Dog Laws in Ohio
Living with a furry friend in Ohio is a joy, but with that joy comes responsibility. Did you know that over 6.3 million households in the USA consider a dog part of the family? That’s a lot of happy tails wagging around!
But to keep those wags worry-free, it’s important to understand the dog laws in your state. Ohio, like all states, has regulations in place to protect both our canine companions and the communities we share.
These laws cover everything from licensing and vaccination requirements to leash laws and restrictions on certain breeds. Don’t worry, deciphering these dog decrees doesn’t have to be ruff! Let’s explore the key areas of Ohio’s dog laws and make sure your pup’s adventures are happy and lawful.
Table of Contents
Dog Bite Laws in Ohio
Living in Ohio with your furry friend can be a tail-wagging good time. But as a responsible dog owner, understanding dog bite laws is crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of both your canine companion and the community. This guide delves into the key aspects of Ohio’s dog bite laws, empowering you with the knowledge you need.
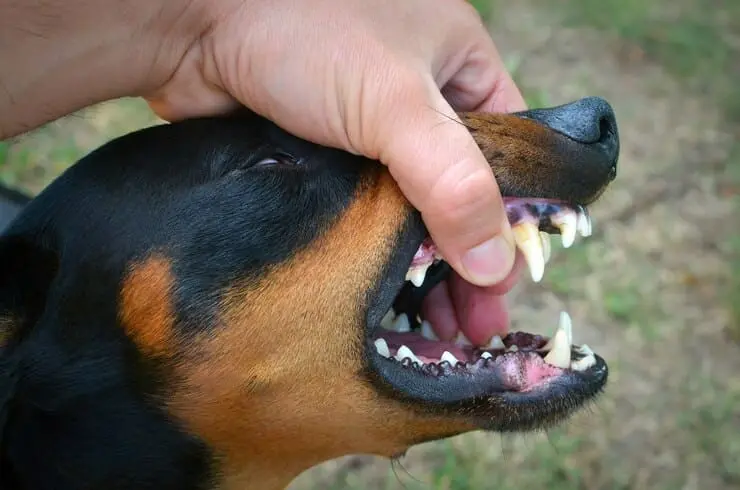
Strict Liability in Ohio
Ohio adheres to a “strict liability” doctrine for dog bites, outlined in Section 955.28 of the Ohio Revised Code. This means that if your dog bites someone without justification, you are held liable for any damages or injuries caused by the bite, regardless of your prior knowledge of the dog’s aggressive tendencies. This strict approach emphasizes the responsibility of dog ownership and prioritizes public safety.
What You Don’t Have to Prove
In a dog bite case under Ohio’s strict liability law, the victim does not need to prove negligence on the owner’s part. Here’s what the victim must prove:
- The bite occurred: Evidence such as medical records or witness testimonies can establish this.
- The bite caused injury or damages: Medical bills and documentation of property damage will be crucial here.
When the “One-Bite” Rule Might Apply
While Ohio primarily operates under strict liability, there’s a common law concept called the “one-bite” rule that may come into play in certain situations. This rule applies when:
- The dog breed is not typically considered vicious.
- The owner had no prior knowledge of the dog’s aggressive tendencies.
- The victim was trespassing on the owner’s property.
However, it’s important to note that the “one-bite” rule is not a guaranteed defense. The court will weigh the evidence in each case to determine liability. Consulting with a legal professional is recommended if you find yourself in such a situation.
Who Can Be Held Liable?
Ohio’s dog bite law extends liability beyond just the owner. The statute also applies to keepers and harborers of the dog. This means that anyone who has control or care of the dog at the time of the bite can be held responsible. For example, if you’re pet-sitting a friend’s dog and it bites someone, you could be liable.
Defenses to a Dog Bite Claim
While Ohio’s dog bite laws favor the victim, there are some potential defenses an owner can raise:
- Provocation: If the victim provoked the dog’s attack, the owner’s liability may be reduced or eliminated.
- Trespassing: If the victim was trespassing on private property when bitten, the owner’s liability may be lessened.
- Self-defense: If the owner or someone else was acting in self-defense when the dog bit the victim, there may be no liability.
Reporting Dog Bites
Ohio law requires reporting dog bites to the local dog warden or animal control agency within 24 hours. This is crucial for public safety and disease control purposes. Failure to report a dog bite can result in penalties.
Quarantine Requirements After a Bite
Any dog that bites a person must be quarantined for ten days at a veterinarian’s office or animal shelter. During this period, the dog will be observed for signs of rabies. The cost of quarantine is typically borne by the dog owner.
Financial Repercussions of a Dog Bite
If your dog bites someone, you could be held financially responsible for a variety of damages, including:
- Medical bills for the victim’s treatment
- Lost wages due to the victim’s injuries
- Pain and suffering
- Emotional distress
- Property damage
Protecting Yourself and Your Pup
The best way to avoid the legal and financial repercussions of a dog bite is to take preventative measures:
- Proper training and socialization: Enroll your dog in obedience training classes and socialize them from a young age.
- Responsible leashing and supervision: Always keep your dog leashed in public and supervise them closely when around others.
- Spay or neuter your dog: Studies suggest that altered dogs may be less likely to bite.
- Maintain proper fencing: Ensure your yard is securely fenced to prevent your dog from escaping.
- Homeowners or renters insurance: Consider getting pet liability coverage as part of your insurance plan.
Dog Barking and Noise Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a furry friend in Ohio brings endless joy. But sometimes, even the most well-behaved pup can become a canine chorus conductor, leaving you wondering – are there laws about excessive dog barking in Ohio? Absolutely! This guide delves into the key aspects of dog barking and noise ordinances in the Buckeye State, helping you ensure your dog’s vocal expressions don’t disrupt the peace.

A Patchwork of Ordinances
Unlike a uniform state law, dog barking regulations in Ohio are primarily enacted at the municipal level. This means each city, town, and county has its own noise ordinance addressing excessive barking. The specific details of these ordinances can vary significantly.
Commonalities in the Canine Chorus
While the specifics may differ, most Ohio noise ordinances share some common elements regarding dog barking:
- Unreasonable Duration and Frequency: The focus is on excessive and continuous barking, not an occasional woof. Many ordinances define a violation as barking for a specific duration (e.g., 20 minutes uninterrupted) or exceeding a certain frequency within a timeframe (e.g., several barking episodes throughout the night).
- Time Restrictions: Some ordinances designate specific times when barking is considered more disruptive, such as nighttime or early morning hours. For example, an ordinance might allow more leniency during the day but have stricter regulations for barking after a certain hour.
- Disturbance of Peace and Quiet: The core principle is that the barking creates a nuisance for others, disturbing the peace and quiet of the neighborhood.
Finding Your Local Ordinance
Here’s how to find the specific dog barking ordinance applicable to your area:
- Municipal Website: Most municipalities have their noise ordinances readily available on their official websites. Simply search for your city or county name followed by “noise ordinance.”
- Animal Control Department: Contact your local animal control department. They can provide information on the specific barking regulations in your area.
- County Courthouse: The county courthouse may have a copy of the relevant ordinance on file.
State Considerations
While state-level dog barking laws are less prevalent, Ohio does have a relevant regulation under the Ohio Administrative Code (OAC). Rule 1501:46-3-08 empowers natural resources officers to address situations where a dog’s barking disrupts the “quiet enjoyment” of public areas under their jurisdiction. This could apply to state parks, forests, or other designated areas.
Addressing Excessive Barking
Living in harmony with your canine companion and your neighbors is key. Here are some proactive steps you can take to address excessive barking:
- Identify the Cause: Understanding why your dog barks excessively is crucial. Common reasons include boredom, anxiety, separation anxiety, territorial behavior, or medical issues.
- Training and Enrichment: Proper training and providing your dog with stimulating activities can significantly reduce barking. Consider obedience classes, interactive toys, and ample exercise.
- Desensitization and Counterconditioning: If triggers like seeing other dogs or hearing noises cause barking, gradually expose your dog to these stimuli in a controlled way while rewarding calm behavior.
- Veterinary Consultation: If you suspect a medical cause for the barking, consult your veterinarian for a check-up.
Engaging Animal Control
If attempts to address barking through training and management prove unsuccessful, and the barking violates your local ordinance, contacting animal control is the next step. They can investigate the situation, issue warnings, and potentially impose fines for repeat offenses.
Remember: Animal control officers are there to help. By working collaboratively, you can find solutions for excessive barking that keep your dog happy and maintain a peaceful neighborhood.
Dog Poop Disposal Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings endless tail wags and muddy paw prints. But with all the joy comes responsibility, and a crucial part of that responsibility is responsible dog waste disposal. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog poop disposal laws in Ohio, ensuring your walks are filled with fun, not fines.

State vs. Local:
While Ohio doesn’t have a statewide law mandating dog waste disposal, most regulations occur at the municipal level. This means each city, town, and county has its own ordinances outlining proper waste disposal procedures for dog owners.
Cleaning Up After Your Pup
Despite the lack of a state law, the core principle across most Ohio municipalities is clear: dog owners are responsible for picking up and disposing of their dog’s waste. This not only promotes a clean and sanitary environment but also minimizes the spread of diseases and parasites that can be harmful to humans and other animals.
Finding Your Local Poop Scoop on the Rules
Here’s how to find the specific dog waste disposal ordinance applicable to your area:
- Municipal Website: Most municipalities have their waste disposal regulations readily available on their official websites. Simply search for your city or county name followed by “waste disposal ordinance” or “animal control regulations.”
- Animal Control Department: Contact your local animal control department. They can provide information on the specific dog waste disposal rules in your area.
- County Courthouse: The county courthouse may have a copy of the relevant ordinance on file.
Public Health Considerations
While not a direct dog waste disposal law, Ohio’s Revised Code (ORC) Section 3707.43 prohibits littering . Dog waste left behind on public or private property (with the exception of the owner’s property) can be considered littering under this statute. Violations may result in fines.
Essential Gear for Responsible Owners
No matter your location in Ohio, carrying poop bags is a must-have for any dog owner. Here’s why:
- Compliance with Local Ordinances: Most ordinances mandate picking up waste, and poop bags are the most convenient way to do so.
- Public Health and Sanitation: Dog waste can harbor harmful bacteria and parasites. Proper disposal via bags minimizes the risk of disease transmission.
- Environmental Protection: Left on the ground, dog waste can pollute waterways and contribute to nutrient overload. Poop bags ensure proper disposal.
Picking Up the Poop
Here are some essential tips for responsible dog waste disposal:
- Always carry poop bags: Make them a permanent fixture in your dog walking gear.
- Double-bag it for extra security: This minimizes the risk of tears or leaks.
- Tie the bag securely: A loose knot can lead to an unpleasant mess.
- Dispose of the bag properly: Look for designated dog waste disposal bins in parks or public areas. If unavailable, dispose of the sealed bag in a trash can. Never leave it on the ground.
Additional Considerations
While poop bags are essential, responsible dog waste disposal goes beyond just picking it up. Here are some additional points to consider:
- Composting Dog Waste: Some municipalities allow composting dog waste in designated bins or at home (with proper composting systems that eliminate pathogens). Check your local regulations for details.
- Flushing Waste: While some dog waste disposal bags claim to be flushable, it’s generally not recommended in most Ohio municipalities. Flushing can clog sewer systems and contribute to water treatment challenges.
Dog Licensing Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings endless joy, playful antics, and unconditional love. However, with the wags and cuddles comes responsibility, and a vital part of that responsibility is ensuring your furry friend is properly licensed. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog licensing laws in Ohio, empowering you to be a responsible dog owner and keep your pup happy and compliant.

The Buckeye State’s Stance on Dog Licensing
Ohio operates under a mandatory dog licensing law, outlined in Section 955.01 of the Ohio Revised Code (ORC). This law applies to all dogs three months of age or older residing in the state.
Benefits of Dog Licensing
Obtaining a dog license isn’t just a legal requirement; it offers several benefits for both you and your canine companion:
- Identification: A dog license serves as an official ID tag for your pup. In case your dog gets lost, the license increases the chances of a safe and swift return.
- Vaccination Verification: Licensing often requires proof of current rabies vaccination, crucial for protecting your dog and the community from this deadly disease.
- Funding for Animal Services: Dog license fees contribute to vital animal control services like sheltering lost animals, enforcing animal welfare regulations, and investigating cruelty cases.
The Licensing Process
The dog licensing process in Ohio is generally straightforward. Here’s what you need to know:
- Where to License: You can typically obtain a dog license from your county auditor’s office, a local animal shelter, or an authorized licensing agent.
- Required Information: Be prepared to provide information like your name, address, dog’s breed, age, and sex.
- Proof of Rabies Vaccination: Most counties require proof of current rabies vaccination for licensing.
- Fees and Payment: Licensing fees vary by county and may depend on factors like your dog’s age and neutering/spaying status. Generally, fees range from $20 to $60 for a one-year license, with discounts available for spaying/neutering.
Keeping Your License Up-to-Date
Ohio dog licenses are valid for one year and require annual renewal. Renewal periods typically occur between December 1st and January 31st each year. Missing the deadline may result in late fees. Many counties offer convenient online renewal options.
Exemptions to Dog Licensing
While most dogs require licensing, there are some exceptions:
- Service Animals: Legally recognized service animals (e.g., guide dogs, hearing assistance dogs) are exempt from licensing requirements.
- Working Dogs: Certain categories of working dogs, like those used by law enforcement or herding livestock, may have specific licensing exemptions determined by your county.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to license your dog in Ohio can result in penalties. These consequences can vary by county but may include:
- Fines: Fines for unlicensed dogs can range from $25 to $100 or more.
- Late Fees: Missing the renewal deadline often incurs additional late fees.
- Impoundment: An unlicensed dog may be impounded by animal control until licensing fees and penalties are paid.
Dog Leash Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a furry friend in Ohio brings endless joy, playful explorations, and happy tail wags. But venturing outside with your canine companion requires responsible ownership, and a crucial aspect of that is leash control. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog leash laws in Ohio, empowering you to ensure safe and compliant walks with your pup.

he Leash Law Landscape: A Patchwork of Local Ordinances
Unlike a uniform state law, dog leash regulations in Ohio primarily reside at the municipal level. This means each city, town, and county has its own leash ordinance outlining where and when dogs must be leashed. The specific details of these ordinances can vary significantly.
Keeping Our Communities Safe
Despite the local variations, most Ohio leash ordinances share a core principle – promoting public safety for both humans and animals. By keeping your dog leashed in designated areas, you minimize the risk of accidents, bites, or disruptions for others enjoying public spaces.
Finding Your Local Leash Law
Here’s how to find the specific dog leash ordinance applicable to your area:
- Municipal Website: Most municipalities have their leash ordinances readily available on their official websites. Simply search for your city or county name followed by “leash ordinance” or “animal control regulations.”
- Animal Control Department: Contact your local animal control department. They can provide information on the specific leash regulations in your area.
- County Courthouse: The county courthouse may have a copy of the relevant ordinance on file.
Common Leash Law Elements
Here are some elements you might encounter in Ohio leash ordinances:
- Leash Length: Many ordinances specify a maximum leash length, often ranging from six to ten feet.
- Designated Leash-Free Areas: Some municipalities have designated dog parks or off-leash areas where responsible owners can allow their dogs to run freely.
- Time Restrictions: Certain ordinances may have specific timeframes when leash use is mandatory, such as nighttime hours.
- Aggressive or Dangerous Dogs: Stricter leash control may be required for dogs classified as aggressive or potentially dangerous.
State Considerations and Exceptions
While state-level dog leash laws are less prevalent, Ohio does have a relevant regulation under the Ohio Revised Code (ORC). Section 955.22 outlines the following:
- General Leash Requirement: Dogs must be physically confined or restrained on their owner’s property by a leash, tether, fence, or supervision to prevent escape. This broadly emphasizes leash usage in public and private settings unless alternative secure confinement is in place.
- Exceptions: The statute allows exceptions for hunting dogs under the control of a hunter in designated hunting areas during lawful hunting seasons and law enforcement dogs performing their duties.
Responsible Leash Use
Following leash laws is crucial, but responsible leash use goes beyond legal compliance. Here are some additional tips:
- Choose the Right Leash: Select a leash with a comfortable length and material appropriate for your dog’s size and temperament.
- Maintain Control: Always maintain slack-free control of the leash to prevent your dog from pulling or lunging.
- Practice Leash Walking: Train your dog to walk calmly and comfortably on a leash to ensure enjoyable outings for both of you.
- Be Respectful of Others: Be mindful of others using shared spaces. Give them ample space and keep your dog leashed when near people or other animals who might be uncomfortable with off-leash interactions.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to leash your dog in violation of local ordinances can result in fines ranging from $25 to $100 or more, depending on the specific jurisdiction and the severity of the offense. Additionally, an unleashed dog may be impounded by animal control until licensing fees and penalties are paid.
Dangerous Dog Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings unconditional love and furry companionship. However, responsible dog ownership also involves understanding the legal landscape, especially regarding potentially dangerous dogs. This guide delves into the key aspects of dangerous dog laws in Ohio, empowering you to ensure both public safety and the well-being of your furry friend.

Defining “Dangerous”: Not Just About Breed
Ohio’s dangerous dog laws don’t solely rely on breed stereotypes. Section 955.11 of the Ohio Revised Code (ORC) defines a “dangerous dog” based on behavior, not breed:
- Unprovoked Attacks: A dog that, without provocation, has caused injury (other than killing or serious injury) to any person or killed another dog.
- Repeated Lack of Control: A dog that has been the subject of three or more violations of leash laws or secure confinement regulations within a one-year period.
The Designation Process: How a Dog Becomes “Dangerous”
The process of designating a dog as dangerous typically involves the following steps:
- Incident Reporting: If a dog attack occurs, the victim or a witness reports the incident to animal control or local law enforcement.
- Investigation: Animal control officers investigate the incident, gathering evidence and witness statements.
- Hearing: A designated official conducts a hearing to determine if the dog meets the definition of “dangerous” based on the investigation’s findings.
The Weight of Evidence
It’s important to note that the designation process is not automatic. The hearing official considers all evidence, including the circumstances of the incident, the dog’s history, and any attempts at training or rehabilitation.
Requirements and Restrictions for Dangerous Dogs
If a dog is designated as dangerous, certain requirements and restrictions are imposed:
- Dangerous Dog Registration: The owner must obtain a special dangerous dog registration and license tag. Renewal is required annually.
- Liability Insurance: The owner may be required to carry liability insurance to cover potential injuries caused by the dog.
- Secure Confinement: The dog must be securely confined on the owner’s property by a strong fence or other appropriate measures to prevent escape.
- Muzzling: Muzzle use may be required in public spaces.
- Warning Signs: The owner may be required to post warning signs on their property indicating the presence of a dangerous dog.
The Importance of Responsible Ownership
Dangerous dog laws in Ohio aim to promote public safety while ensuring due process for dog owners. Here are some ways responsible owners can minimize risks:
- Proper Training and Socialization: Invest in training your dog from a young age. Socialization with other dogs and people is crucial.
- Understanding Breed Tendencies: While breed isn’t the sole factor, research potential behavioral tendencies of your dog’s breed to address specific needs.
- Spaying or Neutering: Altered dogs may be less prone to aggression in some cases.
- Preventing Escapes: Ensure your property fencing is secure and can contain your dog.
Nuisance and Vicious Dogs
Ohio’s dog classification system goes beyond “dangerous.” The ORC also defines:
- Nuisance Dog: A dog that barks excessively or chases/approaches people in a threatening manner while off the owner’s property.
- Vicious Dog: A dog that, without provocation, has killed or caused serious injury to a person.
Nuisance and vicious dog designations often carry stricter requirements and penalties compared to dangerous dogs.
When to Seek Legal Counsel
If your dog is involved in an incident or faces a dangerous dog designation, consulting with a lawyer specializing in animal law is crucial. They can advise you on your rights and legal options throughout the process.
Dog Health and Welfare Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings endless joy, loyalty, and unconditional love. But with that love comes a responsibility – ensuring your dog’s health and well-being. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog health and welfare laws in Ohio, empowering you to be a responsible owner and provide your furry friend with the happy and healthy life they deserve.

State & Local Regulations
Ohio’s dog health and welfare landscape involves a combination of state-level regulations and local ordinances. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas:
- State Laws: The Ohio Revised Code (ORC) outlines several foundational animal cruelty and welfare statutes.
- Local Ordinances: Many municipalities have additional animal control ordinances addressing specific aspects of dog health and welfare within their jurisdictions.
Preventing Animal Cruelty
The core principle behind Ohio’s dog health and welfare laws is preventing animal cruelty. Section 959.13 of the ORC defines cruelty broadly, encompassing acts that cause:
- Physical Pain or Suffering: This includes deliberate infliction of injury, starvation, dehydration, or neglect of medical needs.
- Psychological Distress: Cruelty can encompass acts that cause undue fear, anxiety, or distress to a dog.
- Improper Care and Treatment: Failing to provide adequate food, water, shelter, or veterinary care when necessary can be considered cruelty.
Specific Protections for Dogs
While preventing cruelty forms the foundation, Ohio has additional regulations protecting dog health and welfare:
- Tethering Restrictions: The ORC prohibits tethering a dog unattended for extended periods without access to food, water, and adequate shelter from the elements.
- Transport Requirements: Dogs transported in vehicles must be secured in a way that prevents injury during sudden stops or accidents.
- Flea and Tick Control: Some local ordinances mandate basic parasite prevention measures for dogs.
Finding Your Local Animal Control Ordinances
To gain a comprehensive understanding of dog health and welfare regulations applicable to your area, explore these resources:
- Municipal Website: Most municipalities have their animal control ordinances readily available on their official websites. Search for your city or county name followed by “animal control” or “animal welfare regulations.”
- Animal Control Department: Contact your local animal control department. They can provide specific details on the regulations in your area.
- County Courthouse: The county courthouse may have copies of relevant local ordinances on file.
Fulfilling Your Responsibilities as a Dog Owner
The legal framework provides a foundation, but responsible dog ownership goes beyond following the law. Here are some key aspects to ensure your dog’s well-being:
- Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary checkups, vaccinations, and parasite prevention are crucial for your dog’s health.
- Proper Nutrition: Provide your dog with a balanced diet appropriate for their age, breed, and activity level.
- Exercise and Enrichment: Exercise keeps your dog physically fit and mentally stimulated. Engage in daily walks, playtime, and appropriate training.
- Safe and Secure Environment: Ensure your dog has a clean, comfortable living space with access to fresh water and shelter from extreme weather conditions.
- Identification: Microchipping or securely attached tags with your contact information can ensure your dog finds their way back home if lost.
Reporting Suspected Animal Cruelty: Taking Action
If you suspect an animal is being neglected or abused, it’s your responsibility to report it. Here’s what you can do:
- Contact Animal Control: Your local animal control department is responsible for investigating animal cruelty complaints.
- Gather Evidence: If possible, document the situation with photos or videos to support your report.
- Provide Details: Be as specific as possible regarding the location of the animal and the nature of the suspected abuse.
Dog Public Access Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings endless tail wags, playful adventures, and opportunities for creating lasting memories together. But venturing out with your furry friend raises questions about where they can accompany you. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog public access laws in Ohio, empowering you to navigate public spaces responsibly and enjoy quality time with your pup.

No One-Size-Fits-All Solution
Unlike a uniform state law, dog public access regulations in Ohio primarily reside at the municipal level. This means each city, town, and county has its own ordinances outlining where dogs are allowed and any restrictions in place. These regulations can vary significantly, so understanding your local laws is crucial.
alancing Access with Responsibility
Despite the local variations, most Ohio public access ordinances share a common goal – striking a balance between allowing responsible dog owners to enjoy public spaces with their furry friends and ensuring the safety and comfort of everyone.
Finding Your Local Public Access Ordinance
Here’s how to find the specific dog public access ordinance applicable to your area:
- Municipal Website: Most municipalities have their public access ordinances readily available on their official websites. Simply search for your city or county name followed by “dog access ordinance” or “park regulations.”
- Parks and Recreation Department: The parks and recreation department in your area can provide information on dog access rules for specific parks or trails.
- Animal Control Department: Contact your local animal control department. They can provide details on public access regulations within your jurisdiction.
Understanding Common Public Access Elements
Here are some elements you might encounter in Ohio public access ordinances:
- Designated Dog Parks: Many municipalities have designated off-leash dog parks where responsible owners can allow their dogs to run freely in a safe and controlled environment.
- Leash Requirements: Public spaces other than designated dog parks may require dogs to be kept on leash at all times. Leash length restrictions may also be specified.
- Breed Restrictions: Some public spaces, like dog parks or beaches, might have breed restrictions based on local regulations.
- Waste Disposal Responsibilities: All ordinances emphasize responsible pet ownership, and pet waste disposal is a common requirement in all public spaces.
State Considerations
While state-level dog public access laws are less prevalent, Ohio does have a relevant regulation under the Ohio Administrative Code (OAC). Rule 1501:46-3-08 empowers natural resources officers to address situations where a dog’s presence disrupts the “quiet enjoyment” of public areas under their jurisdiction, such as state parks, forests, or other designated areas.
Responsible Public Access
Following public access ordinances is crucial, but responsible public access goes beyond legal compliance. Here are some additional tips:
- Know Your Dog: Ensure your dog is well-socialized and comfortable in public settings before venturing out.
- Practice Leash Manners: Train your dog to walk calmly and comfortably on a leash to ensure a pleasant experience for everyone.
- Respect Other Park Users: Be mindful of others and their comfort levels around dogs. Give ample space and avoid crowded areas if your dog is nervous or reactive.
- Clean Up After Your Dog: Always carry poop bags and dispose of waste responsibly. Leaving waste behind is not only inconsiderate but also poses health risks.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with public access ordinances, such as entering a dog-prohibited area or not picking up waste, can result in fines ranging from $25 to $100 or more, depending on the specific jurisdiction and the severity of the offense. Additionally, your dog may be removed from the area.
Dog Travel and Transportation Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio opens doors to countless adventures. However, venturing out with your furry friend requires preparation, and understanding the legalities of dog travel and transportation is crucial. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog travel and transportation laws in Ohio, ensuring a smooth and compliant journey for you and your four-legged copilot.
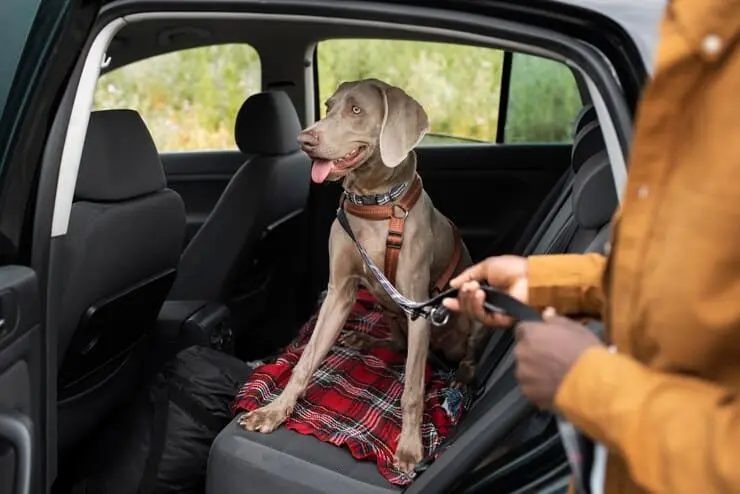

State Laws and Common Carrier Policies
Traveling with your dog in Ohio involves a combination of state-level regulations and the policies of individual common carriers (e.g., airlines, buses, trains).
- State Laws: Ohio doesn’t have a comprehensive dog travel law. However, general animal cruelty prevention statutes (ORC Section 959.13) apply during transportation.
- Common Carrier Policies: Airlines, buses, and trains have their own specific policies regarding pet transportation, including breed restrictions, size limitations, health certificate requirements, and fees.
Planning for a Pawsitive Journey
Here’s how to ensure a smooth and legal travel experience with your dog:
- Research Common Carrier Policies: Start by researching the specific pet travel policies of the airline, bus company, or train service you plan to use. This information is usually readily available on their websites.
- Health Certificate Requirements: Many common carriers require a health certificate issued by a licensed veterinarian within a specific timeframe (often 10 days) before travel.
- Vaccinations: Up-to-date vaccinations, such as rabies, may be mandatory for dog travel.
- Crates and Carriers: Most common carriers require dogs to be transported in airline-approved crates or carriers that meet specific size and ventilation requirements.
- Service Animals: Federal laws protect the rights of passengers with service animals. However, documentation and training requirements may apply.
Considerations for Different Travel Modes:
Here are some additional points to keep in mind for specific travel modes:
- Air Travel: Regulations regarding dog size, breed restrictions, and in-cabin versus cargo hold transport can vary significantly between airlines.
- Bus Travel: Some bus companies may not allow pets at all, while others have restrictions and additional fees.
- Train Travel: Amtrak, for instance, allows some dogs on certain routes with specific crate and documentation requirements.
Responsible Travel Practices
While legal compliance is crucial, responsible travel with your dog goes beyond the rules. Here are some additional tips:
- Acclimate Your Dog: If your dog isn’t used to crates or carriers, gradually introduce them before travel to create a positive association.
- Microchip Your Dog: Microchipping increases the chances of a safe reunion if your dog gets separated from you during travel.
- Travel Essentials: Pack familiar items like food, water bowls, bedding, and toys to keep your dog comfortable on the journey.
- Plan for Rest Stops: Schedule regular breaks during car travel to allow your dog to relieve themselves, stretch their legs, and stay hydrated.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with travel regulations can result in a variety of inconveniences and potential costs:
- Denied Boarding: Your dog may be denied boarding if they don’t meet the specific carrier’s requirements.
- Fines or Fees: Airlines and other carriers may impose fines for non-compliance with their pet travel policies.
- Animal Welfare Concerns: In extreme cases, if your dog exhibits signs of distress during transport due to inadequate preparation, authorities might intervene.
Dog Housing and Accommodation Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings endless love, playful antics, and the desire to create a cozy home together. But navigating the world of dog-friendly housing can be confusing. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog housing and accommodation laws in Ohio, empowering you to find a suitable place for both you and your furry friend.

A Landscape Shaped by Federal and Fair Housing Laws
While there isn’t a single, comprehensive state law governing dog housing in Ohio, two key legal frameworks play a significant role:
- The Fair Housing Act (FHA): This federal law prohibits discrimination based on disability and includes protections for individuals with disabilities who require assistance animals, such as service dogs or emotional support animals (ESAs).
- Local Landlord-Tenant Laws: Municipalities may have additional regulations regarding pet ownership in rental properties. These regulations can vary and may address aspects like breed restrictions or pet deposits.
Understanding Service Animals vs. Emotional Support Animals
The FHA offers clear definitions for service animals and ESAs:
- Service Animal: A dog that is individually trained to do work or perform tasks for the benefit of a person with a disability.
- Emotional Support Animal (ESA): A dog that provides emotional support, comfort, or companionship to alleviate symptoms of a disability, but does not perform specific tasks.
The FHA and Service Animals
The FHA offers strong protections for tenants with service animals. Landlords cannot refuse to rent to someone with a disability based on their service animal. Additionally, they cannot charge extra fees or deposits specifically for a service animal.
Verification and Reasonable Accommodations
Landlords can request written verification from a healthcare professional documenting the tenant’s disability and the necessity of the service animal. However, they cannot ask for specifics about the disability. Landlords are also obligated to make reasonable accommodations for service animals, such as allowing them in “no-pet” buildings.
Understanding ESAs and the Nuances of the FHA
The FHA does not guarantee automatic access for ESAs in housing with “no-pet” policies. Landlords can inquire about the nature of the disability and how the ESA alleviates symptoms. Landlords can also deny unreasonable accommodation requests related to ESAs, such as having multiple large dogs in a small apartment.
Local Regulations and Breed Restrictions
While the FHA limits breed discrimination for service animals, some municipalities in Ohio might have local ordinances allowing breed restrictions in rental properties. Always check with your local fair housing agency to understand any breed-related regulations in your area.
Finding Dog-Friendly Housing
Understanding the legal landscape is crucial, but here are some additional tips for finding dog-friendly housing in Ohio:
- Research Pet Policies: Read rental listings carefully and inquire about pet policies, including any breed restrictions, size limitations, and pet fees.
- Highlight Your Responsible Ownership: During the application process, emphasize your responsible pet ownership history, including references and veterinary records.
- Consider Pet-Friendly Communities: Some apartment complexes or neighborhoods cater specifically to pet owners, offering amenities and a more welcoming environment for dogs.
Dog Adoption and Sale Laws in Ohio
Ohio offers a wealth of options for welcoming a canine companion into your life. Whether you choose adoption from a shelter or responsible purchase from a breeder, understanding the legalities involved is crucial. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog adoption and sale laws in Ohio, empowering you to make an informed and ethical decision when bringing a dog into your home.
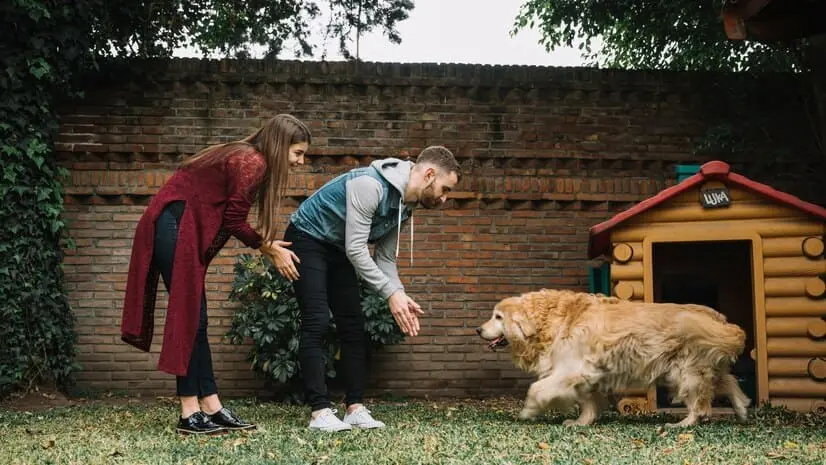

The Adoption Advantage: Saving a Life
Adopting a dog from a shelter or rescue organization is a rewarding experience. You’re giving a deserving animal a loving home while creating a special bond. Here’s what to know about dog adoption in Ohio:
- Shelters and Rescues: Numerous animal shelters and rescue organizations throughout Ohio care for homeless and abandoned dogs. These organizations often have adoption fees to cover the costs of veterinary care, vaccinations, and spaying/neutering.
- Adoption Process: The adoption process typically involves filling out an application, meeting potential canine companions, and discussing your lifestyle and living situation to ensure a good fit.
- Licensing Requirements: Once adopted, your dog will need to be licensed with your local county auditor’s office.
Prioritizing Dog Health and Well-Being
If you choose to purchase a dog from a breeder, prioritize responsible breeding practices that emphasize the health and well-being of the animals. Here’s what to consider:
- Breeder Reputation: Research breeders with a good reputation for ethical breeding practices, prioritizing dog health and temperament. Look for breeders who conduct health screenings on breeding stock.
- Kennel Inspections: The Ohio Department of Agriculture (ODA) inspects dog kennels to ensure compliance with minimum care standards. You can inquire about a breeder’s kennel license and inspection history.
- Contracts and Health Guarantees: Reputable breeders typically have written contracts outlining the purchase agreement, health guarantees, and potential return policies.
Key Ohio Laws for Both Adoption and Sale
Several key Ohio laws apply to both dog adoption and sale:
- Animal Cruelty Prevention: The Ohio Revised Code (ORC) Section 959.13 defines and prohibits animal cruelty. This applies to all breeders, shelters, and individual dog owners.
- Licensing Requirements: All dogs over the age of three months in Ohio must be licensed with the county auditor’s office. License fees can vary depending on the county.
- Vaccinations: Rabies vaccination is mandatory for all dogs over the age of three months in Ohio. Additional vaccinations may be recommended by your veterinarian.
- Microchipping: While not mandatory in Ohio, microchipping your dog is highly recommended. It significantly increases the chances of a safe reunion if your dog gets lost.
Responsible Ownership Practices
Following the law is essential, but being a responsible dog owner goes beyond legal requirements. Here are some additional points to consider:
- Choosing the Right Breed: Research different dog breeds to find one that aligns with your lifestyle, activity level, and living environment.
- Training and Socialization: Invest in training your dog for good behavior and basic commands. Early socialization is crucial for a well-adjusted canine companion.
- Preventative Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary checkups, parasite prevention, and maintaining a healthy diet are essential for your dog’s well-being.
Additional Considerations
While shelters, rescues, and reputable breeders offer the safest options, online marketplaces or private sales might be an avenue some consider. Here’s what to be cautious about:
- Unknown Origins and Health Risks: Dogs from unknown sources may have health problems or behavioral issues.
- Puppy Mills: Be wary of unethical puppy mills that prioritize profit over dog welfare.
- Lack of Guarantees or Support: Private sellers may not offer health guarantees or support after the sale.
Dog Park and Recreation Laws in Ohio
Sharing your life with a canine companion in Ohio brings endless tail wags, playful moments, and a desire to explore the outdoors together. Dog parks offer dedicated spaces for your furry friend to run free, socialize, and burn off energy. However, venturing into public spaces with your dog requires understanding the legalities involved. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog park and recreation laws in Ohio, empowering you to enjoy responsible and safe outings with your four-legged friend.
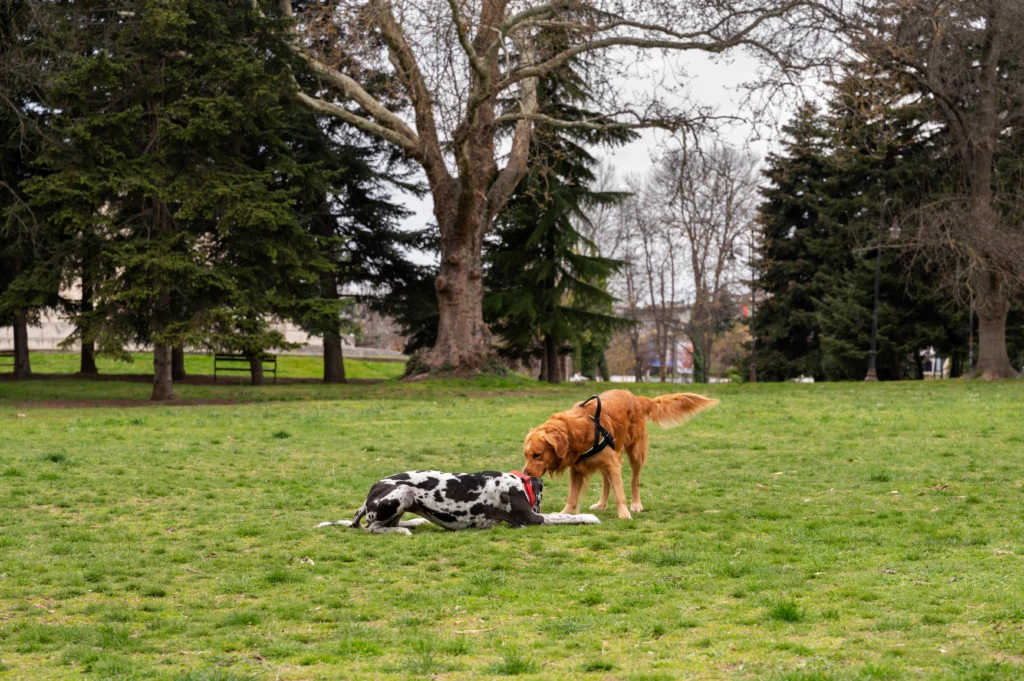

A Landscape of Local Control: No One-Size-Fits-All Solution
Unlike a uniform state law, dog park and recreation regulations in Ohio primarily reside at the municipal level. This means each city, town, and county has its own ordinances outlining dog park rules, leash requirements in public spaces, and access restrictions for specific areas. Understanding your local laws is crucial for responsible dog ownership.
Finding Your Local Dog Park and Recreation Ordinances
Here’s how to find the specific dog park and recreation ordinances applicable to your area:
- Municipal Website: Most municipalities have their public access and dog park rules readily available on their official websites. Simply search for your city or county name followed by “dog park ordinance” or “park regulations.”
- Parks and Recreation Department: The parks and recreation department in your area can provide information on specific dog park rules, leash requirements in various parks, and designated swimming areas for dogs (if applicable).
- Animal Control Department: Contact your local animal control department. They can provide details on public access and dog park regulations within your jurisdiction.
Common Elements of Dog Park and Recreation Ordinances
While specific details may vary, here are some elements you might encounter in Ohio dog park and recreation ordinances:
- Designated Dog Parks: Many municipalities have designated off-leash dog parks where responsible owners can allow their dogs to run freely in a safe and controlled environment. These parks often have separate areas for large and small dogs.
- Leash Requirements: Public spaces other than designated dog parks may require dogs to be kept on leash at all times. Leash length restrictions may also be specified.
- Breed Restrictions: Some dog parks or public spaces might have breed restrictions based on local regulations.
- Waste Disposal Responsibilities: All ordinances emphasize responsible pet ownership, and pet waste disposal is a common requirement in all public spaces.
- Dog Park Rules: Specific dog park rules may address aspects like:
- Vaccinations: Up-to-date vaccinations, such as rabies, might be mandatory for dog park use.
- Aggressive Dog Behavior: Dogs showing aggression towards other dogs or people may be removed from the park.
- Supervision: Owners are typically required to remain within the dog park and maintain control of their dogs at all times.
State Considerations: Supplementing Local Ordinances
While state-level dog park and recreation laws are less prevalent, Ohio does have a relevant regulation under the Ohio Administrative Code (OAC). Rule 1501:46-3-08 empowers natural resources officers to address situations where a dog’s presence disrupts the “quiet enjoyment” of public areas under their jurisdiction, such as state parks, forests, or other designated areas. This rule emphasizes responsible dog ownership and respecting the rights of other park users.
Responsible Dog Park and Recreation Practices
Following public access and dog park ordinances is crucial, but responsible park etiquette goes beyond legal compliance. Here are some additional tips:
- Know Your Dog: Ensure your dog is well-socialized and comfortable in public settings before venturing to dog parks.
- Practice Leash Manners: Even in designated off-leash areas, ensure your dog has good recall and can be controlled on a leash when entering or exiting the park.
- Respect Other Park Users: Be mindful of others and their comfort levels around dogs. Give ample space and avoid crowded areas if your dog is nervous or reactive.
- Clean Up After Your Dog: Always carry poop bags and dispose of waste responsibly. Leaving waste behind is not only inconsiderate but also poses health risks.
- Pick Up After Your Dog, Even Outside Dog Parks: Responsible pet waste disposal applies to all public spaces, not just dog parks.
Dog Food and Nutrition Laws in Ohio
Ensuring your canine companion in Ohio thrives starts with a healthy diet. But with a vast array of dog food options available, navigating the world of pet nutrition can feel overwhelming. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog food and nutrition laws in Ohio, empowering you to make informed choices about your furry friend’s meals.
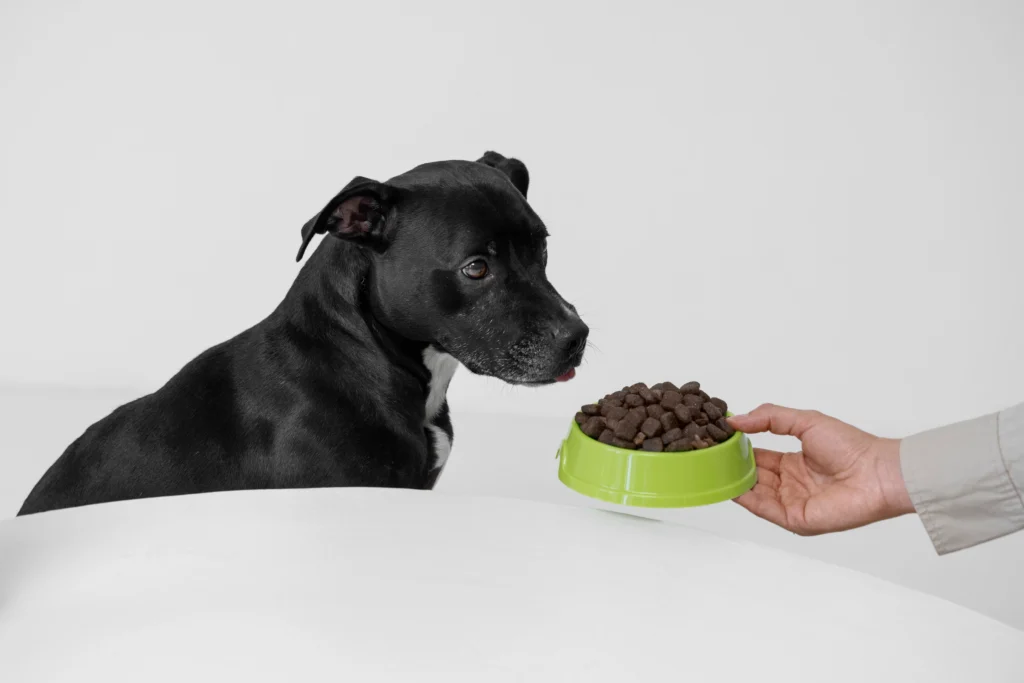

A Patchwork of Federal Oversight and Market Forces
Unlike human food, dog food in the United States isn’t subject to rigorous state-level regulations. The primary authority for ensuring dog food safety and labeling accuracy falls under the purview of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) administered by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The FDA’s Role in Dog Food Safety
The FDA establishes broad guidelines for dog food manufacturers regarding:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs): These ensure hygienic production processes and minimize the risk of contamination.
- Labeling Requirements: Labels must be truthful and not misleading, accurately reflecting ingredients and nutritional information.
- Safety Standards: Dog food ingredients must be safe for consumption and undergo testing to identify potential contaminants.
Market Forces and Industry Standards
The pet food industry operates largely through self-regulation, with organizations like the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) establishing nutritional guidelines for dog food. These guidelines are not legally binding, but most reputable manufacturers adhere to them.
Dog Food Labels in Ohio
While there are no specific Ohio laws regarding dog food labeling, understanding the information on the label is crucial for making informed choices:
- Ingredient List: Ingredients are listed in descending order by weight, with the first ingredient being the most prevalent.
- Nutritional Adequacy Statement: This statement indicates whether the food meets the nutritional needs of a specific life stage (e.g., puppy, adult, senior). Look for AAFCO statements like “complete and balanced” for all life stages.
- Guaranteed Analysis: This section lists the minimum percentages of protein, fat, fiber, and moisture content in the food.
Choosing the Right Food for Your Dog
While legal regulations offer a framework, individual needs should guide your dog food selection. Here are some factors to consider:
- Age and Life Stage: Puppies, adults, and senior dogs have different nutritional requirements. Choose food formulated for your dog’s specific life stage.
- Breed: Certain breeds may benefit from specialized diets based on size, activity level, or potential health concerns.
- Activity Level: Highly active dogs may need a food with higher calorie content for optimal energy levels.
- Health Considerations: If your dog has any health conditions, consult your veterinarian for recommendations on a suitable diet.
Consulting Your Veterinarian
Your veterinarian is your best resource for navigating dog food choices. They can assess your dog’s individual needs, recommend appropriate diets based on health and breed, and address any concerns you might have.
Responsible Dog Feeding Practices
Following broad federal guidelines is essential, but responsible pet ownership goes beyond legal requirements. Here are some additional tips for feeding your dog a healthy diet:
- Portion Control: Overfeeding can lead to obesity and related health problems. Follow the feeding guidelines on the food label and adjust based on your dog’s activity level.
- Fresh Water: Always ensure your dog has access to clean, fresh water throughout the day.
- Healthy Treats: Limit treats and choose healthy options like fruits, vegetables, or lean protein jerky.
- Monitor Weight: Regularly weigh your dog and adjust their feeding regimen if necessary to maintain a healthy weight.
What About Raw Food Diets?
While commercially manufactured dog food is the most common option, some pet owners choose raw food diets. Here are some things to consider:
- Nutritional Completeness: Raw food diets require careful planning to ensure they meet your dog’s nutritional needs. Consult with a veterinarian experienced in raw food diets for guidance.
- Safety Concerns: Raw meat can harbor bacteria harmful to both dogs and humans. Proper handling and sanitation measures are crucial to minimize risks.
Dog Health and Veterinary Care Laws in Ohio
Providing your furry companion in Ohio with a healthy and happy life requires responsible pet ownership, including preventive veterinary care. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog health and veterinary care laws in Ohio, empowering you to understand your obligations and ensure your dog receives the care they deserve.
A Landscape of Shared Responsibility
While there are no specific Ohio laws mandating veterinary care for dogs, several legal frameworks play a role in promoting animal welfare and responsible pet ownership:
- Ohio Revised Code (ORC) Chapter 959: Offenses Relating to Animals: This chapter outlines animal cruelty statutes (ORC Section 959.13) that prohibit neglect and intentional harm to animals. Veterinary care is a crucial aspect of responsible pet ownership, and failing to provide necessary medical attention could be considered a violation.
- Local Animal Control Ordinances: Many municipalities in Ohio have animal control ordinances that may address issues like rabies vaccination requirements and tethering restrictions. These ordinances can vary by location.
The Importance of Preventive Veterinary Care
While legal mandates may be limited, preventive veterinary care is essential for your dog’s well-being. Here are some key benefits:
- Early Detection and Treatment of Disease: Regular checkups allow veterinarians to detect potential health problems early, often when they are more treatable.
- Vaccinations: Vaccinations protect your dog from preventable diseases like rabies, distemper, and parvovirus. Some vaccinations may be required by local ordinances.
- Parasite Prevention: Regular parasite prevention medications safeguard your dog from fleas, ticks, heartworms, and other internal parasites.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Veterinarians can guide you on proper nutrition and exercise to promote a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related health issues.
Your Role as a Responsible Pet Owner
Beyond legal requirements, here are some actions you can take to prioritize your dog’s health:
- Establish a Relationship with a Veterinarian: Find a veterinarian you trust and schedule regular checkups, typically once a year for healthy adult dogs and more frequently for puppies, senior dogs, or those with health conditions.
- Vaccinations: Keep your dog’s vaccinations current based on your veterinarian’s recommendations and any local requirements.
- Parasite Prevention: Administer parasite prevention medications as prescribed by your veterinarian year-round, even in colder months.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Feed your dog a high-quality diet appropriate for their age, breed, and activity level.
- Provide Exercise: Regular exercise is crucial for physical and mental well-being. Tailor the amount and intensity of exercise to your dog’s breed and capabilities.
- Observe Your Dog’s Behavior: Be mindful of any changes in your dog’s behavior, appetite, or physical condition. These can be early signs of a health concern and warrant a visit to the veterinarian.
Financial Considerations and Resources for Veterinary Care
Veterinary care costs can add up. Here are some ways to manage veterinary expenses:
- Pet Insurance: Consider pet insurance to help offset the costs of unexpected illnesses or injuries.
- Veterinary Savings Plans: Some veterinary clinics offer wellness plans that provide discounts on preventive care services.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Non-profit organizations may offer financial assistance for veterinary care in cases of hardship.
Reporting Animal Cruelty
If you suspect an animal is being neglected or abused, it’s your responsibility to report it. Here’s how you can help:
- Contact Your Local Animal Control Agency: They have the authority to investigate animal cruelty complaints.
- Humane Societies and Animal Welfare Organizations: These organizations often have cruelty hotlines and can provide guidance on reporting suspected abuse.
The Importance of Microchipping Your Dog
Microchipping your dog significantly increases the chances of a safe reunion if they get lost. Microchips are tiny implants inserted under the skin that store your dog’s identification information.
Dog Identification and Microchipping Laws in Ohio
Ensuring your dog is properly identified is crucial for responsible pet ownership in Ohio. A lost dog without identification can face a frightening ordeal, and reuniting them with you can be a stressful process. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog identification and microchipping laws in Ohio, empowering you to take proactive steps to safeguard your canine companion.

Licensing: The Mandatory Form of Identification in Ohio
Unlike some states, microchipping isn’t mandatory in Ohio. However, all dogs over three months of age must be licensed with your county auditor’s office. This is the primary form of legal identification required by law (ORC Chapter 955).
The Importance of Dog Licensing in Ohio
Dog licensing offers several benefits:
- Identification: The license tag attached to your dog’s collar displays your contact information, increasing the chances of a safe return if your dog gets lost.
- Funding for Animal Control: Licensing fees help fund animal control services in your county, including sheltering lost and stray animals, investigating animal cruelty complaints, and promoting responsible pet ownership.
- Enforcement of Rabies Vaccination: During the licensing process, you may be required to show proof of your dog’s current rabies vaccination, another crucial aspect of responsible pet ownership.
Obtaining a Dog License in Ohio
The process for obtaining a dog license in Ohio is typically straightforward:
- Contact your county auditor’s office: They will provide you with the necessary application forms and information on fees. Fees can vary by county and may be higher for unaltered dogs.
- Complete the application: Provide accurate information about yourself and your dog, including breed, age, and sterilization status.
- Proof of Rabies Vaccination: You may need to submit a copy of your dog’s current rabies vaccination certificate.
- Payment: Pay the required licensing fee.
The Value of Microchipping
While dog licensing is mandatory, microchipping offers an additional layer of permanent identification:
- A Permanent Implant: A microchip is a tiny rice-sized implant inserted under your dog’s skin between the shoulder blades. The procedure is quick and relatively painless.
- Unique Identification Number: Each microchip contains a unique identification number linked to your contact information in a national database.
- Increased Recovery Rates: If your dog gets lost and is scanned by a veterinarian or animal shelter, the microchip can quickly reunite you with your furry friend.
Microchipping Considerations in Ohio
While not mandated by law, microchipping your dog is highly recommended in Ohio. Here’s why:
- Lost Dog Recovery: Microchips significantly increase the chances of a safe reunion if your dog gets lost, even if their collar falls off or their license tag becomes detached.
- Travel and Excursions: Some states or countries may have microchipping requirements for traveling with your dog.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your dog is microchipped provides peace of mind and allows you to focus on finding them if they go missing.
Where to Get Your Dog Microchipped in Ohio
Several options are available for microchipping your dog in Ohio:
- Veterinarians: Most veterinary clinics offer microchipping services.
- Animal Shelters: Some animal shelters may offer microchipping services, particularly during adoption events.
- Low-Cost Vaccination Clinics: Some organizations may hold low-cost vaccination clinics that include microchipping.
Registering Your Microchip
Microchipping itself is only half the equation. To ensure your contact information is readily accessible, you need to register your microchip with a national database company. The veterinarian or shelter performing the microchipping will typically handle this for you, but it’s crucial to confirm and keep your registration information updated.
Dog Breeding and Genetics Laws in Ohio
Ohio offers a diverse landscape for dog lovers, with opportunities for responsible breeders and pet ownership. This guide delves into the key aspects of dog breeding and genetics laws in Ohio, empowering you to make informed decisions if you’re considering breeding dogs or purchasing a puppy from a breeder.

A Patchwork of Regulations
Unlike some states with comprehensive breeding regulations, Ohio’s legal framework for dog breeding focuses on:
- Animal Welfare: The Ohio Revised Code (ORC) Chapter 959 outlines animal cruelty statutes (ORC Section 959.13) that prohibit neglect and intentional harm to animals. This applies to all dog owners, including breeders.
- Kennel Licensing and Inspections: The Ohio Department of Agriculture (ODA) licenses and inspects dog kennels (OAC Chapter 901:1-6) to ensure minimum care standards are met. These standards address aspects like housing, sanitation, veterinary care, and recordkeeping.
Responsible Breeding Practices
While legal requirements provide a baseline, responsible breeding goes beyond the minimum. Here are some key considerations for ethical breeders:
- Breed Standards: Breeders should have a deep understanding of the breed standard they are working with, focusing on preserving desirable physical and temperament traits.
- Health Testing: Reputable breeders conduct genetic health screenings on breeding stock to identify and avoid passing on inheritable diseases.
- Temperament Evaluation: Responsible breeders consider temperament alongside physical characteristics, striving to produce well-socialized puppies with sound temperaments.
- Proper Care and Socialization: Puppies from reputable breeders are raised in clean, healthy environments and receive proper socialization experiences during their critical developmental stages.
- Transparent Communication: Ethical breeders openly discuss their breeding practices, health testing results, and pedigrees of their dogs.
Finding a Reputable Dog Breeder in Ohio
If you’re considering purchasing a puppy from a breeder in Ohio, here are some tips:
- Research Breeds: Carefully research different dog breeds to find one that aligns with your lifestyle, activity level, and living environment.
- National Breed Clubs: National breed clubs often have breeder referral programs that connect potential puppy buyers with reputable breeders adhering to ethical breeding practices.
- Kennel Inspections: While not a guarantee of ethical breeding, you can inquire about a breeder’s kennel license and inspection history with the Ohio Department of Agriculture.
- On-Site Visit: Always visit the breeder’s facility in person to observe the living conditions of the breeding dogs and puppies, ask questions, and get a sense of their breeding practices.
- Contracts and Guarantees: Reputable breeders typically have written contracts outlining the purchase agreement, health guarantees, and potential return policies.
Understanding Brachycephalic Breeds and Related Regulations
Some dog breeds, brachycephalic breeds like Pugs, Bulldogs, and Shih Tzus, have shortened facial structures that can predispose them to breathing difficulties. While Ohio doesn’t have specific breeding bans on brachycephalic breeds, some animal welfare organizations recommend avoiding breeding practices that exacerbate these health concerns.
The Role of Rescue Organizations and Adoption
If you’re open to welcoming a canine companion into your life, consider adopting from a shelter or rescue organization. Numerous deserving dogs of all breeds and ages are waiting for loving homes, and adoption offers a rewarding alternative to purchasing from a breeder.
Dog Environmental Impact Laws in Ohio
While Ohio offers a wealth of opportunities for dog ownership and outdoor adventures with your canine companion, there aren’t specific state-level laws solely focused on dog environmental impact. However, responsible pet ownership practices and adherence to existing regulations play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental footprint of our furry friends.

A Focus on Shared Responsibility
Several existing legal frameworks and responsible pet ownership practices contribute to mitigating the environmental impact of dogs in Ohio:
- Animal Waste Disposal Laws: Most municipalities in Ohio have animal control ordinances that mandate responsible pet waste disposal. Failing to pick up after your dog in public spaces can result in fines. Leaving waste behind is not only inconsiderate but also poses health risks and environmental concerns.
- Leash Laws and Public Access Restrictions: Many public spaces in Ohio, like parks, trails, and nature preserves, have designated off-leash areas and leash requirements. Following these regulations minimizes disruptions to wildlife and protects sensitive ecosystems.
- Water Quality Protection: The Ohio Environmental Protection Agency (OEPA) enforces regulations aimed at protecting water quality. While not directly targeting dog waste, responsible pet waste disposal helps maintain clean waterways.
Responsible Pet Ownership
Following existing laws is essential, but going the extra mile is key to minimizing your dog’s environmental impact:
- Pick Up After Your Dog – Always: Carry waste bags on walks and dispose of waste properly in designated bins.
- Respect Designated Off-Leash Areas: Only allow your dog off-leash in designated areas and ensure they are under your control.
- Minimize Walking on Fragile Ecosystems: Be mindful of sensitive habitats like wetlands or meadows. Stick to designated trails and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Eco-Friendly Pet Products: Consider using biodegradable waste bags and eco-friendly pet cleaning products to minimize environmental impact.
- Responsible Dog Walking Routes: Avoid walking your dog near bodies of water where waste could directly pollute waterways.
The Importance of Dog Waste Management
Dog waste can have a significant environmental impact if not disposed of properly. Here’s why responsible management matters:
- Water Quality: Dog waste contains bacteria and nutrients that can pollute waterways when left behind. This can harm aquatic life and contribute to algal blooms.
- Public Health: Dog waste can harbor parasites and diseases that pose risks to both humans and other animals.
- Soil Contamination: Left uncollected, dog waste can contaminate soil and make it unsuitable for certain plant life.
Addressing Other Environmental Concerns
While waste management is a primary concern, other factors can contribute to a dog’s environmental footprint:
- Food Production: The production of meat-based dog food requires significant resources. Consider exploring sustainable pet food options.
- Transportation: Driving your dog to walks or parks contributes to carbon emissions. Opt for walking or cycling whenever possible.
- Water Usage: Dogs require water for hydration. Implement water-saving practices during bath time and use a hose with a shut-off nozzle for outdoor cleaning.
The Role of Education and Community Engagement
Raising awareness about responsible pet ownership practices is crucial for minimizing dog environmental impact. Here are some ways to make a difference:
- Lead by Example: Always pick up after your dog and encourage others to do the same.
- Support Local Initiatives: Many communities offer educational programs or waste bag distribution initiatives.
- Advocate for Dog-Friendly Policies: Support policies that create designated dog walking areas and promote responsible pet ownership practices.
Dog Behavioural Training Laws in Ohio
Ohio offers a vibrant dog-loving community, but there aren’t specific state-level laws mandating dog behavioral training. However, responsible pet ownership and addressing behavioral issues are crucial for a harmonious human-canine coexistence. This guide explores the landscape of dog behavioral training in Ohio, empowering you to navigate resources and create a well-mannered canine companion.

Focus on Welfare and Safety
While there are no legal requirements for dog training, several aspects highlight the importance of responsible pet ownership and addressing behavioral problems:
- Animal Welfare Laws: The Ohio Revised Code (ORC) Chapter 959 outlines animal cruelty statutes (ORC Section 959.13) prohibiting neglect and intentional harm. Untrained dogs with severe behavioral issues may be considered neglected if their owner fails to take reasonable steps to address the problem.
- Local Animal Control Ordinances: Many municipalities in Ohio have animal control ordinances addressing issues like public nuisance barking and aggressive behavior. These ordinances may outline consequences for repeat offenders and emphasize responsible pet ownership.
- Public Safety: Untrained dogs posing a threat to public safety, such as those exhibiting biting tendencies, may be subject to intervention by animal control authorities.
The Value of Dog Training
Training goes beyond legal requirements. Here’s how it benefits both you and your dog:
- Improved Communication: Training fosters better communication between you and your dog, strengthening your bond and building trust.
- Safer Interactions: A well-trained dog is more manageable in various situations, minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries to both your dog and others.
- Reduced Stress: Untrained dogs can experience anxiety and exhibit behavioral problems due to frustration. Training provides structure and predictability, reducing stress for both you and your dog.
- Enhanced Socialization: Training helps dogs learn appropriate social skills, enabling them to interact safely and confidently with other dogs and people.
Finding the Right Dog Trainer in Ohio
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to dog training. Here’s how to find a qualified trainer in Ohio:
- Identify Your Training Needs: Consider what specific behavioral issues you want to address or general obedience training goals.
- Trainer Credentials: Look for trainers certified by reputable organizations like the Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers (CCPDT) or the Association of Professional Dog Trainers (APDT).
- Training Methods: Choose a trainer who utilizes positive reinforcement methods based on reward and motivation rather than punishment-based techniques.
- Meet and Greet: Schedule a consultation with potential trainers to discuss your dog’s needs and ensure a good fit.
Alternative Training Options in Ohio
Several training options are available in Ohio beyond traditional dog training classes:
- Online Resources: Numerous online resources offer dog training tutorials and courses. While convenient, ensure the information is from reputable sources.
- Group Classes: Group obedience classes provide a structured learning environment for both you and your dog while offering opportunities for socialization.
- Private Training: Private training sessions allow for personalized attention to your dog’s specific needs and behavioral challenges.
The Role of Veterinarians in Dog Behavior
Veterinarians play a crucial role in dog behavior. Here’s how they can contribute:
- Ruling Out Medical Causes: Some behavioral problems can stem from underlying medical conditions. Your veterinarian can conduct a checkup to rule out any medical factors influencing your dog’s behavior.
- Referral to Trainers: Veterinarians can recommend qualified dog trainers based on your dog’s specific needs and your training goals.
- Ongoing Support: Your veterinarian can provide ongoing support and guidance throughout your dog’s training journey.
Dog Protection and Rescue Laws in Ohio
Ohio offers a haven for dog lovers, with numerous opportunities for pet ownership and outdoor adventures. However, ensuring the well-being of our canine companions requires understanding the legal framework for dog protection and rescue in the state. This guide delves into the key aspects of these laws, empowering you to play a vital role in safeguarding and rescuing dogs in need.

Ohio’s Legal Landscape
While there isn’t a single, comprehensive law governing dog protection and rescue in Ohio, several legal frameworks work in tandem to promote animal welfare:
- Ohio Revised Code (ORC) Chapter 959: Offenses Relating to Animals: This chapter outlines animal cruelty statutes (ORC Section 959.13) that prohibit neglect and intentional harm to animals. This forms the foundation for protecting dogs from abuse and neglect.
- Local Animal Control Ordinances: Many municipalities in Ohio have animal control ordinances that address specific issues like tethering restrictions, animal cruelty reporting procedures, and sheltering procedures for stray and abandoned dogs. These ordinances can vary by location.
Enforcement of Animal Cruelty Laws
The Ohio Revised Code defines animal cruelty broadly, encompassing actions like:
- Depriving an animal of necessary food, water, or shelter
- Abandoning an animal
- Subjecting an animal to unnecessary pain or suffering
- Killing an animal in a cruel manner
If you suspect an animal is being neglected or abused, it’s your responsibility to report it. Here’s how you can help:
- Contact your local animal control agency: They have the authority to investigate animal cruelty complaints.
- Humane Societies and Animal Welfare Organizations: These organizations often have cruelty hotlines and can provide guidance on reporting suspected abuse.
- Gather Evidence (if possible): Documenting the situation with photos or videos can strengthen your report.
The Role of Animal Shelters and Rescue Organizations
Animal shelters and rescue organizations play a critical role in protecting and rescuing dogs in Ohio:
- Animal Shelters: Many municipalities operate animal shelters that house stray, abandoned, and surrendered dogs. Shelters work to find these dogs permanent, loving homes through adoption.
- Rescue Organizations: Numerous non-profit rescue organizations specialize in rescuing dogs from various situations, including high-kill shelters, neglectful environments, or commercial breeding facilities.
The Adoption Process in Ohio
If you’re considering adopting a dog from a shelter or rescue organization in Ohio, here’s what to expect:
- Adoption Application: Most shelters and rescues require you to complete an application to assess your suitability as a pet owner.
- Meet and Greet: You’ll have the opportunity to meet the dog you’re interested in to ensure a good fit.
- Adoption Fees: Adoption fees typically cover the cost of vaccinations, spaying/neutering, and microchipping.
- Adoption Contract: You’ll sign a contract outlining your responsibilities as the dog’s new owner.
Responsible Pet Ownership
The legal framework provides a foundation for dog protection, but responsible pet ownership goes beyond legal mandates. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Proper Care and Nutrition: Provide your dog with a healthy diet, clean water, and proper veterinary care.
- Safe and Secure Environment: Ensure your home is escape-proofed and provide your dog with a comfortable and secure place to live.
- Exercise and Enrichment: Exercise your dog regularly and provide them with mental stimulation through toys and training.
- Identification and Licensing: Microchip your dog and obtain a dog license as required by law in most Ohio counties.
Advocacy for Dog Welfare
You can play an active role in advocating for dog welfare in Ohio:
- Support Local Animal Shelters and Rescues: Consider volunteering your time, donating supplies, or adopting a dog in need.
- Speak Up for Animal Welfare Legislation: Contact your local representatives and voice your support for laws that promote animal welfare.
- Educate Others: Raise awareness about responsible pet ownership and the importance of spaying/neutering to prevent pet overpopulation.
Dog Entertainment and Work Laws in Ohio
Ohio boasts a vibrant dog-loving community, and many dog owners dream of including their canine companions in various activities. However, navigating the legal landscape surrounding dog entertainment and work in Ohio can be confusing. This guide delves into the key aspects of these regulations, empowering you to understand the possibilities and limitations for your furry friend.

Entertainment: Sharing the Spotlight (with Limitations)
While Ohio doesn’t have a single law specifically dedicated to dog entertainment, several factors influence whether your dog can participate:
- Venue-Specific Regulations: Movie sets, theme parks, and other entertainment venues often have their own policies regarding animals. These policies may restrict or prohibit dogs altogether, even for performances or appearances. Always contact the venue directly to inquire about their animal policies.
- Animal Welfare Concerns: The primary focus should always be on your dog’s well-being. Activities should be age-appropriate, stress-free, and not put your dog in dangerous or uncomfortable situations.
- Licensing and Training: Some entertainment activities, like participating in dog shows or competitions, may require specific licenses or certifications for both the dog and handler.
Exploring Entertainment Options in Ohio
Despite limitations, several dog-friendly entertainment options exist in Ohio:
- Dog-Friendly Events: Many communities host dog-friendly events like parades, costume contests, or agility demonstrations.
- Pet-Friendly Businesses: Some restaurants and cafes offer outdoor seating where well-behaved dogs are welcome.
- Dog Parks and Recreation Areas: Numerous dog parks and off-leash areas provide opportunities for dogs to socialize and exercise in a safe and controlled environment.
Understanding the Restrictions
Ohio doesn’t have specific laws outlining regulations for working dogs. However, several factors determine whether your dog can participate in work-related activities:
- Breed and Temperament: Certain breeds are naturally suited for specific tasks, like search and rescue or herding livestock. Your dog’s temperament and training are crucial considerations.
- Federal Regulations: Some working dog roles, like service animals or emotional support animals, are protected by federal laws like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). These laws dictate access rights and protections for qualified dogs.
- Private Business Policies: Many businesses have the right to set their own policies regarding working dogs on their premises. Always check with the business beforehand to ensure your dog is welcome.
Exploring Work Opportunities for Dogs in Ohio
While restrictions exist, some potential work opportunities for dogs in Ohio include:
- Therapy Dogs: Certified therapy dogs can provide emotional support in various settings like hospitals, schools, or nursing homes.
- Search and Rescue Dogs: Trained search and rescue dogs can assist law enforcement or emergency responders in locating missing people.
- Detection Dogs: Dogs with keen senses of smell can be trained for tasks like detecting drugs, explosives, or medical conditions.
Important Considerations for Dog Entertainment and Work
Before involving your dog in any activity, ensure:
- Your Dog’s Well-Being: Priority number one is a stress-free and positive experience for your dog.
- Proper Training: Whether for entertainment or work, adequate training is crucial for safety and success.
- Licenses and Certifications: Research any necessary licenses or certifications for the specific activity.
- Respectful Participation: Always adhere to venue policies and be a responsible dog owner.
Dog Technology and Innovation Laws in Ohio
Ohio offers a dynamic environment for dog lovers and innovation. Pet technology is evolving rapidly, presenting exciting possibilities for dog health, training, and well-being. However, the legal landscape surrounding dog technology and innovation in Ohio is still developing. This guide explores the current state of regulations and considerations for utilizing these advancements with your canine companion.

The Evolving Legal Framework
Currently, Ohio doesn’t have specific laws directly governing the use of pet technology products or innovations in dog health technology. Regulatory oversight often falls under federal agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Here’s a breakdown of the relevant regulatory bodies:
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA regulates animal drugs, medical devices, and pet food. Products claiming to diagnose, treat, or prevent diseases in animals require FDA approval.
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC): The FTC protects consumers from unfair or deceptive advertising practices. Marketing claims for pet technology products should be truthful and substantiated.
- Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC): The CPSC ensures the safety of consumer products, including some pet tech products like GPS trackers or collars.
Exploring Dog Technology Options in Ohio
Despite the absence of specific state laws, a variety of dog technology products are available in Ohio:
- Wearable Tech: GPS trackers, activity monitors, and even smart collars that monitor vital signs are becoming increasingly popular.
- Training Tools: Electronic training collars, clickers, and even smartphone apps offering training tutorials are widely available.
- Remote Monitoring Systems: Pet cameras and interactive feeders allow you to monitor your dog remotely and even dispense treats while you’re away.
- Telehealth for Pets: Emerging technologies allow for virtual consultations with veterinarians, potentially increasing accessibility to pet healthcare.
Important Considerations Before Using Dog Technology
While dog technology offers exciting possibilities, proceed with caution:
- Research Products Thoroughly: Read reviews, understand the functionalities, and ensure the technology is safe and appropriate for your dog.
- FDA Approval: Look for products with FDA approval, especially for devices claiming health benefits.
- Data Privacy: Be mindful of data collection practices associated with certain dog tech products.
- Veterinarian Consultation: Discuss any new technology with your veterinarian to ensure it aligns with your dog’s specific needs and well-being.
The Future of Dog Technology and Innovation
The future of dog technology holds immense promise:
- Advanced Health Monitoring: Wearable technology may become more sophisticated, offering real-time monitoring of vital signs and early detection of potential health issues.
- Personalized Training Solutions: Technology-aided training tools could personalize training approaches based on your dog’s individual learning style.
- Improved Communication: Advanced technology might bridge the communication gap between humans and dogs, fostering deeper understanding.
Staying Informed and Engaged
As dog technology continues to evolve, staying informed is crucial:
- Follow Reputable Sources: Subscribe to reputable pet tech websites or publications to receive updates on new innovations.
- Engage with Professional Organizations: Connect with veterinary organizations or pet tech industry associations for insights and recommendations.
- Advocate for Responsible Innovation: Support regulations that ensure the safety, efficacy, and ethical use of dog technology.
Human Coexistence Laws in Ohio
Ohio fosters a thriving dog-loving community, and creating a harmonious life with your canine companion is an aspiration for many. While there aren’t specific state-level laws solely dedicated to promoting dog-human cohabitation, several legal frameworks and responsible pet ownership practices lay the groundwork for a successful human-dog relationship. This guide explores these aspects, empowering you to cultivate a strong bond with your furry friend.

A Legal Framework for Coexistence
Several existing laws and regulations in Ohio indirectly promote responsible pet ownership and a positive human-dog bond:
- Animal Cruelty Laws: The Ohio Revised Code (ORC) Chapter 959 outlines animal cruelty statutes (ORC Section 959.13) that prohibit neglect and intentional harm. Fulfilling your dog’s basic needs and providing proper care are essential for a healthy and happy relationship.
- Leash Laws and Public Access Restrictions: Many public spaces in Ohio have designated off-leash areas and leash requirements. Following these regulations allows for safe and enjoyable outings with your dog, fostering positive interactions between humans and dogs.
- Service Animal Protections: The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) guarantees access rights for qualified service animals to accompany people with disabilities in public spaces. This recognition highlights the valuable role dogs can play in human lives.
Responsible Ownership for a Fulfilling Bond
Building a strong human-dog bond goes beyond legal requirements. Here are key practices for responsible pet ownership:
- Meeting Your Dog’s Needs: Provide your dog with adequate food, water, shelter, exercise, and mental stimulation. A fulfilled dog is a happy dog, ultimately strengthening your bond.
- Training and Socialization: Invest in positive reinforcement training to build communication and trust. Early socialization helps your dog interact confidently with humans and other animals, fostering a peaceful coexistence.
- Veterinary Care: Regular veterinary checkups ensure your dog’s health and well-being. A healthy dog will be more receptive to training and enjoy a longer, happier life by your side.
- Quality Time and Affection: Dedicate time for walks, playtime, cuddles, and interactive activities. These moments of connection strengthen the emotional bond between you and your dog.
Fostering a Dog-Friendly Environment
Creating a dog-friendly environment at home promotes cohabitation and relaxation:
- Dog-Proofing Your Home: Secure electrical cords, remove toxic plants, and provide safe chew toys to prevent accidents and anxieties.
- Creating a Cozy Space: Offer your dog a comfortable bed, familiar items, and a quiet space to retreat when needed.
- Establishing Routines: Maintain consistent feeding times, walk schedules, and training routines. Predictability provides your dog with a sense of security and reduces stress.
Community Resources for Human-Dog Bonding
Numerous resources in Ohio can help strengthen the bond between you and your dog:
- Dog Trainers: Certified trainers can provide personalized guidance on communication, obedience, and behavioral issues.
- Dog Parks and Recreation Areas: Off-leash areas allow your dog to socialize with other dogs and enjoy safe outdoor exercise, creating positive experiences for both you and your furry friend.
- Dog-Friendly Events: Many communities host dog-friendly events like walks, agility courses, or social gatherings. These events offer opportunities for socialization and interaction, fostering a sense of community for both humans and dogs.
The Importance of Responsible Breeding and Adoption
Choosing the right dog is crucial for a successful human-dog relationship:
- Responsible Breeders: If considering purchasing a puppy, research reputable breeders who prioritize health testing, socialization, and ethical breeding practices.
- Adoption from Shelters or Rescues: Many shelters and rescues house dogs of all breeds and ages. Adopting a dog in need offers a second chance and can create a uniquely rewarding bond.
Other Relevant Dog Laws in Ohio
Canine Good Citizen (CGC) Programs and Legal Benefits in Ohio
- Canine Good Citizen (CGC) Programs: These programs offered by the American Kennel Club (AKC) evaluate a dog’s basic obedience skills, socialization manners, and temperament in various situations. While not mandated by law in Ohio, completing a CGC program can demonstrate responsible pet ownership and potentially offer benefits:
- Reduced Dog Licensing Fees: Some Ohio counties offer discounts on dog licenses for CGC-certified dogs.
- Relaxed Restrictions in Dog-Friendly Communities: Apartment complexes or homeowner associations may have relaxed pet policies, like breed restrictions, for CGC-certified dogs.
Dog Insurance and Coverage Laws in Ohio
- Dog Insurance: Dog insurance is not mandatory in Ohio, but it’s a wise financial decision. It helps cover veterinary expenses for accidents, illnesses, and even surgeries. There are no specific state laws governing dog insurance coverage; policies vary by provider.
- Important Considerations: Research different insurance companies, compare coverage options (accident-only vs. comprehensive), and understand exclusions (e.g., pre-existing conditions) before purchasing a policy.
Laws Regarding Dogs in Hot Cars and Animal Endangerment in Ohio
- Animal Cruelty Laws (ORC Section 959.13): Leaving a dog unattended in a hot car can be considered animal cruelty. These laws protect animals from neglect and suffering. If you see a dog in distress in a hot car, call animal control immediately.
- Hot Car Dangers: Even on moderately warm days, car interiors can reach dangerously high temperatures within minutes, causing heatstroke and potentially death for dogs left unattended.
Legal Aspects of Dog Parks and Shared Spaces in Ohio
- Local Leash Laws and Park Ordinances: Many Ohio municipalities have leash laws and specific park ordinances regarding dog behavior and off-leash areas. Always research and adhere to the posted regulations for each park you visit.
- Shared Responsibility: Dog park usage requires responsible pet ownership. Ensure your dog is up-to-date on vaccinations, well-behaved, and properly socialized before using off-leash areas. Clean up after your dog and be mindful of other park users.
Dog-Related Property Damage and Homeowner’s Insurance in Ohio
- Dog Bite Liability: Ohio follows the “one-bite rule” in dog bite cases. A dog owner is generally liable for damages if their dog bites someone and the owner knew or should have known the dog had a propensity to bite.
- Homeowner’s Insurance: Most homeowner’s insurance policies cover dog-related liability to a certain extent. However, exclusions or limitations may apply depending on the breed, bite history, or specific circumstances. It’s crucial to review your policy details with your insurance provider.
Service and Working Dog Laws in Employment and Public Access in Ohio
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): This federal law protects the rights of individuals with disabilities to be accompanied by qualified service animals in public spaces. Service animals are not pets; they are trained to perform specific tasks that mitigate a disability.
- Ohio Revised Code (ORC Section 5610.04): This statute protects the rights of service animals to accompany their handlers in public accommodations, employment settings, and transportation services.
Animal Welfare and Protection Laws Against Neglect and Abandonment in Ohio
- Animal Cruelty Laws (ORC Section 959.13): These laws form the foundation for animal welfare protection in Ohio. They prohibit neglect, abandonment, intentional harm, and fighting animals.
- Reporting Animal Cruelty: If you suspect animal neglect or abuse, report it to your local animal control agency or a humane society.
While Ohio doesn’t have a single, comprehensive dog law, a patchwork of regulations and responsible ownership practices ensure the well-being of our canine companions. Understanding animal cruelty statutes, leash laws, and dog park etiquette fosters safe human-dog interactions.
Responsible ownership goes beyond legal mandates. Training, socialization, and proper care strengthen the bond with your dog, enriching your lives together. By complying with dog laws and prioritizing responsible pet ownership, we create a safer and more harmonious environment for all Ohio residents, with and without four paws.
FAQs
Can I take my dog to the park?
Yes, you can take your dog to most parks in Ohio, but leash laws and specific regulations may apply. Always check for posted signs at the park entrance outlining leash requirements, designated off-leash areas, and any other dog-related rules.
Are there any restrictions on specific dog breeds in Ohio?
Ohio doesn’t have a statewide ban on any dog breed. However, some municipalities might have breed-specific restrictions within their city limits. Research local ordinances before adopting a dog breed that might face limitations in your area.
What are the rules for traveling with my dog in Ohio?
There are no specific state laws regarding dog travel within Ohio. However, some public transportation options like buses or trains might have restrictions on pet travel. Always check with the specific carrier beforehand. For traveling out of state, research rabies vaccination requirements and any other regulations at your destination.
What happens if my dog bites someone?
Ohio follows the “one-bite rule” in dog bite cases. This means a dog owner is generally liable for damages if their dog bites someone and the owner knew or should have known the dog had a propensity to bite. It’s crucial to ensure your dog is properly socialized and trained to minimize the risk of biting incidents.
Can my landlord restrict my dog in my apartment?
Yes, landlords can have pet policies that restrict the type, size, or number of dogs allowed in their rental properties. These policies should be outlined in your lease agreement. Always confirm any pet restrictions before signing a lease.







