escalate situations before they escalate.
- Addressing Underlying Issues: If your dog exhibits aggression, consult a certified animal behaviorist to identify potential triggers and develop a behavior modification plan.
- Secure Containment: Ensure your property is properly fenced and secure to prevent your dog from escaping and potentially harming others.
Dog Health and Welfare Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, picturesque landscapes, and millions of cherished canine companions, prioritizes the well-being of all animals, including dogs. A robust legal framework protects dog health and welfare, ensuring responsible ownership and promoting a high quality of life for our furry companions. Delving into these laws empowers you to be a responsible dog owner and advocate for animal welfare.

New York’s Anti-Cruelty Laws
New York’s Animal Law, under the Agriculture and Markets Law (AGM) Article 7, establishes anti-cruelty provisions that encompass dog health and welfare:
- Prohibition of Overdriving, Overloading, Torturing, or Injuring: This law prohibits acts of cruelty towards animals, including dogs. This encompasses neglecting to provide necessary sustenance (food and water), proper shelter, or veterinary care when needed. Willfully injuring, maiming, or torturing a dog is a punishable offense.
- Duty to Provide Necessary Sustenance: Owners have a legal obligation to ensure their dogs have access to clean, fresh water and nutritious food appropriate for their age, breed, and activity level. Deliberately depriving a dog of these basic necessities violates animal cruelty laws.
- Adequate Shelter: New York law mandates providing adequate shelter to protect dogs from the elements. This includes shelter that’s appropriately sized, insulated, and free from hazards. Leaving a dog chained or tethered outdoors for extended periods, especially in extreme weather conditions, constitutes a violation.
- Veterinary Care: While not explicitly mandated by law, ensuring your dog receives necessary veterinary care falls under the umbrella of responsible ownership. This includes preventive care (vaccinations, parasite control), addressing illnesses or injuries promptly, and seeking professional guidance for behavioral issues.
Additional Considerations for Dog Welfare
New York’s commitment to dog welfare extends beyond just the anti-cruelty provisions:
- Tethering Restrictions: Some municipalities have specific regulations regarding tethering dogs outdoors. These regulations might limit the duration, require access to food, water, and shelter, and restrict tethering in extreme weather conditions. Always check local ordinances.
- Flea and Tick Control: While not a legal requirement, ensuring your dog receives regular flea and tick control measures is crucial for their health and well-being. Fleas and ticks can transmit diseases and cause significant discomfort.
- Humane Transport: When transporting your dog, ensure they have adequate space, ventilation, and protection from the elements. Never leave your dog unattended in a parked car, especially during hot weather, as this can be life-threatening.
- Access to Exercise and Socialization: Dogs are social creatures with a natural instinct for exercise. Providing your dog with regular opportunities for physical activity and social interaction is essential for their mental and physical well-being.
Reporting Animal Cruelty
If you suspect a dog is being neglected or abused, don’t hesitate to report it:
- Contact Your Local Animal Control: Most municipalities have dedicated animal control departments responsible for investigating cruelty complaints.
- Humane Societies and Shelters: Humane societies and animal shelters can also be resources for reporting animal cruelty and advocating for animal welfare.
- Gather Evidence: If possible, document the suspected cruelty with photos or videos to support your report. Witness testimonies can also be helpful.
Enhancing Dog Welfare
By understanding and adhering to dog health and welfare laws, we can collectively create a more humane environment for our canine companions. Here’s how you can contribute:
- Be a Responsible Owner: Provide proper food, water, shelter, veterinary care, and opportunities for exercise and socialization.
- Educate Others: Spread awareness about responsible dog ownership and the importance of animal welfare.
- Support Animal Welfare Initiatives: Donate to animal shelters, volunteer your time, or advocate for legislation protecting animals.
Fines and Penalties for Violations
Violating New York’s anti-cruelty laws or local ordinances regarding dog welfare can result in fines, typically ranging from $25 to $1,000, depending on the severity of the offense. Repeated violations might lead to harsher penalties, including jail time or the confiscation of the animal.
The Importance of Responsible Ownership
Dog ownership is a privilege, and with that privilege comes a responsibility to ensure the health and well-being of your canine companion. Understanding and complying with dog health and welfare laws is just one aspect of responsible ownership.
Dog Public Access Laws in New York
New York, a state pulsating with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and millions of cherished canine companions, recognizes the joy dogs bring to our lives. However, navigating public spaces with your furry friend can sometimes feel like a confusing maze. Understanding dog public access laws in New York empowers you to confidently explore the state with your dog while respecting regulations and fostering positive human-canine interactions.

Decentralized Approach: Local Ordinances Reign Supreme
Unlike some states with a centralized framework, New York follows a decentralized approach to dog public access:
- Municipal Control: Most municipalities in New York establish their own ordinances regarding dog access to public spaces. These ordinances can vary considerably, so it’s crucial to research the specific regulations in your area and any places you plan to visit.
- Key Considerations: Local ordinances might address:
- Leash Requirements: Whether leashes are mandatory in all public spaces or if designated off-leash areas exist. Leash length restrictions might also be specified.
- Restricted Areas: Certain areas, like playgrounds, government buildings, or public beaches, might be entirely off-limits to dogs.
- Business Policies: Individual businesses can set their own pet policies, so check signage or inquire directly before entering with your dog.
- Finding Local Regulations: The best way to access detailed information on dog public access laws in your area is to:
- Visit Your Municipality’s Website: Most municipal websites have dedicated sections outlining animal control regulations, including dog public access laws.
- Contact Your Local Animal Control Department: Animal control officers can provide specific details about local ordinances and answer any questions you might have.
General Considerations for Dog Public Access
While local regulations reign supreme, some general principles apply to dog public access in New York:
- Responsible Ownership: Always be a responsible dog owner. Ensure your dog is up-to-date on vaccinations, properly socialized, and well-behaved in public spaces.
- Leash Laws: Unless explicitly designated as an off-leash area, keep your dog leashed in public spaces. Leashes provide control and promote safety for both your dog and others.
- Clean Up After Your Dog: Always carry waste disposal bags and promptly clean up after your dog’s waste. This is not only a legal requirement but also a courtesy to fellow citizens.
- Respecting Others: Be mindful of others using public spaces. Avoid allowing your dog to jump on people, block walkways, or disrupt their enjoyment of the space.
- Be Prepared: Bring water for your dog, especially on hot days, and consider using a portable water bowl for easy access.
Exploring Off-Leash Adventures
Many municipalities in New York provide designated off-leash areas, also known as dog runs, where dogs can socialize and exercise freely:
- Understanding Guidelines: Each off-leash area might have specific guidelines, such as requiring proof of vaccination for entry. Always familiarize yourself with the rules before letting your dog loose.
- Responsible Supervision: Even in off-leash areas, responsible supervision remains crucial. Ensure your dog has good recall and interacts appropriately with other animals.
- Respecting Fellow Dog Owners: Maintain an awareness of other dogs and their owners, ensuring your dog’s behavior doesn’t infringe on their enjoyment of the space.
Exploring Dog-Friendly Businesses
While some businesses might be off-limits to dogs, New York has a growing number of dog-friendly establishments:
- Identifying Dog-Friendly Businesses: Look for signage indicating the business welcomes well-behaved dogs. Some online resources and apps also list dog-friendly businesses in your area.
- Understanding Policies: Each dog-friendly business might have its own policies regarding dog behavior and location restrictions (e.g., allowing dogs on patios but not indoors). Respect these guidelines.
- Maintaining Canine Etiquette: Ensure your dog remains well-behaved and doesn’t disrupt the business operations or other patrons’ experiences.
Building a More Welcoming Public Sphere for Dogs
By understanding and adhering to dog public access laws, we can cultivate a more welcoming atmosphere for responsible dog owners and their furry companions:
- Advocate for Dog-Friendly Initiatives: Support businesses, restaurants, and parks that embrace dog-friendly policies.
- Promote Responsible Ownership: Educate others about responsible dog ownership practices, fostering a positive image of dogs in public spaces.
- Be an Ambassador for Positive Canine Interactions: Ensure your dog’s behavior reflects positively on responsible dog owners, building trust and acceptance within the community.
Dog Travel and Transportation Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and millions of adventurous dog owners, offers exciting opportunities for canine exploration. Whether you’re embarking on a road trip across the state or venturing further afield, understanding dog travel and transportation laws in New York ensures a smooth and compliant journey for you and your furry companion.

Planning for Safe and Legal Travel
Before hitting the road with your canine co-pilot, some essential considerations require your attention:
- Vaccinations: Ensure your dog is up-to-date on all core vaccinations, including rabies. Some states or localities might have additional vaccination requirements, so research your destination’s regulations. Carry proof of vaccination documentation during your travels.
- Health Certificates: Certain situations, like crossing state lines or flying with your dog, might require a health certificate issued by a licensed veterinarian within a specific timeframe (typically 30 days) before travel. Consult your veterinarian and the airline/transportation company for specific requirements.
- Identification: Ensure your dog has a collar with a visible identification tag containing your contact information and, ideally, a microchip for enhanced security and quicker reunification if separated.
Navigating New York Roads
Traveling with your dog by car necessitates prioritizing safety and comfort:
- Secure Transport: Utilize a crate or pet carrier that’s appropriately sized for your dog, ensuring comfortable movement and preventing them from becoming projectiles in case of sudden stops. Harnesses and tethers secured to anchored points within the vehicle can also be an option for larger dogs.
- Climate Control: Maintain a comfortable temperature within the car for your dog. Never leave your dog unattended in a parked vehicle, especially during hot or cold weather, as this can be life-threatening. Take frequent breaks for your dog to stretch, relieve themselves, and stay hydrated.
- Distraction-Free Driving: Focus on driving and avoid distractions caused by interacting with your dog. Consider having a designated passenger responsible for your dog’s needs during the trip.
Public Transportation with Your Pup
New York offers various public transportation options, some of which are dog-friendly with specific regulations:
- Subways and Buses: Most public transportation authorities in New York, like the MTA (Metropolitan Transportation Authority), allow dogs on board under certain conditions. Dogs typically need to be confined in a carrier or other suitable container that doesn’t annoy other passengers. Size restrictions and limitations during peak hours might apply. Always check the specific regulations of the transportation authority you plan to use.
- Trains: Regulations for dog travel on commuter rail lines can vary. Some, like Long Island Rail Road (LIRR), might not permit dogs on board unless they are service animals. Research the specific policies of the train service you’re considering.
- Taxis: While some taxi drivers might be accommodating, dog policies are often at the driver’s discretion. It’s best to call ahead and inquire about their pet policy before hailing a cab.
Flying with Your Furry Friend: Airline Regulations
If your travel plans involve air travel, understanding airline regulations for pet transport is crucial:
- Airline Research: Each airline has its own specific pet policies regarding fees, size and breed restrictions, documentation requirements, and in-cabin or cargo transport options. Research the airline’s pet policies well in advance of your trip and make the necessary reservations for your dog.
- Health Certificates and Acclimation: Airlines typically require a health certificate issued by a licensed veterinarian within a specific timeframe before the flight. Some airlines might have additional requirements like acclimation certificates for brachycephalic (short-nosed) breeds.
- Travel Crates and Comfort: Ensure your dog has a travel crate that meets airline specifications for size, ventilation, and security. Familiarize your dog with the crate beforehand to minimize stress during the flight.
Considerations for Interstate Travel
When traveling beyond New York’s borders, additional considerations come into play:
- State-Specific Regulations: Research the dog travel and transportation laws of your destination state. Vaccination requirements, health certificate needs, and restrictions for specific breeds might differ.
- Crossing International Borders: International travel with your dog involves a more complex set of regulations, including import/export permits, rabies vaccinations, microchipping, and potential quarantine periods. Consult with your veterinarian and the embassy or consulate of your destination country well in advance to ensure a smooth entry process.
Dog Housing and Accommodation Laws in New York
New York, a state pulsating with vibrant cities, picturesque landscapes, and millions of dog-loving residents, recognizes the importance of finding suitable housing for both humans and their furry companions. However, navigating the legalities of dog-friendly housing can sometimes feel like a tangled leash. Understanding dog housing and accommodation laws in New York empowers you to find a welcoming home for your canine friend while respecting landlord and tenant rights.

State vs. Local Laws
Unlike some states with a single, overarching pet law, New York employs a two-tiered approach to dog housing regulations:
- New York State Pet Laws: These laws establish a baseline framework for pet ownership in rental housing. The key takeaway: landlords cannot categorically deny pets in rental units. However, they can implement reasonable restrictions, such as:
- Breed Restrictions: Certain breeds might be prohibited, particularly those with a history of aggression or size limitations not suitable for specific dwellings.
- Weight Limits: Landlords might set weight restrictions for dogs allowed in their properties.
- Number of Pets: The number of pets permitted in a single unit might be limited.
- Pet Deposits and Fees: Landlords can require pet deposits (refundable) and potentially additional fees (non-refundable) to cover potential pet-related damages.
- Municipal and Local Ordinances: Municipalities and localities within New York might have additional ordinances regarding dog ownership in rental housing. These can encompass specific noise restrictions, leash requirements within common areas, or designated pet waste disposal areas.
The 90-Day Pet Rule: A Temporary Solution
New York’s “90-Day Pet Rule” offers a temporary haven for responsible tenants seeking to introduce a dog into their pet-prohibited rental unit:
- Understanding the Rule: If a lease agreement explicitly prohibits pets, the 90-Day Pet Rule allows tenants to keep a dog in the unit for a 90-day trial period without facing eviction from the landlord.
- Conditions for Application: This rule applies to existing tenants who have already signed a lease agreement without pets. It doesn’t necessarily apply to new tenants seeking pet-friendly units.
- Demonstrating Responsibility: The 90-day period is an opportunity for tenants to showcase responsible pet ownership. This includes keeping the dog properly vaccinated, controlling noise, and promptly cleaning up after the dog within the property.
- Negotiation Potential: If the dog doesn’t cause any problems during the 90-day period, tenants can use this as leverage to negotiate an amendment to the lease agreement, allowing the dog to stay permanently.
Resources and Considerations
Finding dog-friendly housing in New York requires some proactive steps:
- Researching Online Platforms: Many online rental platforms allow filtering searches by pet-friendly criteria, making your search more efficient.
- Contacting Landlords Directly: While a property listing might not explicitly advertise as dog-friendly, contacting the landlord directly to inquire about their pet policy can reveal hidden gems.
- Considering Alternative Housing Options: Explore options like dog-friendly apartment buildings, co-living spaces that welcome pets, or even pet-friendly rentals outside the city center.
- Understanding Pet Deposits and Fees: Be prepared for potential pet deposits and fees associated with dog-friendly housing. Factor these costs into your budget when searching for a suitable place.
The Rights and Responsibilities of Tenants with Dogs
Once you find a dog-friendly haven, understanding your rights and responsibilities as a tenant is crucial:
- Abide by Lease Agreement: Carefully review and adhere to the terms outlined in your lease agreement regarding pet ownership.
- Maintain a Clean and Healthy Environment: Ensure your dog is properly housebroken and doesn’t cause excessive noise or damage to the property. Regularly clean up after your dog to prevent odors and sanitation issues.
- Vaccinations and Licensing: Keep your dog up-to-date on vaccinations and licensing requirements within your municipality.
- Respectful Coexistence: Be mindful of other tenants and their pets. Control your dog on common grounds and ensure they don’t cause disturbances or pose a threat.
Dog Adoption and Sale Laws in New York
New York, a state brimming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and a deep love for animals, offers numerous avenues for welcoming a canine companion into your life. Whether you choose adoption – giving a deserving dog a loving home – or purchase from a responsible breeder, understanding New York’s dog adoption and sale laws empowers you to make an informed and ethical decision.

Prioritizing Responsible Dog Acquisition
Before diving into legalities, it’s important to emphasize the ethical imperative of responsible dog acquisition:
- Supporting Rescue Organizations: Consider adopting a dog from a shelter or rescue organization. These organizations work tirelessly to care for abandoned, neglected, or surrendered dogs, offering them a second chance at a happy life.
- Combating Puppy Mills: By choosing adoption or a reputable breeder, you avoid supporting inhumane puppy mill operations that prioritize profit over animal welfare.
Giving a Dog a Second Chance
Adopting a dog from a shelter or rescue organization is a heartwarming experience that benefits both you and the dog:
- Licensing Requirements for Shelters and Rescues: Shelters and rescue organizations must be licensed by the New York State Department of Agriculture and Markets (AGM) to operate legally. This licensing ensures adherence to animal welfare standards.
- Adoption Process: The adoption process typically involves an application, reference checks, and a meet-and-greet with the dog to ensure compatibility. Adoption fees might apply, which help shelters and rescues care for other animals.
- Health Considerations: Reputable shelters and rescues will ensure the dog is up-to-date on vaccinations, spayed/neutered (except in specific circumstances), and receive any necessary medical care before adoption. Be sure to inquire about the dog’s medical history and ongoing needs.
- Post-Adoption Support: Many shelters and rescues offer post-adoption support resources to help you adjust to life with your new furry friend.
Understanding New York’s Spay/Neuter Laws
New York has a strong focus on promoting responsible pet ownership through spaying and neutering:
- Requirements for Shelters and Rescues: AGM regulations mandate that shelters and rescues spay/neuter all dogs eight weeks and older before adoption, with some exceptions for medical reasons documented by a veterinarian.
- Municipal Ordinances: Some municipalities within New York might have additional spay/neuter ordinances, so check with your local animal control department for specific regulations.
The Responsible Breeder Route
If you choose to purchase a dog from a breeder, prioritize finding a reputable source that prioritizes ethical breeding practices:
- Breeder Research: Conduct thorough research to identify reputable breeders who prioritize breed health, temperament evaluation, and proper socialization of their puppies.
- Kennel Club Recognition: Consider breeders who work with reputable kennel clubs like the American Kennel Club (AKC) that uphold breeding standards and ethical practices.
- Visiting the Breeding Facility: Request a visit to the breeder’s facility to assess the overall environment, breeding practices, and the general health and well-being of the parent dogs and puppies.
- Contracts and Health Guarantees: Reputable breeders will provide a written contract outlining the terms of the sale, health guarantees for the puppy, and potential return policies if unforeseen health issues arise.
Licensing Requirements for Dog Sales
New York has specific licensing requirements for dog sales, depending on the seller:
- Pet Dealer Licensing: Individuals selling more than nine dogs per year for profit require a pet dealer license from the AGM. This license ensures adherence to animal welfare standards during breeding, housing, and sale of dogs.
- Breeder Exemptions: Breeders selling fewer than 25 dogs per year raised on their residential premises are exempt from the pet dealer licensing requirement. However, they still need to comply with animal welfare standards.
Protecting Consumers: The “Lemon Law” for Pet Sales
New York’s “Lemon Law” offers some protections for consumers who purchase a dog from a pet dealer:
- Coverage and Timeframe: This law applies to dogs purchased from pet dealers, not breeders exempt from licensing. It covers situations where the dog develops a serious congenital or hereditary condition within one year of purchase.
- Replacement or Refund: Under the “Lemon Law,” consumers might be entitled to a replacement puppy, a full refund of the purchase price, or a partial refund if they keep the dog and cover treatment costs.
Dog Park and Recreation Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, picturesque landscapes, and millions of dog-loving residents, recognizes the importance of providing safe and stimulating spaces for canine recreation. Dog parks and designated off-leash areas offer a haven for dogs to socialize, exercise, and bond with their human companions. However, navigating the legalities surrounding these spaces ensures responsible enjoyment for both dogs and their owners.

Local Ordinances Reign Supreme
Unlike some states with a centralized framework for dog parks and recreation, New York follows a decentralized approach:
- Municipal Control: Most municipalities in New York establish their own ordinances regarding dog parks and off-leash areas. These ordinances can vary considerably, so it’s crucial to research the specific regulations in your area.
- Key Considerations: Local ordinances might address:
- Park Hours and Access: Dog park hours of operation might be designated, and some parks might require permits or registration for entry.
- Size and Breed Restrictions: Certain dog parks might have size or breed restrictions based on safety considerations or to cater to specific needs (e.g., separate areas for small and large dogs).
- Dog Park Etiquette: Local ordinances might outline expected behavior within the dog park, such as responsible owner supervision, ensuring proper waste disposal, and maintaining control of your dog.
- Finding Local Regulations: The best way to access detailed information on dog park and recreation laws in your area is to:
- Visit Your Municipality’s Website: Most municipal websites have dedicated sections outlining animal control regulations, including dog park ordinances.
- Contact Your Local Animal Control Department: Animal control officers can provide specific details about local dog park regulations and answer any questions you might have.
General Dog Park Etiquette
While local regulations reign supreme, some general principles apply to responsible use of dog parks in New York:
- Responsible Ownership: Always be a responsible dog owner. Ensure your dog is up-to-date on vaccinations, properly socialized, and well-behaved in public spaces.
- Respecting Other Dogs and Owners: Maintain an awareness of your surroundings and ensure your dog doesn’t disrupt or intimidate other dogs. Be mindful of other owners and their preferences.
- Cleaning Up After Your Dog: Always carry waste disposal bags and promptly clean up after your dog’s waste. This is a legal requirement and a courtesy to fellow dog park users.
- Supervision and Control: Maintain control of your dog at all times, even in off-leash areas. Leashes are typically required for entering and exiting the dog park.
- Understanding Your Dog’s Behavior: Be familiar with your dog’s temperament and social cues. If your dog exhibits aggressive behavior, remove them from the park immediately.
Exploring Off-Leash Recreation Areas
Some municipalities within New York designate specific public spaces as off-leash areas, offering alternative options for canine exploration:
- Understanding Guidelines: Similar to dog parks, off-leash areas might have specific guidelines, such as requiring proof of vaccination for entry. Always familiarize yourself with the rules before letting your dog loose.
- Responsible Supervision: Even in off-leash areas, responsible supervision remains crucial. Ensure your dog has good recall and interacts appropriately with other animals.
- Respecting Fellow Dog Owners: Maintain an awareness of other dogs and their owners, ensuring your dog’s behavior doesn’t infringe on their enjoyment of the space.
Ensuring Public Safety
Understanding leash laws in New York is crucial for responsible dog ownership in public spaces outside designated off-leash areas:
- Leash Requirements: Unless explicitly designated as an off-leash area, keep your dog leashed in public spaces. Leashes provide control and promote safety for both your dog and others.
- Leash Length Restrictions: Some municipalities might have specific leash length restrictions. Always check local regulations to ensure compliance.
- Respecting Others: Be mindful of others using public spaces, such as pedestrians, cyclists, or people enjoying outdoor activities. Avoid allowing your dog to jump on people or block walkways.
Dog Food and Nutrition Laws in New York
New York, a state pulsating with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and millions of devoted dog owners, prioritizes the well-being of all its residents, including furry companions. While there aren’t specific laws solely focused on dog food and nutrition in New York, understanding the federal framework and responsible pet ownership practices empowers you to make informed choices about your dog’s diet.

The Federal Framework: AAFCO and FDA Lead the Way
The Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) play a significant role in regulating pet food in the United States, which indirectly impacts New York:
- AAFCO Nutrient Profiles: AAFCO establishes nutrient profiles for various dog life stages and activity levels. These profiles serve as a guideline for pet food manufacturers to ensure their products provide the necessary nutrients for optimal canine health. While not legally binding, reputable pet food companies strive to formulate their products according to AAFCO guidelines.
- FDA Oversight: The FDA is responsible for ensuring the safety of pet food in the United States. They conduct inspections of pet food manufacturing facilities, investigate pet food recalls, and enforce regulations concerning pet food labeling.
Understanding Dog Food Labels
Understanding dog food labels empowers you to make informed choices about your canine companion’s diet:
- Ingredient List: The ingredients on a dog food label are listed in descending order by weight. The first few ingredients typically make up the bulk of the food.
- Guaranteed Analysis: This section provides the minimum percentages of protein, fat, fiber, and moisture content in the food. It also lists the maximum percentages of ash (mineral content) and water.
- Nutritional Adequacy Statement: This statement indicates whether the food meets the nutrient profiles established by AAFCO for a specific life stage (e.g., puppy, adult, senior) or activity level.
Choosing the Right Food for Your Dog
While the label provides valuable information, consider these additional factors when choosing dog food for your furry friend:
- Age and Activity Level: A growing puppy requires different nutritional content than a senior dog. Similarly, highly active dogs need more calories and protein than their less active counterparts.
- Breed-Specific Considerations: Certain breeds might have specific dietary needs due to size, activity level, or potential health concerns.
- Dietary Restrictions: Some dogs might have allergies or sensitivities to certain ingredients, requiring a specialized diet. Consult your veterinarian to determine the best course of action.
Fresh Food Options: Navigating the Landscape
While commercially available dog food is the most common option, some dog owners explore fresh food diets:
- Homemade Diets: Carefully research and consult with a veterinarian before formulating a homemade diet for your dog. Ensuring it meets all their nutritional needs is crucial.
- Subscription-Based Services: Subscription services deliver fresh, pre-portioned dog food to your doorstep. These services might consult with veterinarians to formulate their recipes. However, research the company’s reputation and consult your veterinarian before switching your dog’s diet.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
Raw food diets, consisting of uncooked meat, bones, and vegetables, are gaining popularity. However, these diets come with potential risks:
- Nutritional Imbalances: Ensuring a raw food diet meets all your dog’s nutritional needs requires careful planning and consultation with a veterinarian.
- Bacterial Contamination: Raw meat can harbor harmful bacteria that can pose a health risk to both dogs and humans. Proper handling and sanitation measures are essential.
Veterinarian Guidance: A Crucial Role in Dog Nutrition
Your veterinarian plays a vital role in ensuring your dog receives proper nutrition:
- Annual Wellness Exams: Regular veterinary checkups provide an opportunity to discuss your dog’s diet and address any potential nutritional concerns.
- Weight Management: Your veterinarian can help you determine the ideal weight for your dog and create a feeding plan to maintain a healthy body condition.
- Addressing Allergies and Sensitivities: If your dog exhibits signs of food allergies or sensitivities, your veterinarian can help diagnose the problem and recommend a suitable diet.
Working with Responsible Pet Food Retailers
Reputable pet food retailers can be valuable resources for dog owners:
- Knowledgeable Staff: Ask the staff about different dog food brands and their suitability for your dog’s specific needs.
- Sample Packs: Some stores offer sample packs of dog food, allowing you to try different options before committing to a large bag.
- Return Policies: Inquire about return policies in case your dog doesn’t take well to a particular food.
Dog Health and Veterinary Care Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and millions of devoted dog owners, recognizes the importance of safeguarding animal welfare. While there aren’t specific laws solely mandating veterinary care in New York, the state prioritizes responsible pet ownership and encourages practices that ensure canine health and well-being. Understanding these indirect regulations and best practices empowers you to make informed decisions regarding your dog’s healthcare.

The Ethical Obligation of Responsible Pet Ownership
Beyond legal mandates, responsible pet ownership in New York necessitates prioritizing your dog’s health and well-being:
- Preventative Care: Regular veterinary checkups, vaccinations, and parasite control measures are crucial for early disease detection, prevention of illness, and overall canine health.
- Addressing Medical Needs: If your dog exhibits signs of illness or injury, seeking prompt veterinary care is essential to ensure their well-being. Delaying treatment can worsen health issues and potentially lead to complications.
- Meeting Nutritional Needs: Providing your dog with a balanced and nutritious diet appropriate for their age, breed, and activity level is fundamental for optimal health.
Vaccinations: Safeguarding Your Dog and the Community
Vaccinations are a vital component of preventative healthcare for dogs in New York:
- Core Vaccinations: While not mandated by law, core vaccinations are highly recommended to protect your dog from potentially life-threatening diseases. These typically include vaccinations for rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and canine adenovirus.
- Non-Core Vaccinations: Depending on your dog’s lifestyle and risk factors, your veterinarian might recommend additional non-core vaccinations, such as those for leptospirosis, Bordetella (kennel cough), and canine influenza.
- Proof of Vaccination Requirements: Some public places like dog parks or boarding facilities might require proof of vaccination for entry.
Parasite Prevention: Protecting Your Dog and Your Family
Parasites, both internal and external, can pose significant health risks to dogs and potentially transmit to humans:
- Internal Parasites: Regular deworming treatments are crucial to prevent infestations of roundworms, hookworms, tapeworms, and other internal parasites.
- External Parasites: Using effective flea and tick preventatives year-round, even during colder months, protects your dog from these pesky and potentially disease-carrying parasites.
- Mosquito-Borne Diseases: Depending on your location within New York, your veterinarian might recommend preventative measures against mosquito-borne diseases like heartworm.
Microchipping: Enhancing Recovery and Identification
Microchipping is a safe and permanent method of identification for dogs in New York:
- The Microchipping Process: A veterinarian implants a tiny microchip containing a unique identification number under your dog’s skin. This chip can be scanned by animal shelters and veterinary clinics to retrieve your contact information if your dog gets lost or separated from you.
- Increased Recovery Chances: A microchip significantly increases the chances of reuniting with your dog if they become lost or stolen. Consider microchipping your dog as early as possible.
Animal Cruelty Laws: Protecting Dogs from Neglect and Abuse
New York has strong animal cruelty laws that protect dogs from neglect and abuse:
- Definition of Animal Cruelty: Agriculture and Markets Law (AGM) defines various acts of cruelty against animals, including denying necessary food, water, shelter, or veterinary care.
- Reporting Animal Cruelty: If you suspect a dog is being neglected or abused, you have a legal and ethical obligation to report it to your local animal control department or the NYS Department of Agriculture and Markets.
- Penalties for Animal Cruelty: Violations of animal cruelty laws can result in fines, jail time, and the potential for animal confiscation.
Finding a Reputable Veterinarian in New York
Having a trusted veterinarian is essential for your dog’s health and well-being:
- Location and Convenience: Consider factors like location, appointment availability, and emergency services offered when choosing a veterinarian.
- Veterinarian Qualifications: Look for a veterinarian licensed by the New York State Education Department (NYSED). Board certification in a specific area like canine medicine can be an added benefit.
- Communication and Trust: Choose a veterinarian you feel comfortable communicating with and who prioritizes your dog’s well-being.
Understanding Veterinary Costs and Insurance Options
Veterinary care can incur unexpected costs. Here’s what to consider:
- Discussing Costs Upfront: Ask about estimated costs for procedures or treatments before proceeding. Some clinics offer payment plans or financing options.
- Pet Insurance: Consider pet insurance to help manage potential veterinary expenses. Research different plans and choose one that best suits your dog’s needs
Dog Identification and Microchipping Laws in New York
New York, a state pulsating with vibrant cities, picturesque landscapes, and millions of dog-loving residents, prioritizes responsible pet ownership and animal welfare. While there isn’t a single, overarching law mandating dog identification in New York, a patchwork of regulations and best practices empowers you to ensure your furry friend is properly identified and has the best chance of returning home if lost. Understanding these legalities and exploring microchipping as a permanent identification solution empowers you to be a responsible dog owner.

The Importance of Dog Identification
While legal mandates might not be the sole driving force, dog identification in New York is crucial for several reasons:
- Increased Recovery Chances: A properly identified dog has significantly higher odds of being reunited with their owner if they become lost or separated.
- Reduced Time in Shelters: Prompt identification helps animal shelters return lost dogs to their rightful families, minimizing their time in unfamiliar and potentially stressful environments.
- Peace of Mind for Owners: Knowing your dog is properly identified offers peace of mind and allows you to focus on finding them if the unthinkable happens.
Traditional Dog Identification Methods in New York
Several traditional methods help identify dogs in New York:
- Collar and ID Tags: A properly fitting collar with a securely attached ID tag is the most basic form of dog identification. The tag should include your dog’s name, your phone number, and potentially your address.
- License Tags: While not mandatory statewide, some municipalities in New York require dog licensing. These licenses often come with a physical tag that attaches to the dog’s collar and serves as an additional form of identification.
Microchipping: A Permanent and Secure Identification Solution
Microchipping offers a permanent and secure method of dog identification in New York:
- The Microchipping Process: A veterinarian implants a tiny microchip containing a unique identification number under your dog’s skin. The chip is roughly the size of a grain of rice and is a painless procedure.
- Retrieving Contact Information: The microchip itself doesn’t store any personal information. A microchip scanner, readily available at animal shelters and veterinary clinics, can read the chip’s unique ID number. This number is then linked to a database containing your contact information, allowing authorities to reach you if your dog is found.
- Recovery Advantages: Microchipping offers a significant advantage over traditional methods like collar tags, which can fall off or become illegible. A microchip remains permanently implanted, ensuring your dog’s identification information remains accessible.
Microchipping Laws in New York: A Decentralized Approach
Unlike some states with a centralized microchipping mandate, New York follows a decentralized approach:
- No Statewide Mandate: Currently, there is no law in New York that mandates microchipping for all dogs.
- Municipal Regulations: Certain municipalities within New York might have ordinances encouraging or requiring microchipping for dogs. Always check with your local animal control department to understand any local regulations.
- Focus on Pet Shops and Rescue Groups: New York City has a specific law requiring pet shops and rescue groups to microchip all dogs and cats before adoption and register the microchip information with the owner’s contact details.
Encouraging Responsible Pet Ownership Through Microchipping
While not legally mandated statewide, promoting microchipping as a responsible pet ownership practice offers numerous benefits:
- Reduced Shelter Intake: Increased microchipping rates can lead to a decrease in the number of unclaimed dogs entering shelters, allowing them to focus on rescuing animals in need.
- Faster Reunifications: Prompt identification through microchipping minimizes the time lost dogs spend in shelters and allows for quicker reunions with their families.
- Reduced Euthanasia Rates: By reuniting lost dogs with their owners, microchipping can potentially help decrease the number of dogs euthanized due to being unclaimed.
Choosing a Microchip and Registration Service
There are various microchip options available for dog owners in New York:
- Veterinarian Recommendations: Consult your veterinarian for advice on choosing a microchip brand and a reputable registration service.
- Universal Compatibility: Ensure the chosen microchip meets universal scanning standards, allowing any animal shelter or veterinary clinic to read the chip’s unique ID.
- Lifetime Registration: Opt for a microchip registration service that offers lifetime registration, ensuring your contact information remains updated even if you move or change your phone number.
Dog Breeding and Genetics Laws in New York
New York, a state brimming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and a deep love for animals, recognizes the importance of ethical and responsible dog breeding practices. While there isn’t a single, overarching law governing dog breeding in New York, a combination of regulations and best practices empowers you to make informed decisions when considering a purebred puppy or supporting responsible breeders.

Prioritizing Ethical Breeding
Responsible dog breeding goes beyond just following the law. Here’s what truly matters:
- Animal Welfare: Ethical breeders prioritize the health and well-being of their breeding dogs. They ensure proper nutrition, veterinary care, socialization, and avoid excessive breeding practices.
- Breed Standards: Reputable breeders strive to maintain breed standards established by kennel clubs like the American Kennel Club (AKC) to promote desirable traits and minimize health concerns.
- Genetic Screening: Ethical breeders conduct genetic testing for known hereditary conditions within their chosen breed to reduce the risk of passing them on to puppies.
Navigating the Legal Landscape: Pet Dealer Licensing
New York has specific licensing requirements for dog breeders, categorized based on the scale of their operation:
- Pet Dealer Licensing: Individuals selling more than nine dogs or cats per year require a pet dealer license issued by the New York State Department of Agriculture and Markets (AGM). This ensures adherence to animal welfare standards during breeding, housing, and sale of dogs.
- Breeder Exemptions: Breeders selling fewer than 25 dogs per year raised on their residential premises are exempt from pet dealer licensing. However, they are still subject to unspecified animal welfare standards outlined by the AGM.
Understanding the Importance of Regulations
While breeder licensing is the primary legal framework for dog breeding in New York, understanding the rationale behind these regulations is crucial:
- Protecting Animal Welfare: Regulations aim to prevent inhumane breeding practices and ensure dogs used for breeding purposes receive proper care and live in healthy environments.
- Consumer Protection: Licensing helps ensure transparency in dog sales and provides consumers with a recourse if they encounter unethical breeders.
- Promoting Responsible Breeding: Regulations encourage responsible breeding practices that prioritize breed health, temperament, and overall well-being of the dogs.
Finding a Reputable Dog Breeder in New York
Finding a reputable dog breeder in New York requires research and due diligence:
- Kennel Club Affiliations: Consider breeders who are members of reputable kennel clubs like the AKC. These organizations uphold breed standards and often have breeder referral programs.
- Breeder Reputation: Research the breeder’s reputation online and among dog owners familiar with the breed. Look for positive reviews and testimonials.
- Facility Visits: Request a visit to the breeder’s facility to assess the overall environment, breeding practices, and the general health and well-being of the parent dogs and puppies.
- Contracts and Guarantees: Reputable breeders provide written contracts outlining the terms of the sale, health guarantees for the puppy, and potential return policies if unforeseen health issues arise.
Understanding Brachycephalic Breed Restrictions
New York City has specific regulations concerning the breeding and sale of brachycephalic dog breeds:
- Brachycephalic Breeds: These breeds have short snouts and flat faces, such as Pugs, Bulldogs, and Shih Tzus. They can be prone to breathing difficulties, especially in hot weather.
- Breeding Restrictions: New York City pet shops and rescue groups are prohibited from selling brachycephalic dogs under 12 weeks old. This aims to discourage breeding practices that perpetuate these health concerns.
The Ethical Alternative: Adoption
Considering adopting a dog from a shelter or rescue organization offers a heartwarming alternative to purchasing from a breeder:
- Saving a Life: Adoption gives a deserving dog a second chance at a loving home.
- Variety of Breeds: Shelters and rescues house dogs of all breeds, mixes, and ages.
- Reduced Demand for Puppy Mills: By choosing adoption, you avoid supporting inhumane puppy mill operations that prioritize profit over animal welfare.
The Future of Dog Breeding in New York
The conversation surrounding dog breeding in New York is constantly evolving:
- Advocacy for Responsible Breeding Practices: Organizations like the ASPCA work to promote responsible breeding practices and educate consumers about the importance of ethical breeders.
- Potential for Further Regulations: Discussions regarding stricter regulations for dog breeding, including mandatory licensing for all breeders, might arise in the future.
Dog Environmental Impact Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, picturesque landscapes, and a dedicated dog-loving community, recognizes the interconnectedness between humans, animals, and the environment. While there aren’t specific laws solely targeting dog waste, several regulations and best practices promote responsible dog ownership that minimizes their environmental impact. Understanding these guidelines empowers you to be a considerate dog owner and contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment for everyone.

The Importance of Responsible Dog Ownership
Responsible dog ownership goes beyond legal mandates. It’s about being a considerate pet parent who minimizes their dog’s environmental footprint:
- Waste Management: Always carry waste disposal bags and promptly clean up after your dog’s waste. Leaving waste behind pollutes waterways, attracts pests, and poses health risks for humans and wildlife.
- Respecting Public Spaces: Be mindful of other park users and avoid letting your dog disrupt natural environments or damage public property.
- Following Leash Laws: Always keep your dog leashed in designated areas to minimize their impact on wildlife and vegetation.
Dog Waste and its Environmental Impact
Dog waste, if not disposed of properly, can have a significant environmental impact:
- Water Contamination: Left on the ground, dog waste can be washed away by rain or storm water runoff, contaminating nearby waterways. Bacteria from dog waste can harm aquatic life and render water sources unsafe for recreation.
- Nutrient Overload: Dog waste decomposes, releasing nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. Excessive levels of these nutrients can contribute to algal blooms, harming aquatic ecosystems.
- Public Health Concerns: Dog waste can harbor harmful bacteria and parasites that pose health risks to humans and other animals.
Waste Disposal Regulations
New York has established regulations regarding proper waste disposal in public spaces, which indirectly apply to dog waste management:
- Pooper Scooper Laws: Many municipalities within New York have pooper scooper laws mandating dog owners to clean up after their pets’ waste in public spaces. Fines can be levied for non-compliance.
- Park and Public Space Regulations: Most parks and public spaces have signage outlining waste disposal expectations. Always adhere to these guidelines and dispose of dog waste in designated waste bins.
Picking Up After Your Dog: Essential Practices for Responsible Owners
Being a responsible dog owner means taking proactive steps to manage your dog’s waste:
- Always Carry Waste Disposal Bags: Make carrying waste disposal bags a regular habit whenever venturing out with your dog. Stockpile them readily accessible in your car, bag dispenser, or pockets.
- Double Bagging: Consider double bagging waste for added security and odor control, especially in warmer weather.
- Dispose of Waste Properly: Tie the bag securely and deposit it in designated waste bins. Never leave waste bags lying around in parks or public spaces.
Minimizing Your Dog’s Environmental Impact
Several practices go beyond waste management to minimize your dog’s environmental impact:
- Sustainable Dog Food Options: Research dog food companies committed to sustainable practices, such as using recycled packaging or sourcing ingredients from responsible producers.
- Water Conservation: Use a water bowl with a built-in reservoir to minimize water waste while ensuring your dog stays hydrated.
- Eco-Friendly Dog Supplies: Consider using eco-friendly dog supplies made from recycled materials, such as toys, leashes, and collars.
Public Education and Community Initiatives
Promoting responsible dog ownership through public education and community initiatives plays a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Municipal authorities and animal welfare organizations can launch campaigns educating dog owners about proper waste disposal and responsible pet ownership practices.
- Providing Waste Disposal Resources: Parks and public spaces can be equipped with sufficient designated waste bins and readily available waste disposal bags for dog owners.
- Community Clean-Up Events: Organizing park clean-up events encourages dog owners and the community to work together to maintain a clean and healthy environment.
Working Towards a Cleaner Future
By working together, dog owners, municipalities, and animal welfare organizations can create a cleaner and healthier environment for all:
- Advocacy for Responsible Ownership: Dog owners can advocate for initiatives promoting responsible ownership practices and access to proper waste disposal resources.
- Supporting Sustainable Businesses: Supporting dog food companies and pet suppliers committed to sustainability encourages environmentally conscious practices within the industry.
- Collaboration for a Greener Future: Collaboration between municipalities, animal welfare organizations, and dog owners fosters a collective effort towards a cleaner environment for everyone, including our canine companions.
Dog Behavioural Training Laws in New York
New York, a state pulsating with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and a multitude of dog-loving residents, prioritizes responsible pet ownership. While there aren’t specific laws mandating dog behavioral training, the state encourages practices that promote well-behaved canine companions. Understanding these indirect regulations and the importance of training empowers you to raise a happy, well-adjusted dog who integrates seamlessly into your community.

The Ethical Responsibility of Training Your Dog
Beyond legal requirements, training your dog is an ethical obligation for every pet owner in New York:
- Safety for All: Proper training equips your dog with the skills to navigate social situations appropriately, minimizing the risk of bites or injuries to yourself, other animals, and the general public.
- Happy and Fulfilled Dogs: Training provides mental stimulation for dogs, strengthens the bond between you and your furry friend, and fosters a more enjoyable life together.
- Respectful Coexistence: A well-trained dog is a joy to live with and allows for smoother integration into dog parks, social gatherings, and public spaces.
Addressing Specific Behavioral Issues
While there are no mandated training requirements, New York addresses specific behavioral issues through regulations:
- Aggressive Dogs: Following a dog bite incident, local animal control authorities might require the owner to enroll the dog in behavior modification training with a qualified professional. The aim is to address the underlying cause of the aggression and prevent future incidents.
- Nuisance Barking: Some municipalities within New York have noise ordinances that might address excessive or disruptive barking from dogs. These ordinances might not mandate training but could potentially lead to fines for persistent violations.
The Importance of Positive Reinforcement Training Techniques
Positive reinforcement training methods are highly recommended for dog owners in New York:
- Reward-Based Approach: Positive reinforcement focuses on rewarding desired behaviors with treats, praise, or affection. This approach is humane, effective, and fosters a positive relationship between you and your dog.
- Building Trust and Confidence: Positive reinforcement builds trust and confidence in your dog, leading to better communication and a more enjoyable training experience.
- Addressing Underlying Issues: While positive reinforcement focuses on rewarding good behavior, it can also be used to address unwanted behaviors by identifying the triggers and teaching alternative responses.
Finding a Reputable Dog Trainer in New York
Choosing the right dog trainer is crucial for success:
- Qualifications and Experience: Look for trainers certified by reputable organizations like the Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers (CCPDT). Experience with your dog’s breed or specific behavioral concerns is a plus.
- Training Methods: Ensure the trainer utilizes positive reinforcement techniques and prioritizes humane and ethical training practices.
- Communication and Compatibility: Choose a trainer who has excellent communication skills, actively listens to your concerns, and fosters a comfortable environment for you and your dog.
Understanding Dog Licensing Requirements
While not a direct mandate for training, some municipalities in New York require dog licensing:
- Potential Training Incentives: Some licensing programs might offer discounts or incentives for completing dog obedience training courses. This encourages responsible pet ownership and promotes basic training skills.
- Identification and Responsible Ownership: Licensing promotes responsible ownership by ensuring dogs are properly identified and their owners can be held accountable for their pet’s behavior.
Public Education and Community Resources
Promoting responsible pet ownership and access to training resources benefits both dogs and communities in New York:
- Community Dog Training Workshops: Local animal shelters, park departments, or pet stores might offer affordable or free dog training workshops to educate owners on basic obedience skills.
- Online Resources: Numerous reputable online resources offer information and guidance on dog training techniques. However, these resources cannot replace the personalized guidance of a qualified dog trainer.
The Future of Dog Training in New York
The conversation surrounding dog training in New York might evolve in the future:
- Advocacy for Responsible Ownership: Animal welfare organizations and dog training professionals might advocate for increased public education on the importance of dog training.
- Potential for Training Requirements: Discussions regarding mandatory training requirements for certain dog breeds or following bite incidents could arise.
Dog Protection and Rescue Laws in New York
New York, a state brimming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and a dedicated community of dog lovers, prioritizes the welfare of animals. While there isn’t a single, overarching law encompassing all aspects of dog protection and rescue, a robust legal framework and network of organizations work together to safeguard canine well-being. Understanding these legalities and resources empowers you to play a vital role in protecting and potentially rescuing a dog in need.

The Importance of Animal Cruelty Prevention
Beyond specific laws, preventing animal cruelty is a core principle in New York:
- Ethical Obligation: Every pet owner has an ethical obligation to provide their dog with proper food, water, shelter, veterinary care, and a safe and loving environment.
- Definition of Animal Cruelty: New York’s Agriculture and Markets Law (AGM) defines animal cruelty as intentionally, knowingly, or recklessly causing pain, injury, or death to an animal, or depriving them of necessary sustenance or veterinary care.
- Reporting Animal Cruelty: If you suspect a dog is being neglected or abused, you have a legal and moral responsibility to report it to your local animal control department or the NYS Department of Agriculture and Markets.
Protecting Dogs from Neglect and Abuse
New York has strong animal cruelty laws that protect dogs from various forms of neglect and abuse:
- Failure to Provide Necessities: Denying a dog necessary food, water, shelter, or veterinary care constitutes animal cruelty.
- Abandonment: Abandoning a dog is illegal and can result in penalties. Leaving a dog tethered for extended periods or in harsh weather conditions also falls under this category.
- Infliction of Injury: Intentionally causing physical harm to a dog through abuse or neglect is a crime.
- Fighting or Baiting Animals: Dogfighting and using dogs as bait for other animals are illegal and carry severe penalties.
Reporting Suspected Animal Cruelty
If you suspect a dog is being neglected or abused, take action through proper reporting channels:
- Gather Evidence: If possible, document the situation with photos or videos while ensuring your own safety.
- Contact Local Authorities: Report suspected animal cruelty to your local animal control department or the NYS Department of Agriculture and Markets cruelty hotline.
- Cooperate with Investigations: Assist animal control officers with their investigation to ensure the dog’s safety.
The Role of Animal Shelters and Rescue Organizations
Animal shelters and rescue organizations play a critical role in protecting and rehoming dogs in New York:
- Municipal Shelters: These shelters impound stray and surrendered dogs and work to find them adoptive homes.
- Private Rescue Organizations: Numerous private rescues focus on specific breeds, age groups, or dogs with special needs.
- Adoption Process: The adoption process typically involves an application, meet-and-greet sessions, and potentially a home visit to ensure a good fit for both the dog and the potential owner.
Responsible Ownership Practices to Prevent Neglect and Abandonment
By following responsible ownership practices, you can help prevent neglect and abandonment:
- Meeting Needs and Providing Care: Ensure your dog receives proper food, water, shelter, veterinary care, and sufficient exercise.
- Identification and Microchipping: Properly identify your dog with a collar and ID tag and consider microchipping for permanent identification.
- Planning for the Future: Think long-term about your commitment to dog ownership and consider potential changes in your lifestyle before welcoming a dog into your life.
Supporting Responsible Rescue Organizations
Supporting responsible rescue organizations plays a vital role in dog protection:
- Volunteering: Donate your time to help with dog walking, socialization, or fostering dogs in need.
- Donations: Financial contributions help shelters and rescues provide food, medical care, and other essentials for dogs in their care.
- Advocacy: Raise awareness about animal welfare issues and responsible pet ownership practices.
Leash Laws and Off-Leash Dog Parks
Leash laws and designated off-leash dog parks play a role in protecting dogs from harm and promoting responsible ownership:
- Leash Laws: Most municipalities in New York have leash laws requiring dogs to be leashed in public spaces. These laws help prevent dog bites, injuries, and ensure general public safety.
- Off-Leash Dog Parks: Designated off-leash dog parks allow dogs to socialize and exercise freely under responsible owner supervision. Always ensure your dog is properly socialized and has good recall before utilizing off-leash areas.
Dog Entertainment and Work Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and a dedicated dog-loving community, recognizes the multifaceted roles dogs play in our lives. While there aren’t specific laws solely dedicated to dog entertainment or work, a framework exists that indirectly governs these activities. Understanding these regulations and best practices empowers you to ensure your canine companion enjoys safe and enriching experiences, whether for entertainment or work purposes.

The Importance of Enrichment for Dogs
Beyond entertainment, providing enrichment activities for your dog is crucial for their well-being:
- Combating Boredom: Engaging activities help prevent boredom, a common cause of destructive behaviors like chewing or digging.
- Mental Stimulation: Mental stimulation keeps dogs mentally sharp and can even help prevent cognitive decline in older dogs.
- Strengthening the Bond: Shared activities create positive experiences and strengthen the bond between you and your dog.
Exploring Dog Entertainment Options in New York
New York offers a plethora of dog-friendly entertainment options:
- Dog Parks: Designated off-leash dog parks allow dogs to socialize, play fetch, and run freely under responsible owner supervision. Always ensure your dog is properly socialized and has good recall before utilizing off-leash areas.
- Dog-Friendly Hiking Trails: Numerous hiking trails across New York welcome well-behaved, leashed dogs. Explore scenic landscapes and bond with your furry friend in nature.
- Dog-Friendly Restaurants and Breweries: Many restaurants and breweries in New York have outdoor patios where well-behaved, leashed dogs are welcome. Enjoy a meal or beverage with your canine companion.
- Dog-Friendly Events: Events like dog festivals, agility competitions, or lure coursing can provide fun and stimulating experiences for your dog.
Understanding Regulations for Dog Entertainment Activities
Several regulations indirectly govern dog entertainment activities in New York:
- Leash Laws: Most municipalities in New York have leash laws requiring dogs to be leashed in public spaces, including dog parks. These laws ensure public safety and prevent confrontations with other dogs.
- Waste Disposal: Always carry waste disposal bags and promptly clean up after your dog’s waste in public spaces, including dog parks. Leaving waste behind is not only inconsiderate but can also pose health risks.
- Vaccinations: Some dog parks or dog-friendly establishments might require proof of vaccination for your dog before entry. Ensure your dog’s vaccinations are up-to-date to protect them and other dogs.
A Framework for Responsible practices
While there isn’t a single law governing all working dogs, several regulations and best practices ensure responsible animal welfare practices:
- Federal Regulations: The Federal Animal Welfare Act (AWA) establishes minimum care standards for certain types of working animals, including those used in exhibitions, research, or transport.
- State Oversight: The New York State Department of Agriculture and Markets (AGM) might oversee specific working dog activities depending on the industry (e.g., service animals used in agriculture).
- Breed Suitability: Choosing a breed well-suited for the intended work is crucial. For example, German Shepherds are often used as police dogs due to their intelligence and trainability.
Common Working Dog Roles in New York
Several dog breeds excel in various working roles in New York:
- Service Animals: Guide dogs, hearing dogs, and other service animals assist people with disabilities. Federal laws protect their right to accompany their handlers in public spaces.
- Law Enforcement and Military: Certain breeds like German Shepherds, Belgian Malinois, and Bloodhounds are trained for tasks like search and rescue, drug detection, and patrol work.
- Therapy Dogs: Therapy dogs provide emotional support and comfort in settings like hospitals, nursing homes, or schools. They typically undergo specific training and temperament evaluations.
- Livestock Guardian Dogs: Breeds like Great Pyrenees or Anatolian Shepherds protect livestock from predators on farms or ranches.
Ensuring Responsible Working Dog Practices
Prioritizing responsible practices is paramount when involving dogs in work:
- Proper Training: Working dogs require specialized training to perform their tasks effectively and safely.
- Welfare Considerations: Working dogs should have access to proper rest, hydration, nutrition, and veterinary care.
- Breed-Specific Needs: Understanding the specific needs of the working dog breed is essential for their well-being.
Dog Technology and Innovation Laws in New York
New York, a state pulsating with innovation and a deep love for dogs, is witnessing a surge in pet technology advancements. While there aren’t specific laws directly regulating all dog tech products, a framework exists to ensure the safety and well-being of canine companions within this evolving landscape. Understanding these regulations and the exciting possibilities of dog tech empowers you to make informed decisions for your furry friend.

The Rise of Dog Technology and its Potential Benefits
Dog technology encompasses a vast array of innovative products and services designed to enhance the lives of both dogs and their owners:
- Wearable Trackers: GPS trackers and activity monitors allow you to track your dog’s location, monitor their activity levels, and gain insights into their overall health.
- Remote Training Devices: Certain devices offer remote training functionalities through sound or vibration, potentially aiding in obedience training.
- Interactive Toys: Tech-enabled toys provide mental stimulation and entertainment for dogs while you’re away.
- Smart Feeders and Water Dispensers: These devices automatically dispense food and water, ensuring your dog stays fed and hydrated even when you’re not home.
- Telehealth Consultations: Video conferencing with veterinarians can offer convenient access to veterinary care for non-emergency situations.
Indirect Regulations for Dog Tech
While there isn’t a single law governing all dog tech products in New York, several regulations indirectly apply:
- Federal Oversight: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates certain pet tech products, particularly those with claims related to animal health or disease diagnosis. Look for FDA approval when considering these products.
- Consumer Protection Laws: New York consumer protection laws apply to pet tech products, ensuring fair business practices and addressing potential product liability concerns. Research the product and its manufacturer before making a purchase.
- Data Privacy Considerations: Some dog tech products collect data about your dog’s activity or location. Be mindful of data privacy practices and ensure the company adheres to data security regulations.
Choosing Safe and Effective Dog Tech Products
With the ever-expanding dog tech market, choosing safe and effective products requires careful consideration:
- Research and Reviews: Read product reviews and research the company’s reputation before investing in dog tech. Look for products with positive user experiences and a focus on animal welfare.
- Consult Your Veterinarian: Discuss potential dog tech options with your veterinarian to ensure they are appropriate for your dog’s breed, age, and health needs.
- Focus on Functionality: Prioritize products that address a specific need or enhance your dog’s well-being. Avoid novelty items that might be more stressful than beneficial.
The Future of Dog Health Technology in New York
The future of dog health technology in New York is brimming with possibilities:
- Advanced Wearables: Wearables might evolve to monitor vital signs, detect potential health issues at an early stage, and even integrate with telemedicine platforms for remote consultations.
- AI-Powered Training Tools: Artificial intelligence might be used to personalize training programs, analyze dog behavior, and provide real-time feedback.
- Precision Medicine and Genomics: Advancements in genomics could lead to personalized health plans and targeted therapies for specific canine diseases.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
While dog tech offers exciting possibilities, ethical considerations are paramount:
- Over-Reliance on Technology: Never replace human interaction and supervision with dog tech products. Prioritize quality time and walks with your furry friend.
- Data Security and Privacy: Be mindful of the data collected by dog tech devices and ensure the companies prioritize data security.
- Animal Welfare at the Forefront: Always prioritize your dog’s well-being above convenience. Use dog tech responsibly and ensure it enhances, not replaces, proper care.
Human Coexistence Laws in New York
New York, a state teeming with vibrant cities, breathtaking landscapes, and a dedicated dog-loving community, recognizes the profound bond between humans and their canine companions. While there isn’t a single, overarching law solely focused on promoting human-dog cohabitation, a network of regulations and best practices empowers responsible dog ownership and fosters harmonious coexistence. Understanding these legalities and responsible ownership practices allows you to create a happy and fulfilling life with your furry friend.

The Importance of Human-Dog Coexistence
Responsible dog ownership goes beyond legal requirements. It’s about fostering a strong bond with your dog that enriches both your lives:
- Mutual Benefits: Dogs provide companionship, emotional support, and motivation for an active lifestyle. In return, responsible owners provide for their dog’s physical and emotional needs, creating a mutually beneficial relationship.
- Socialization for a Well-Adjusted Dog: Proper socialization through positive interactions with humans and other dogs is crucial for a dog’s well-being. This includes providing opportunities for playtime, walks in public spaces, and attending dog-friendly events.
- Responsible Ownership for a Better Community: Well-trained and socialized dogs contribute to a more positive and enjoyable environment for everyone in the community.
Understanding Regulations that Enable Human-Dog Coexistence
Several regulations in New York indirectly promote human-dog cohabitation:
- Leash Laws: Most municipalities in New York have leash laws requiring dogs to be leashed in public spaces. This ensures safety for both dogs and the general public, allowing for more enjoyable shared experiences.
- Dog Parks: Designated off-leash dog parks allow dogs to socialize and exercise freely under responsible owner supervision. These parks provide a safe space for dogs to interact with each other and their human companions.
- Public Transportation: Some public transportation options in New York, like specific subway lines or commuter trains, might allow well-behaved, leashed dogs on board under certain conditions. These regulations allow dog owners to integrate their furry friends into their daily routines.
Responsible Ownership Practices for a Harmonious Relationship
Beyond legal regulations, responsible ownership practices are crucial for successful human-dog cohabitation:
- Training and Socialization: Invest in positive reinforcement training and socialization to ensure your dog is well-behaved and comfortable interacting with humans and other dogs.
- Meeting Needs: Provide proper food, water, shelter, veterinary care, and ample exercise to ensure your dog’s physical and mental well-being. Meeting their needs fosters trust and strengthens your bond.
- Quality Time and Interaction: Spend quality time with your dog through walks, playtime, and cuddling. These interactions solidify your connection and provide mental stimulation for your dog.
Living Arrangements and Human-Dog Coexistence
Finding dog-friendly housing is crucial for some dog owners in New York:
- Landlord-Tenant Laws: Some municipalities have regulations limiting breed restrictions or requiring landlords to consider pet applications fairly. Always research local tenant laws before applying for a rental with your dog.
- Dog-Friendly Apartment Complexes: Many apartment buildings and communities cater to dog owners, offering amenities like dog runs, pet waste disposal stations, or dog-walking services. Consider these options when searching for a new home.
Community Initiatives for Dog Owners
Community initiatives can play a significant role in promoting human-dog cohabitation:
- Dog-Friendly Events: Events like dog festivals, charity walks, or dog-friendly movie nights provide opportunities for dog owners to socialize and strengthen the bond with their furry companions.
- Dog Training Classes: Community centers or pet stores might offer affordable dog training classes, promoting responsible ownership and fostering well-behaved canine citizens.
- Dog Parks and Walking Trails: Investing in well-maintained dog parks and dog-friendly walking trails encourages dog owners to get outside with their dogs, promoting exercise and human-dog interaction.
The Future of Human-Dog Coexistence in New York
The future of human-dog cohabitation in New York is promising:
- Increased Advocacy for Dog-Friendly Policies: Dog owner advocacy groups might push for more dog-friendly policies in workplaces, public spaces, and transportation options.
- Focus on Mental Well-being: Increased awareness of the mental health benefits of dog ownership could lead to more initiatives promoting human-dog interaction.
- Advancements in Dog Technology: Emerging dog tech products like interactive toys or wearable trackers might enhance communication and understanding between humans and dogs.
Other Relevant Dog Laws in New York
Canine Good Citizen (CGC) Programs and Legal Benefits
- CGC Programs: The American Kennel Club (AKC) offers Canine Good Citizen (CGC) programs, a non-competitive training series certifying well-mannered and socialized dogs.
- Potential Benefits: While not a legal requirement, completing a CGC program might offer benefits like:
- Discounts on dog licensing fees (offered by some municipalities)
- Reduced homeowner’s insurance premiums (offered by some insurance companies for CGC-certified dogs)
- Improved insurability (demonstrating a well-trained dog might be attractive to insurers)
Dog Insurance and Coverage Laws in New York
- Regulation: Dog insurance is not mandated by law in New York.
- Coverage Options: Dog insurance policies vary but can cover veterinary care, accidents, liability for bites or injuries, and even theft (depending on the breed).
- Considerations: Researching different pet insurance providers and coverage options is crucial to find a plan that suits your needs and budget.
Laws Regarding Dogs in Hot Cars and Animal Endangerment
- New York Agriculture and Markets Law (AGM): This law prohibits leaving an animal in a parked motor vehicle under conditions that could cause harm due to extreme heat, cold, or lack of adequate ventilation.
- Potential Penalties: Violations can result in fines and even animal cruelty charges.
- Community Awareness: Leaving a dog in a hot car can be fatal. Be aware of the dangers and never leave your dog unattended in a vehicle, especially during hot weather.
Legal Aspects of Dog Parks and Shared Spaces
- Leash Laws and Off-Leash Areas: Most municipalities have leash laws requiring dogs to be leashed in public spaces. Designated off-leash dog parks allow controlled off-leash interaction under owner supervision.
- Waste Disposal: Always carry waste disposal bags and clean up after your dog’s waste in public spaces, including dog parks. Leaving waste behind is illegal and inconsiderate.
- Socialization and Responsible Ownership: Dog parks are intended for social interaction. Ensure your dog is well-socialized and has good recall before utilizing off-leash areas. Be a responsible owner and maintain control of your dog at all times.
Dog-Related Property Damage and Homeowner’s Insurance in New York
- Homeowner’s Insurance: Most homeowner’s insurance policies cover dog-related damage to your own property, with limitations and exclusions depending on the policy.
- Liability for Damage to Others’ Property: Your homeowner’s insurance might also cover damage your dog causes to someone else’s property, depending on the policy and circumstances.
- Importance of Coverage: Review your homeowner’s insurance policy and discuss dog-related coverage options with your insurance provider.
Service and Working Dog Laws in Employment and Public Access
- Federal Laws: The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) protects the rights of individuals with disabilities to use service animals in public spaces and workplaces.
- Definition of Service Animal: The ADA defines service animals as dogs (or miniature horses) trained to perform specific tasks to assist people with disabilities.
- Public Access Rights: Service animals are generally allowed in most public spaces and workplaces, with some exceptions (e.g., sterile environments like operating rooms). Business owners cannot ask about a service animal’s disability but may inquire about the tasks the animal performs.
- Emotional Support Animals (ESAs): ESAs are not protected by the ADA but might be allowed in housing situations under the Fair Housing Act (FHA) with proper documentation.
Animal Welfare and Protection Laws Against Neglect and Abandonment
- New York Agriculture and Markets Law (AGM): This law defines animal cruelty and outlines the responsibilities of animal owners to provide proper food, water, shelter, veterinary care, and a safe environment.
- Reporting Animal Cruelty: Anyone suspecting animal cruelty has a legal and moral obligation to report it to their local animal control department or the NYS Department of Agriculture and Markets cruelty hotline.
- Importance of Responsible Ownership: Preventing animal cruelty starts with responsible ownership. Providing your dog with proper care and a loving home is essential.
This comprehensive guide explored the legal landscape surrounding dog ownership in New York. While there isn’t a single, overarching law, a network of regulations and best practices empowers responsible ownership. From understanding leash laws and waste disposal etiquette to exploring dog park regulations and service animal rights, the article provided insights into various aspects of dog life in the state.
Compliance with dog laws is not just about avoiding fines; it’s about creating a safe and enjoyable environment for everyone. Responsible dog ownership fosters well-behaved canine citizens, strengthens the human-dog bond, and contributes to a more harmonious community for both dog lovers and non-dog owners alike. By following the law and prioritizing responsible pet care, we can ensure a happy and fulfilling life for our furry companions and ourselves.
FAQs
Can I bring my dog to restaurants in New York?
Maybe. While there’s no statewide law, some restaurants in New York have outdoor patios where well-behaved, leashed dogs are welcome. Always check with the restaurant’s policy before bringing your dog.
What are the rules for traveling with my dog on public transportation in New York?
It depends. Some subway lines or commuter trains in New York might allow small, well-behaved dogs on board in carriers during off-peak hours. Always check with the specific public transportation provider for their pet policy and any restrictions on size, breed, or time of day.
Are there any limitations on the number of dogs I can own in New York?
Generally, no. However, some municipalities might have ordinances limiting the number of dogs allowed per household. Always check with your local regulations to avoid any violations.
What are the requirements for microchipping my dog in New York?
There is no mandatory microchipping law in New York. However, microchipping your dog is highly recommended. It’s a permanent form of identification that can significantly increase the chances of your dog being reunited with you if they get lost.
What resources are available to help me find dog-friendly activities in New York?
Many resources can help! You can use online apps or websites dedicated to finding dog-friendly parks, trails, restaurants, and events. Local animal shelters or pet stores might also offer recommendations for dog-friendly activities in your area.







